
Jonathan Wille
@jonathanwille.bsky.social
❄️ Polar meteorologist and climatologist.
Studying #polar #meteorology #climatology with focus on atmospheric rivers, mass balance impacts, and high-res climate modeling.
Post-doc researcher at ETH Zurich.
Studying #polar #meteorology #climatology with focus on atmospheric rivers, mass balance impacts, and high-res climate modeling.
Post-doc researcher at ETH Zurich.
This proposal to revoke the Endangerment Finding will prevent the government from regulating greenhouse gas emissions now and even in the future. There will be an opportunity to publicly comment on this proposal and remind the EPA that almost all climate scientists think this report is a joke.
July 30, 2025 at 12:23 PM
This proposal to revoke the Endangerment Finding will prevent the government from regulating greenhouse gas emissions now and even in the future. There will be an opportunity to publicly comment on this proposal and remind the EPA that almost all climate scientists think this report is a joke.
I've given it a quick read and quickly realized that the sections concerning CO2 as plant food were full of confirmation bias and cherry picking. Further sections about climate change scenarios used strawman arguments. I fed the report into ChatGPT which agreed with my suspicions.
July 30, 2025 at 12:23 PM
I've given it a quick read and quickly realized that the sections concerning CO2 as plant food were full of confirmation bias and cherry picking. Further sections about climate change scenarios used strawman arguments. I fed the report into ChatGPT which agreed with my suspicions.
