Tue L. Nielsen presented our MITO-DYS-IR study results in the plenary hall, uncovering the causal role of #muscle #mitochondrial defects in #diabetes pathophysiology
Grateful to our collaborators and @easdnews.bsky.social Early Career Academy for the Best Abstract Award

Tue L. Nielsen presented our MITO-DYS-IR study results in the plenary hall, uncovering the causal role of #muscle #mitochondrial defects in #diabetes pathophysiology
Grateful to our collaborators and @easdnews.bsky.social Early Career Academy for the Best Abstract Award
“LBA SO 02 – Thinking Big About Treating Obesity”
📍 Short Oral Station 23 (Hall C)
📅 Tuesday, 16 Sept
⏰ 13:15
@easdnews.bsky.social

“LBA SO 02 – Thinking Big About Treating Obesity”
📍 Short Oral Station 23 (Hall C)
📅 Tuesday, 16 Sept
⏰ 13:15
@easdnews.bsky.social
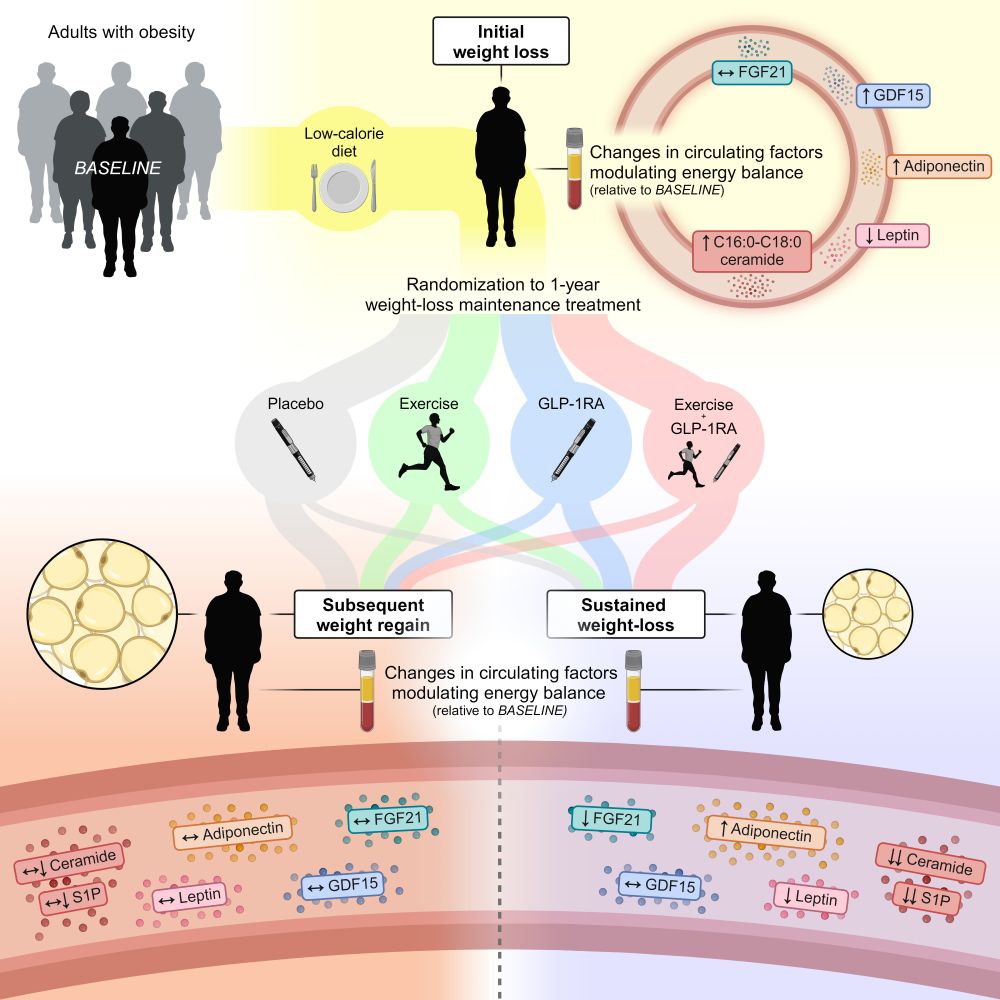
Likewise, a multitude of sphingolipid species were differentially regulated in weight maintainers vs. regainers.

Likewise, a multitude of sphingolipid species were differentially regulated in weight maintainers vs. regainers.

Remarkably, the initial weight loss and the subsequent weight-loss maintenance phase evoked divergent alterations in a subset of ceramides causally linked to obesity.

Remarkably, the initial weight loss and the subsequent weight-loss maintenance phase evoked divergent alterations in a subset of ceramides causally linked to obesity.



we confirmed that disrupted GLUT4 trafficking is a key molecular mechanism by which mitochondrial oxidants impair muscle insulin action.

we confirmed that disrupted GLUT4 trafficking is a key molecular mechanism by which mitochondrial oxidants impair muscle insulin action.

we employed an in vivo mechanistic approach to interrogate whether the causal link between mitochondrial oxidative stress and insulin resistance translates to humans.

we employed an in vivo mechanistic approach to interrogate whether the causal link between mitochondrial oxidative stress and insulin resistance translates to humans.


