
We find an observational constraint implying more future global ocean heat uptake, cloud feedback, and warming than the CMIP6 mean.
This contrasts with previous estimates based on past warming trends.
🔗 esd.copernicus.org/articles/16/...
I am happy and proud to present our #platformist team effort out in @nature.com!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We examine if, when, and why #Antarctic #ice shelves will no longer be viable, at the latest, due to changes in #atmosphere and #ocean conditions.
A little 🧵 for the experts...
1/7

I am happy and proud to present our #platformist team effort out in @nature.com!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We examine if, when, and why #Antarctic #ice shelves will no longer be viable, at the latest, due to changes in #atmosphere and #ocean conditions.
A little 🧵 for the experts...
1/7
🌊 We discuss how well mechanisms of variability in the subpolar gyre are represented in climate models, finding that models that do this best are also the models in which abrupt shifts are found 😬.
It's a technical story, so here's a simple overview 🧵
doi.org/10.5194/esd-...

🌊 We discuss how well mechanisms of variability in the subpolar gyre are represented in climate models, finding that models that do this best are also the models in which abrupt shifts are found 😬.
It's a technical story, so here's a simple overview 🧵
doi.org/10.5194/esd-...
A lecturer position is opening at LOCEAN on the topic: ‘Impact of climate change on marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean’ (permanent position with the French Natural History Museum, for a researcher that will be based at LOCEAN, in the centre of Paris).
A lecturer position is opening at LOCEAN on the topic: ‘Impact of climate change on marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean’ (permanent position with the French Natural History Museum, for a researcher that will be based at LOCEAN, in the centre of Paris).
We find an observational constraint implying more future global ocean heat uptake, cloud feedback, and warming than the CMIP6 mean.
This contrasts with previous estimates based on past warming trends.
🔗 esd.copernicus.org/articles/16/...

We find an observational constraint implying more future global ocean heat uptake, cloud feedback, and warming than the CMIP6 mean.
This contrasts with previous estimates based on past warming trends.
🔗 esd.copernicus.org/articles/16/...

We find an observational constraint implying more future global ocean heat uptake, cloud feedback, and warming than the CMIP6 mean.
This contrasts with previous estimates based on past warming trends.
🔗 esd.copernicus.org/articles/16/...
Looking for a #postdoc to join us at @ipsl.bsky.social within the #ANR project #AIAI (AI to improve coupling between the Antarctic 🧊 and the 🌊/🌧️), a collaboration between @igegrenoble.bsky.social , @lsce-ipsl.bsky.social and #LOCEAN!
Deadline: Aug 8th
Apply here: emploi.cnrs.fr/Offres/CDD/U...
Looking for a #postdoc to join us at @ipsl.bsky.social within the #ANR project #AIAI (AI to improve coupling between the Antarctic 🧊 and the 🌊/🌧️), a collaboration between @igegrenoble.bsky.social , @lsce-ipsl.bsky.social and #LOCEAN!
Deadline: Aug 8th
Apply here: emploi.cnrs.fr/Offres/CDD/U...
This one explores the looming peer review crisis. As many of you know, it's becoming significantly more difficult for journal editors to find scholars willing to serve as peer reviewers for submitted manuscripts.

This one explores the looming peer review crisis. As many of you know, it's becoming significantly more difficult for journal editors to find scholars willing to serve as peer reviewers for submitted manuscripts.
authors.elsevier.com/c/1lMUI8yuR6...
#philsci #metasci 🧪 ⚒️

authors.elsevier.com/c/1lMUI8yuR6...
#philsci #metasci 🧪 ⚒️
Yes, especially for local CO2 fluxes, where wave breaking can enhance variability by up to 40%. That’s an important consideration for #mCDR, where fluxes could otherwise be miscalculated. More in our paper here: [https://doi.org/10.1029/2024GB008382]