But much more research is needed before these experimental models can be operationalised for local climate services. Again I want to thank my co-authors for supporting this research.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
But much more research is needed before these experimental models can be operationalised for local climate services. Again I want to thank my co-authors for supporting this research.
So is there an added value for using these high resolution, yet limited run time models? It seems mostly a yes for extreme precipitation events, especially as the nextGEMS models compared well with a regional climate model. They can provide coverage to the globally underserved in climate prediction
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
So is there an added value for using these high resolution, yet limited run time models? It seems mostly a yes for extreme precipitation events, especially as the nextGEMS models compared well with a regional climate model. They can provide coverage to the globally underserved in climate prediction
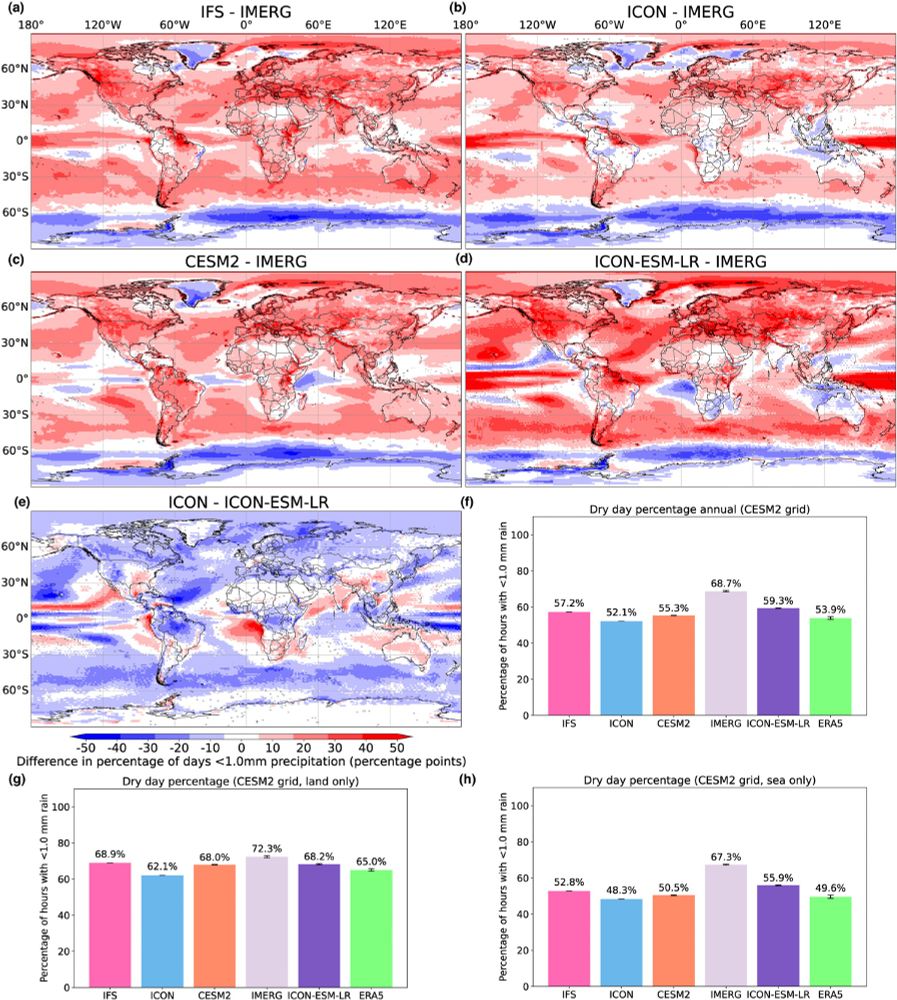
Finally, looking at the global daily dry fraction on a common, coarse resolution, the differences between the models is diminished suggesting that resolution is the main driver of improvements. One big theme though is the difficulty of validating extreme precipitation with Obs and reanalysis.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
Finally, looking at the global daily dry fraction on a common, coarse resolution, the differences between the models is diminished suggesting that resolution is the main driver of improvements. One big theme though is the difficulty of validating extreme precipitation with Obs and reanalysis.
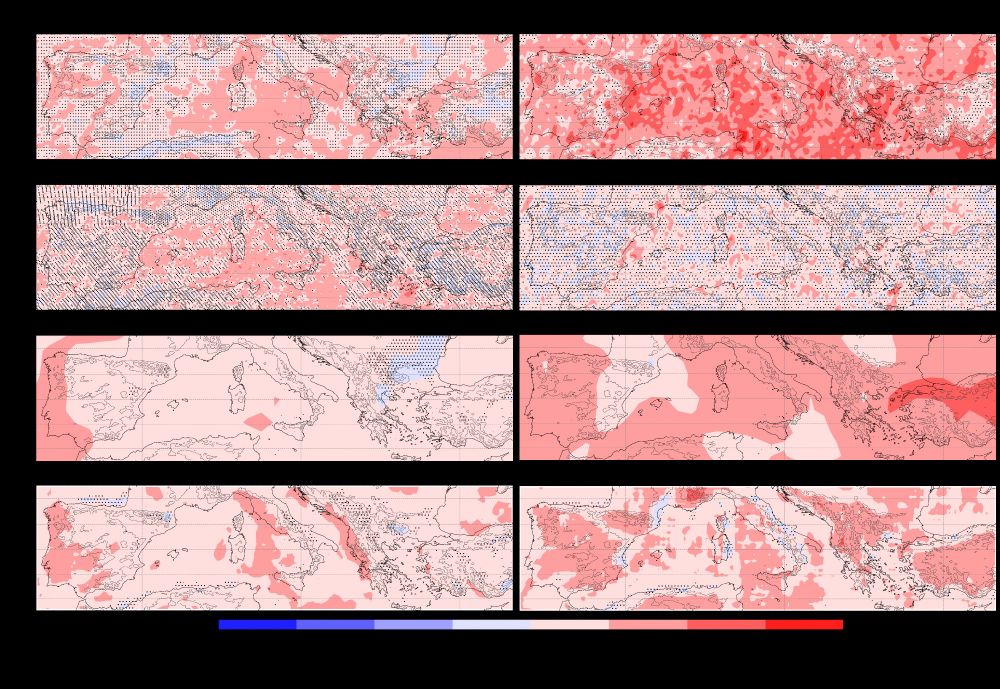
