
https://laskerlab.org/

Join us!

Join us!
🧠 AI & IDP phase behavior | 🌱 Protein thermosensing | ❄️ Cryo-EM
🧬 GTPase activity | 🛠️ Engineered condensates | 🤖 Deep learning | 💧 Phase separation

🧠 AI & IDP phase behavior | 🌱 Protein thermosensing | ❄️ Cryo-EM
🧬 GTPase activity | 🛠️ Engineered condensates | 🤖 Deep learning | 💧 Phase separation

14a/ Why does this matter? 🧬
Replacing PopZ with a filament-deficient mutant is toxic to Caulobacter crescentus. To investigate, we tagged ParB, a protein anchored by PopZ and crucial for DNA segregation. 🔍✨

14a/ Why does this matter? 🧬
Replacing PopZ with a filament-deficient mutant is toxic to Caulobacter crescentus. To investigate, we tagged ParB, a protein anchored by PopZ and crucial for DNA segregation. 🔍✨
Putting it all together ⬇️

Putting it all together ⬇️
In the dilute phase, the client-binding region binds the OD region needed for assembly.
Upon condensation, an IDR-driven conformational change:
1️⃣ Reveals OD interfaces for condensate formation.
2️⃣ Exposes client-binding sites to recruit partners.
A molecular multitasker!

In the dilute phase, the client-binding region binds the OD region needed for assembly.
Upon condensation, an IDR-driven conformational change:
1️⃣ Reveals OD interfaces for condensate formation.
2️⃣ Exposes client-binding sites to recruit partners.
A molecular multitasker!
By separating the OD from the IDR, we uncovered:
1️⃣ The OD is necessary and sufficient for condensation.
2️⃣ OD-only condensates are filamentous, resembling those formed by the full-length protein.
3️⃣ The IDR inhibits condensation
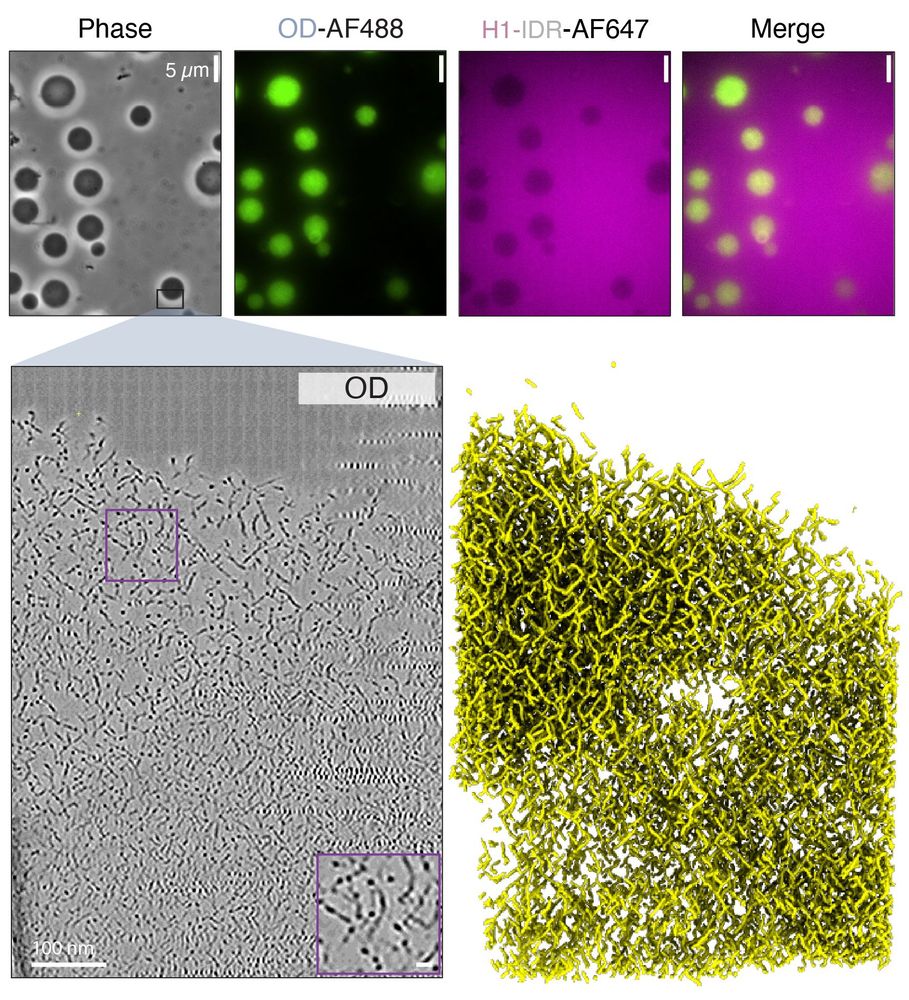
By separating the OD from the IDR, we uncovered:
1️⃣ The OD is necessary and sufficient for condensation.
2️⃣ OD-only condensates are filamentous, resembling those formed by the full-length protein.
3️⃣ The IDR inhibits condensation
PopZ filaments assemble via a non-cooperative isodesmic model—binding affinities stay constant regardless of filament length.