Yes, especially for local CO2 fluxes, where wave breaking can enhance variability by up to 40%. That’s an important consideration for #mCDR, where fluxes could otherwise be miscalculated. More in our paper here: [https://doi.org/10.1029/2024GB008382]
What processes control the efficiency of ocean heat uptake under CO₂ forcing?
We show that Southern Ocean stratification and overturning are key, check out our publication in Ocean Science here:
doi.org/10.5194/os-2...
More details below 🧵👇
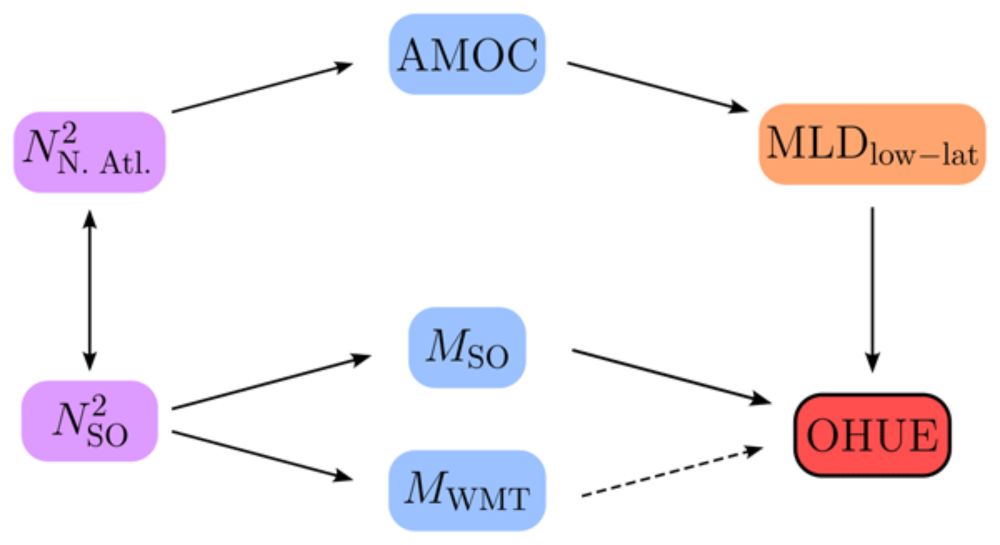
What processes control the efficiency of ocean heat uptake under CO₂ forcing?
We show that Southern Ocean stratification and overturning are key, check out our publication in Ocean Science here:
doi.org/10.5194/os-2...
More details below 🧵👇
New insight into how sea ice controls the ocean uptake of carbon dioxide around Antarctica, obtained from the unique year-round Rothera Time Series.
Delighted to be part of this study, led by the very excellent Elise Droste.
🧪❄️🥼🌊
www.nature.com/articles/s43...
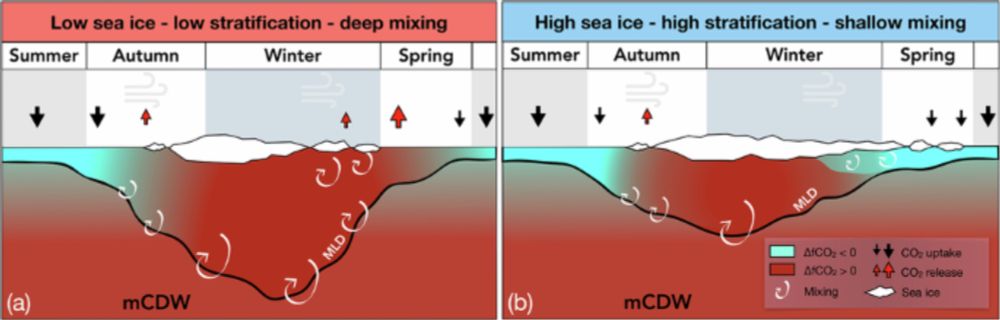
New insight into how sea ice controls the ocean uptake of carbon dioxide around Antarctica, obtained from the unique year-round Rothera Time Series.
Delighted to be part of this study, led by the very excellent Elise Droste.
🧪❄️🥼🌊
www.nature.com/articles/s43...