One possible culprit is the missing connection between moisture convergence and extreme precipitation in ICON. The lack of convection parameterization means ICON generates more bubbly, isolated convective cells instead of organized precipitation along frontal boundaries
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
One possible culprit is the missing connection between moisture convergence and extreme precipitation in ICON. The lack of convection parameterization means ICON generates more bubbly, isolated convective cells instead of organized precipitation along frontal boundaries
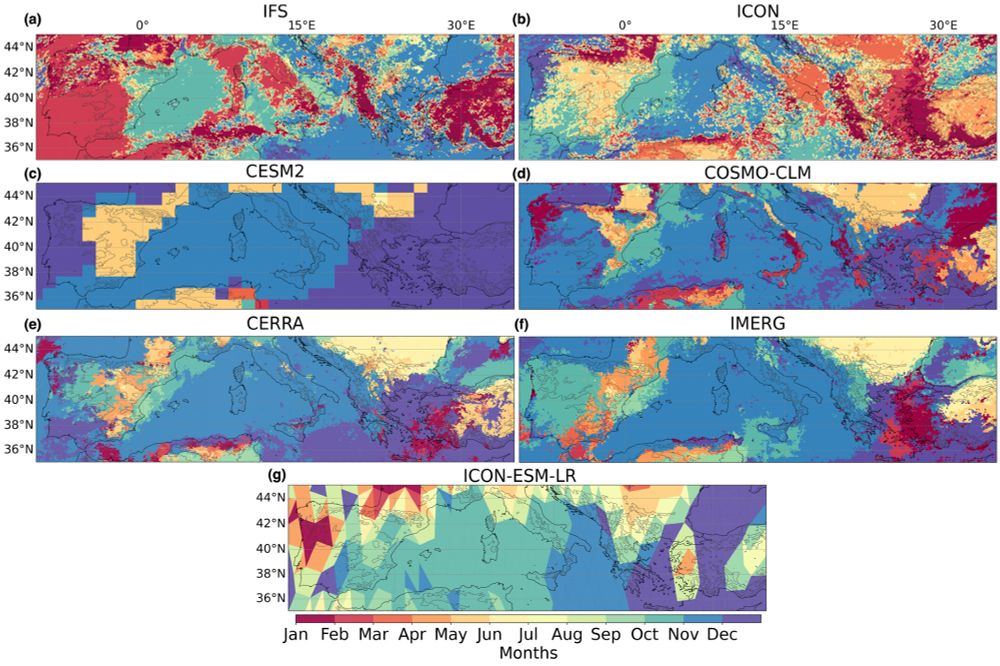
To better understand what factors drive precipitation patterns in the models, we looked at which month contains the most extreme rainfall. Normally autumn is the primary time for extreme weather in the Mediterranean, but ICON misses this meaning a less consistent extreme precipitation forcing
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
To better understand what factors drive precipitation patterns in the models, we looked at which month contains the most extreme rainfall. Normally autumn is the primary time for extreme weather in the Mediterranean, but ICON misses this meaning a less consistent extreme precipitation forcing
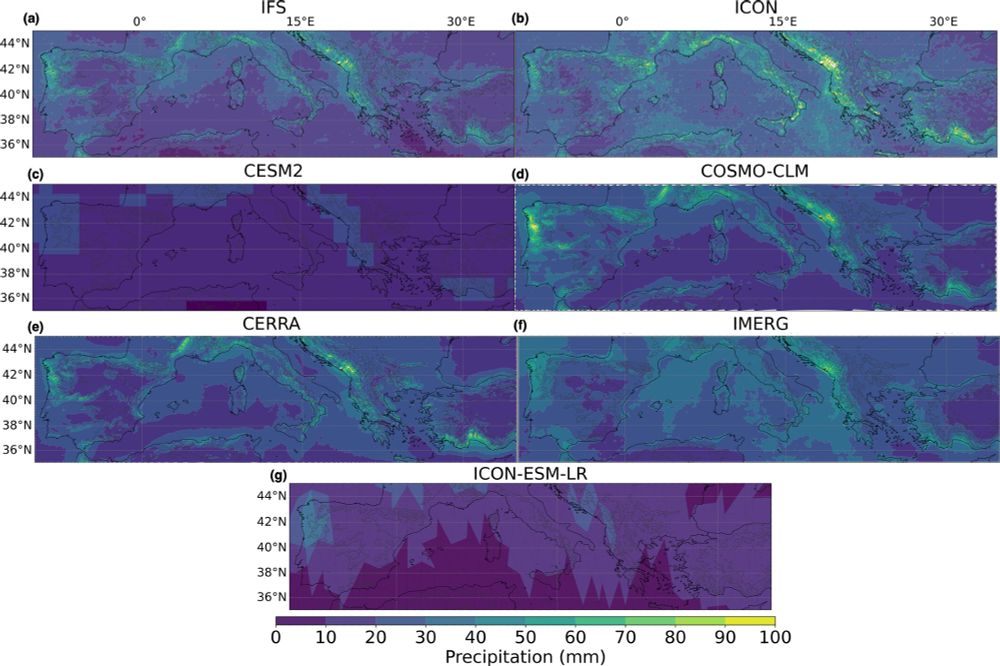
The benefits of higher resolution are seen again in the 95th quantile of daily precipitation where IFS and ICON show higher rainfall values in mountainous terrain.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
The benefits of higher resolution are seen again in the 95th quantile of daily precipitation where IFS and ICON show higher rainfall values in mountainous terrain.