PopZ filaments assemble via a non-cooperative isodesmic model—binding affinities stay constant regardless of filament length.
Using cryo-ET (in collaboration with the Park Lab), we revealed that PopZ condensates are built from filaments—a crucial insight into their structural organization.
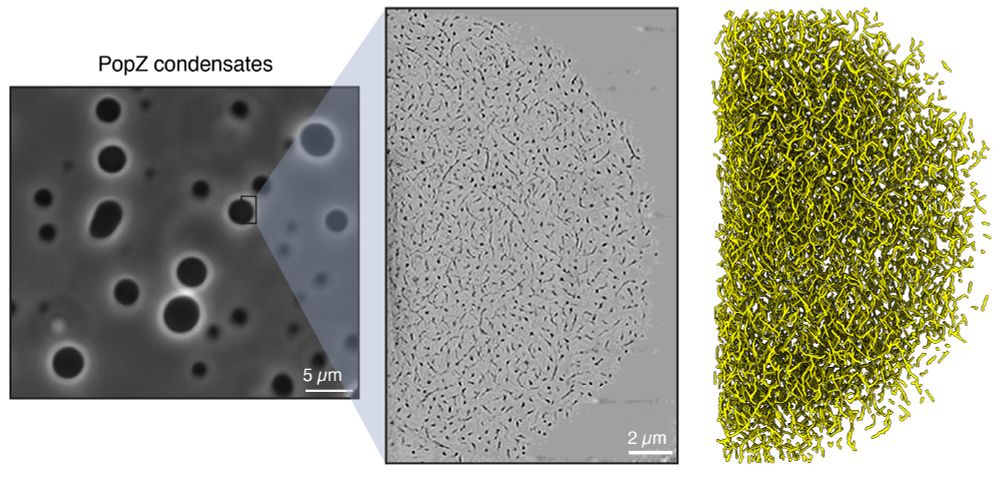
Using cryo-ET (in collaboration with the Park Lab), we revealed that PopZ condensates are built from filaments—a crucial insight into their structural organization.
PopZ is modular, featuring three key regions:
• A C-terminal oligomerization domain (OD) that drives condensation
• A negatively charged, proline-rich IDR that regulates fluidity
• An N-terminal helical region (H1) that binds clients

PopZ is modular, featuring three key regions:
• A C-terminal oligomerization domain (OD) that drives condensation
• A negatively charged, proline-rich IDR that regulates fluidity
• An N-terminal helical region (H1) that binds clients
PopZ is a small, largely disordered protein that helps microbes 🦠 in α-proteobacteria organize their cytoplasm.
We study C. crescentus PopZ, discovered in 2008.
Check out this tomogram (previous work with @thevillalab.bsky.social) showing PopZ forming ribosome-free microdomains!

PopZ is a small, largely disordered protein that helps microbes 🦠 in α-proteobacteria organize their cytoplasm.
We study C. crescentus PopZ, discovered in 2008.
Check out this tomogram (previous work with @thevillalab.bsky.social) showing PopZ forming ribosome-free microdomains!

