Counting everything I can, but still appreciating the beauty of qualitative findings.
https://johanneswilbertz.github.io/
For a general term like "in this study", the results for 2023-2024 were exactly on the trendline based on the 2014-2022 data. So probably, there is no reason to believe that publication numbers rose in general after 2022, but only certain word frequencies changed.

For a general term like "in this study", the results for 2023-2024 were exactly on the trendline based on the 2014-2022 data. So probably, there is no reason to believe that publication numbers rose in general after 2022, but only certain word frequencies changed.
Unexpectedly, there was a drop in abstracts using widespread words like "our results" or "we show" after 2022. This might indicate the use of LLMs by researchers, as LLM-generated text often uses passive rather than active language ("this shows" versus "we show").


Unexpectedly, there was a drop in abstracts using widespread words like "our results" or "we show" after 2022. This might indicate the use of LLMs by researchers, as LLM-generated text often uses passive rather than active language ("this shows" versus "we show").
Some words are clearly more frequently found in biomedical literature after 2022, such as "pertinent", "treasure trove" or "shedding light". This could be due to overall publication numbers increasing for LLM-unrelated reasons.



Some words are clearly more frequently found in biomedical literature after 2022, such as "pertinent", "treasure trove" or "shedding light". This could be due to overall publication numbers increasing for LLM-unrelated reasons.





Our study therefore shows that ARPC2 inhibition can rescue early PMDS-related hyperdifferentiation phenotypes. We believe that human stem cell models will significantly advance the discovery and evaluation of new, safe neurodevelopmental treatments in the future.

Our study therefore shows that ARPC2 inhibition can rescue early PMDS-related hyperdifferentiation phenotypes. We believe that human stem cell models will significantly advance the discovery and evaluation of new, safe neurodevelopmental treatments in the future.
SHANK3 is a crucial synaptic scaffolding protein, but on the electrophysiological level we did not find any rescuing effects of ARPC2 inhibition. This might be caused by the fact that the SHANK3 protein level inside of synapses remains unchanged after ARPC2 inhibition.

SHANK3 is a crucial synaptic scaffolding protein, but on the electrophysiological level we did not find any rescuing effects of ARPC2 inhibition. This might be caused by the fact that the SHANK3 protein level inside of synapses remains unchanged after ARPC2 inhibition.
The ARPC2-targetting compound Benproperine also rescued increased synapse numbers when administered early during differentiation, but had little impact when added later during neuronal differentiation.

The ARPC2-targetting compound Benproperine also rescued increased synapse numbers when administered early during differentiation, but had little impact when added later during neuronal differentiation.
We found that ARPC2 was expressed in out cells and that its inhibition rescued the decreased proliferation in SHANK3-deficient young neurons and rescued ARPC2 colocalization with ß-actin.

We found that ARPC2 was expressed in out cells and that its inhibition rescued the decreased proliferation in SHANK3-deficient young neurons and rescued ARPC2 colocalization with ß-actin.
Next we performed a drug screen with >7,000 small molecules with known mode-of-action to rescue the hyperdifferentiation phenotype in CRISPR-engineered SHANK3-deficient cells.

Next we performed a drug screen with >7,000 small molecules with known mode-of-action to rescue the hyperdifferentiation phenotype in CRISPR-engineered SHANK3-deficient cells.
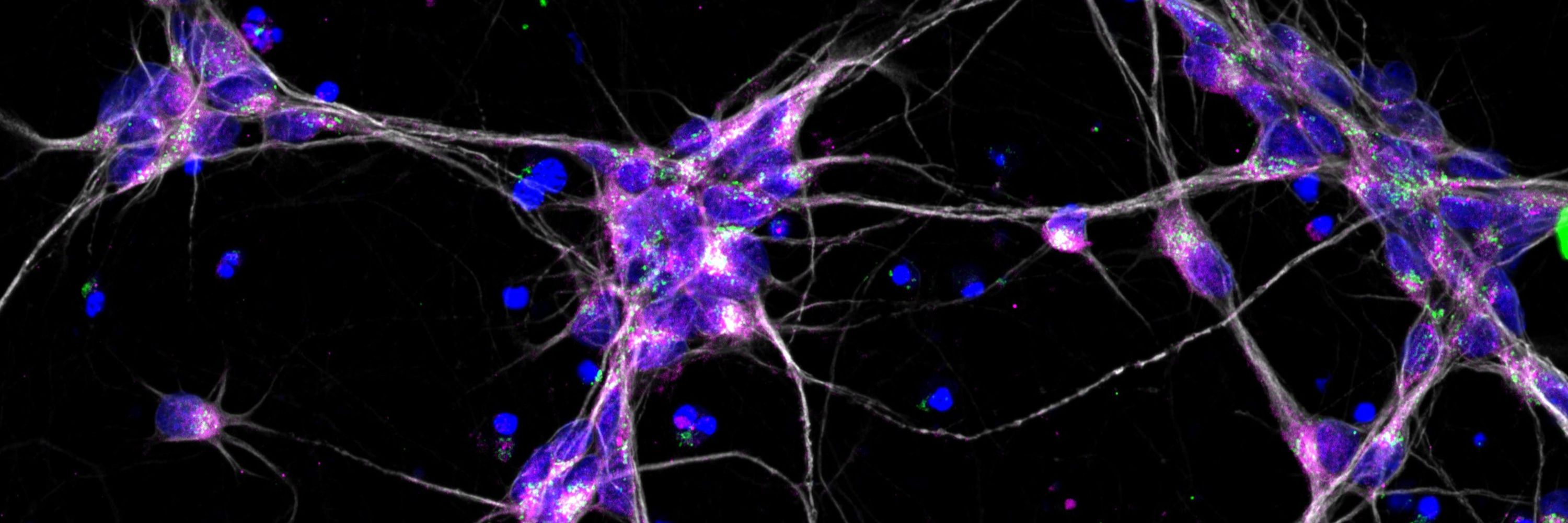
SHANK3 haploinsufficiency does not only impact early differentiation, but leads to increased MAP2 network length and pre-synaptic spots, variable synapse numbers, and decreased total SHANK3 content and neuronal activity in SHANK3-deficient neurons.

SHANK3 haploinsufficiency does not only impact early differentiation, but leads to increased MAP2 network length and pre-synaptic spots, variable synapse numbers, and decreased total SHANK3 content and neuronal activity in SHANK3-deficient neurons.
PMDS arises from mutations in the terminal region of chromosome 22q13, impacting the SHANK3 gene. We found that PMDS patient-derived and CRISPR-engineered cell lines lacking one SHANK3 copy show decreased proliferation & increased differentiation, mirroring traits of PMDS.

PMDS arises from mutations in the terminal region of chromosome 22q13, impacting the SHANK3 gene. We found that PMDS patient-derived and CRISPR-engineered cell lines lacking one SHANK3 copy show decreased proliferation & increased differentiation, mirroring traits of PMDS.
#PMDS #StemCells
Read the paper (rdcu.be/dKnYt) & the thread. 1/n

#PMDS #StemCells
Read the paper (rdcu.be/dKnYt) & the thread. 1/n