Come by my #EGU25 presentation where I will show new insights from oxygen stable isotopes!
🗓️: Monday April 28
🕰️: 14:32 - 14:42
⛓️💥: meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU25/EGU25-...

Come by my #EGU25 presentation where I will show new insights from oxygen stable isotopes!
🗓️: Monday April 28
🕰️: 14:32 - 14:42
⛓️💥: meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU25/EGU25-...
We attempted to answer these questions in this study:
rdcu.be/eh0e8
1/14
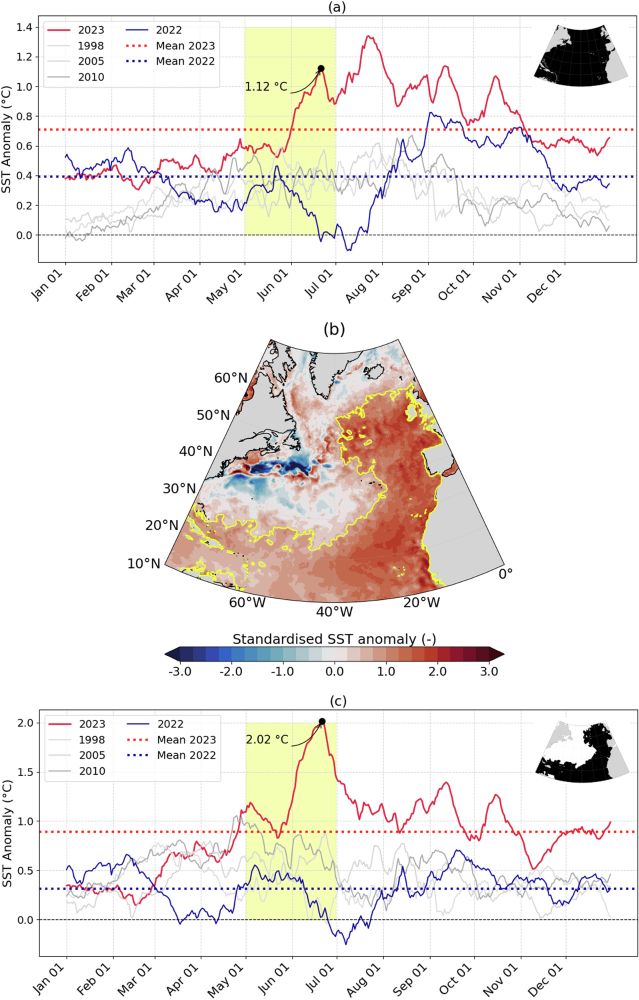
We attempted to answer these questions in this study:
rdcu.be/eh0e8
1/14
This composite model-based estimate of the ocean carbon sink from 1959 to 2022 is similar in magnitude to the best estimate of the Global Carbon Budget but 70 % less uncertain.
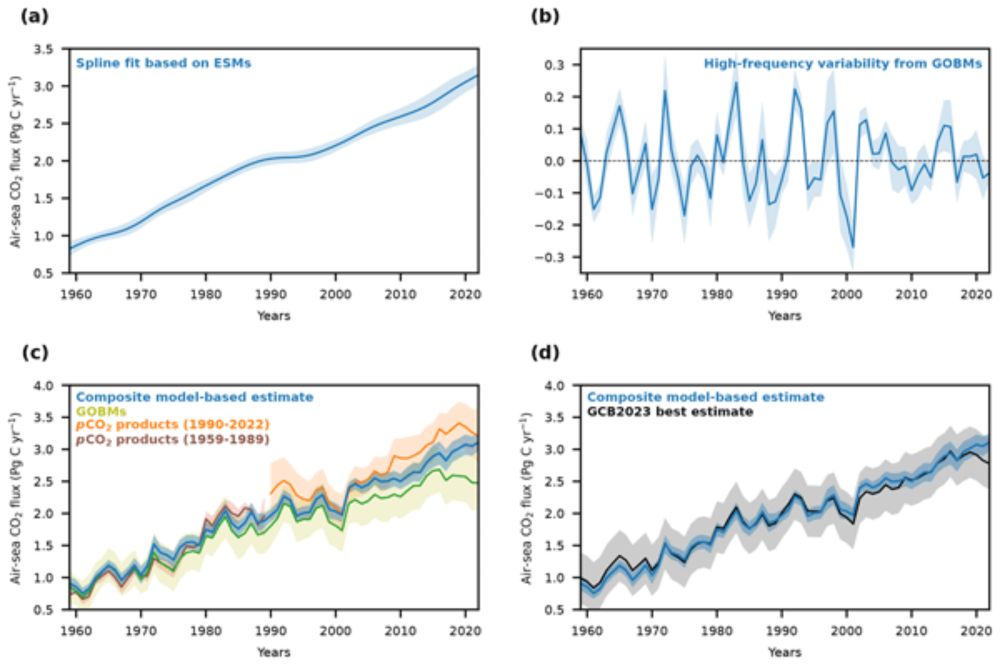
This composite model-based estimate of the ocean carbon sink from 1959 to 2022 is similar in magnitude to the best estimate of the Global Carbon Budget but 70 % less uncertain.