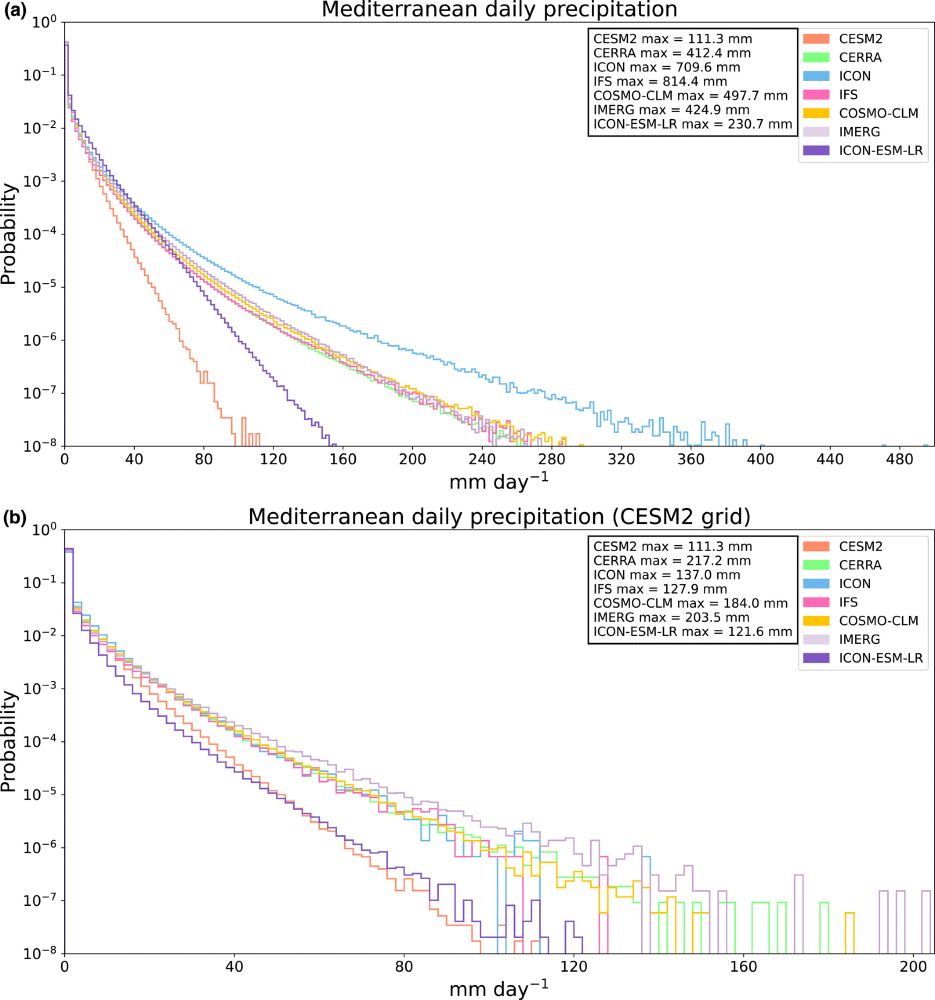
Moving to the high-tail end of precipitation extremes, IFS produced very high, yet reasonable values of extreme rainfall. When controlling for resolution, this improvement over CESM2 persists for both IFS and ICON. This is important for having a climate model directly simulate flooding rains.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
Moving to the high-tail end of precipitation extremes, IFS produced very high, yet reasonable values of extreme rainfall. When controlling for resolution, this improvement over CESM2 persists for both IFS and ICON. This is important for having a climate model directly simulate flooding rains.
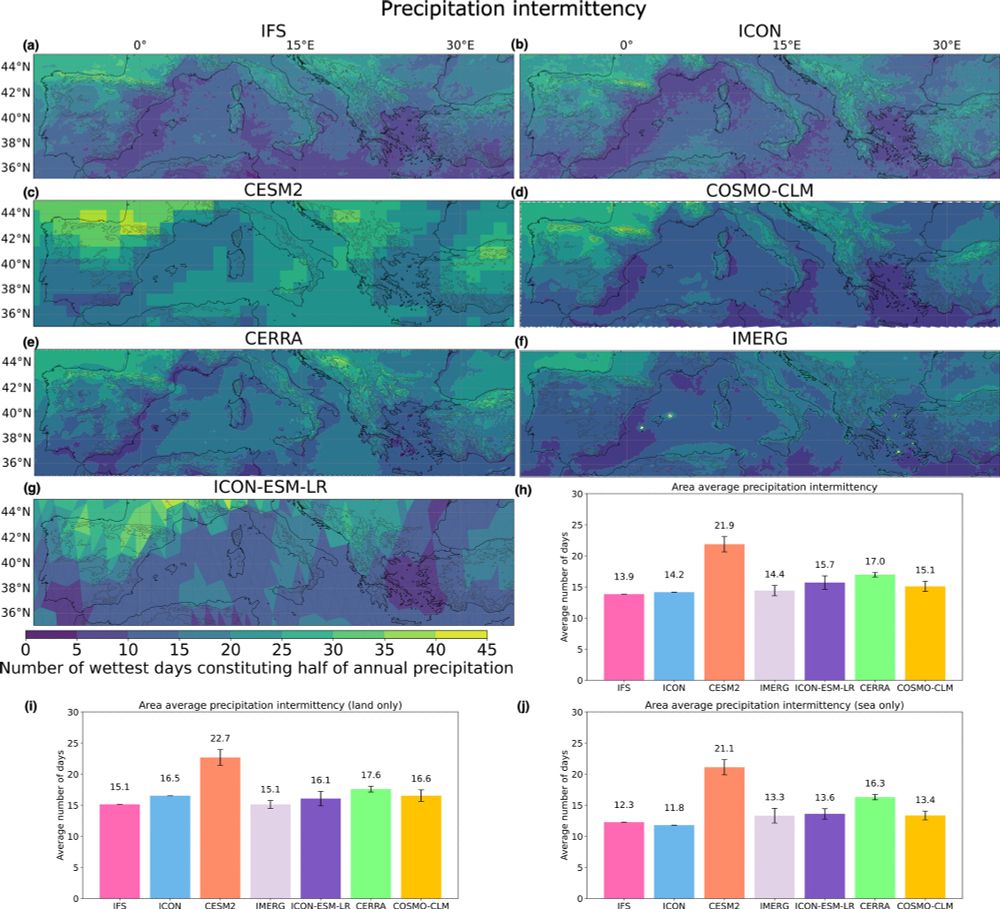
Precipitation intermittency represents how precipitation is distributed during the year. Is it light and frequent, or intense and rare? Here IFS and ICON show clear improvements over the CESM2 which has too diffuse precipitation leading to the common "drizzle bias"
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
Precipitation intermittency represents how precipitation is distributed during the year. Is it light and frequent, or intense and rare? Here IFS and ICON show clear improvements over the CESM2 which has too diffuse precipitation leading to the common "drizzle bias"
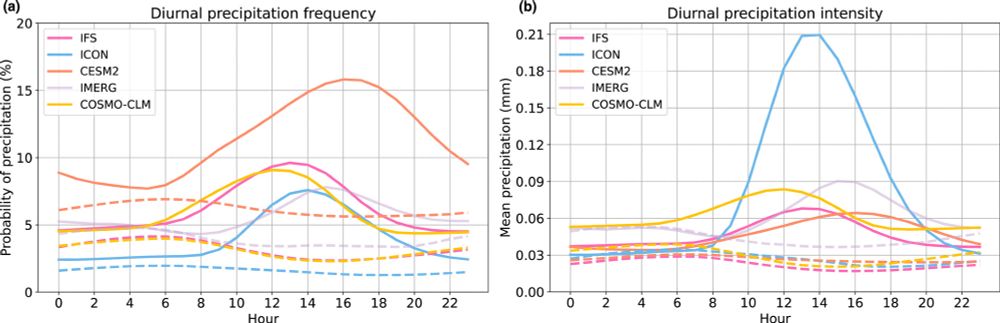
We know that ICON has no convection parameterization which leads allows it to produce more convective showers and thunderstorms, thus breaking up the dry spells over land. But this also causes the afternoon storms to be far too intense.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
We know that ICON has no convection parameterization which leads allows it to produce more convective showers and thunderstorms, thus breaking up the dry spells over land. But this also causes the afternoon storms to be far too intense.