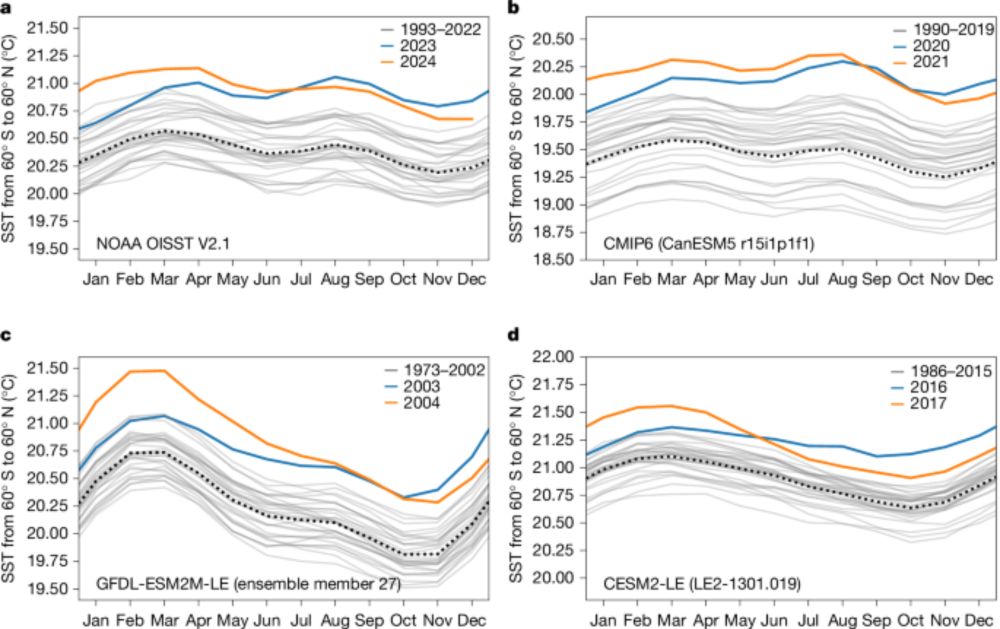
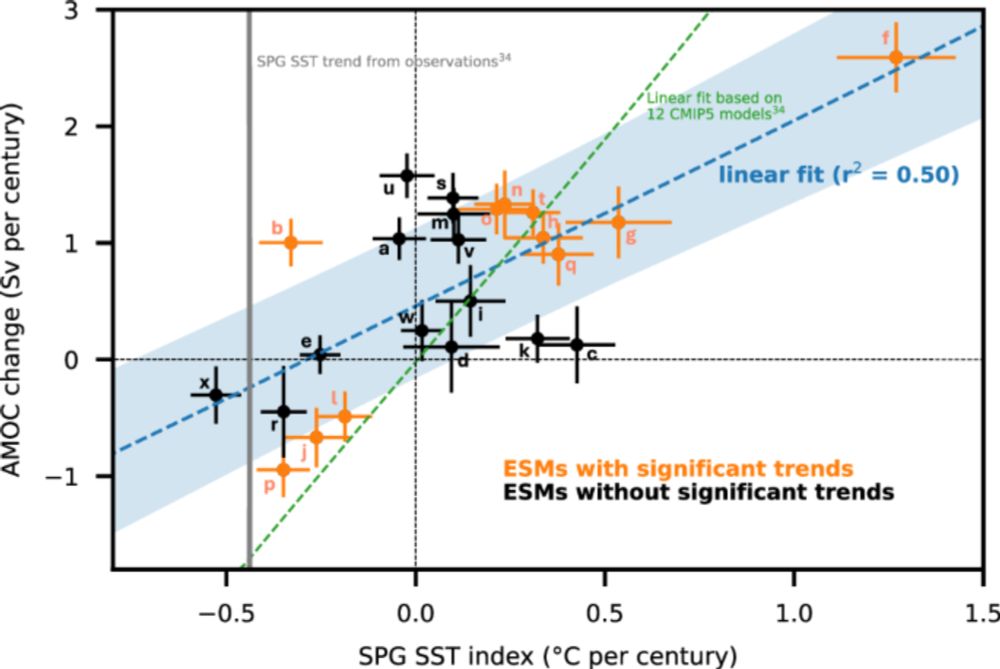
• A rare 1-in-512-year event
• Only possible due to human-caused global warming
• Climate models capture it—no signs of unexpected climate change
More details below 👇
Is it true that climate models cannot simulate such SST jumps? What is common to such jumps? How will SSTs evolve over the next months and years? Are we in uncharted territory? More from our recent study in Nature is here👇
• A rare 1-in-512-year event
• Only possible due to human-caused global warming
• Climate models capture it—no signs of unexpected climate change
More details below 👇
Is it true that climate models cannot simulate such SST jumps? What is common to such jumps? How will SSTs evolve over the next months and years? Are we in uncharted territory? More from our recent study in Nature is here👇

Is it true that climate models cannot simulate such SST jumps? What is common to such jumps? How will SSTs evolve over the next months and years? Are we in uncharted territory? More from our recent study in Nature is here👇
Optimizing Southern Ocean Carbon Sink Observations Using Autonomous Floats ( @bgc-argo.bsky.social )
Supervisors: JB Sallée ; Collaboration: H. Claustre ; P. Landschutzer ; E. McDonagh
Location: IPSL (LOCEAN), Paris, Fr
emploi.cnrs.fr/Offres/CDD/U...

Optimizing Southern Ocean Carbon Sink Observations Using Autonomous Floats ( @bgc-argo.bsky.social )
Supervisors: JB Sallée ; Collaboration: H. Claustre ; P. Landschutzer ; E. McDonagh
Location: IPSL (LOCEAN), Paris, Fr
emploi.cnrs.fr/Offres/CDD/U...
The Future Evolution of Global Ocean Overturning Cells at Different Global Warming Levels (2 years)
Deadline for application: 1 April 2025
Supervisors: Jean-Baptiste Sallée, Roland Séférian
Location: CNRM, Toulouse, France
More info: docs.google.com/document/d/1...
The Future Evolution of Global Ocean Overturning Cells at Different Global Warming Levels (2 years)
Deadline for application: 1 April 2025
Supervisors: Jean-Baptiste Sallée, Roland Séférian
Location: CNRM, Toulouse, France
More info: docs.google.com/document/d/1...
Thanks to the #GO2NE team for hosting me!
📽️ youtu.be/i3zc1bjcFDI?...
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
📽️ www.youtube.com/watch?v=i3zc...
#ocean #deoxygenation
Thanks to the #GO2NE team for hosting me!
📽️ youtu.be/i3zc1bjcFDI?...
📄 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
She showed that growing seaweed (macroalgae) is not an effective way to remove atmospheric CO₂. 🌊

She showed that growing seaweed (macroalgae) is not an effective way to remove atmospheric CO₂. 🌊