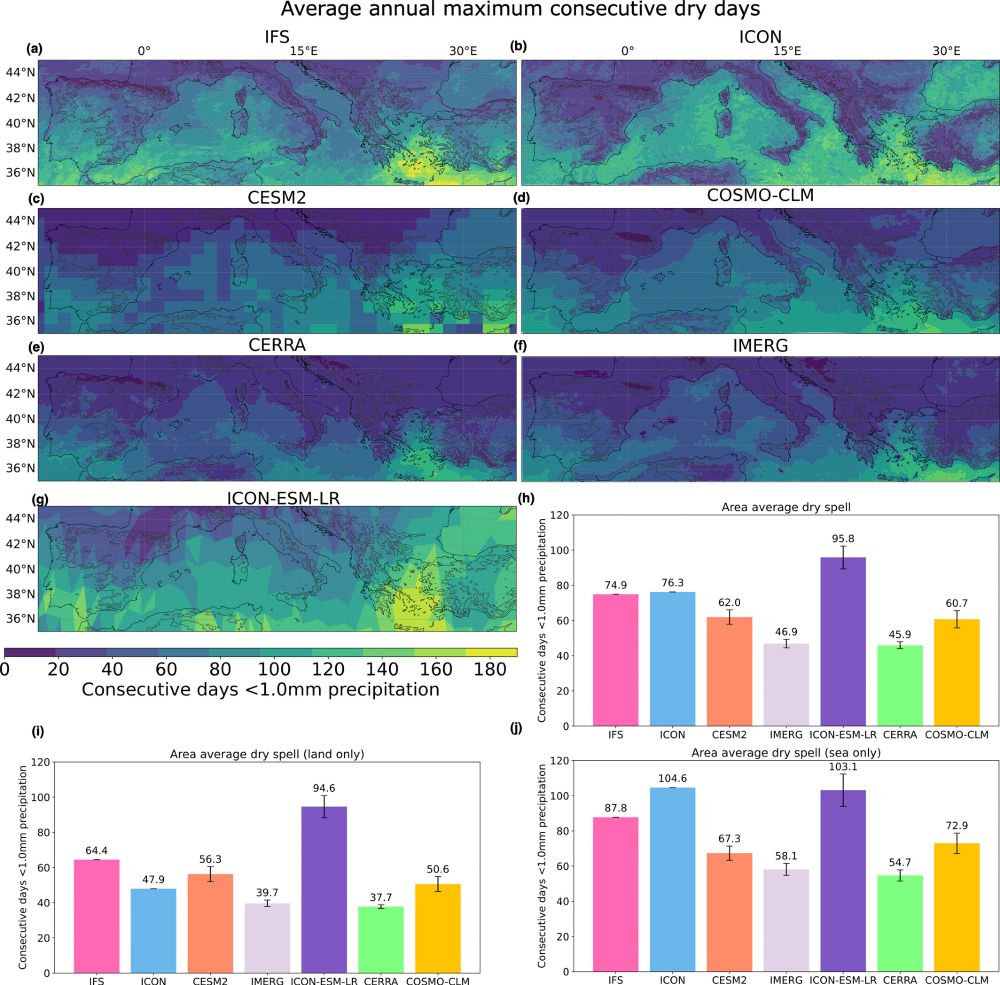
Greater differences are found in the average maximum annual dry spell. Here IFS and ICON produce very long dry spells compared to observations and a coarser global climate model (CESM2). The important exception here is the ICON model over land.
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
Greater differences are found in the average maximum annual dry spell. Here IFS and ICON produce very long dry spells compared to observations and a coarser global climate model (CESM2). The important exception here is the ICON model over land.
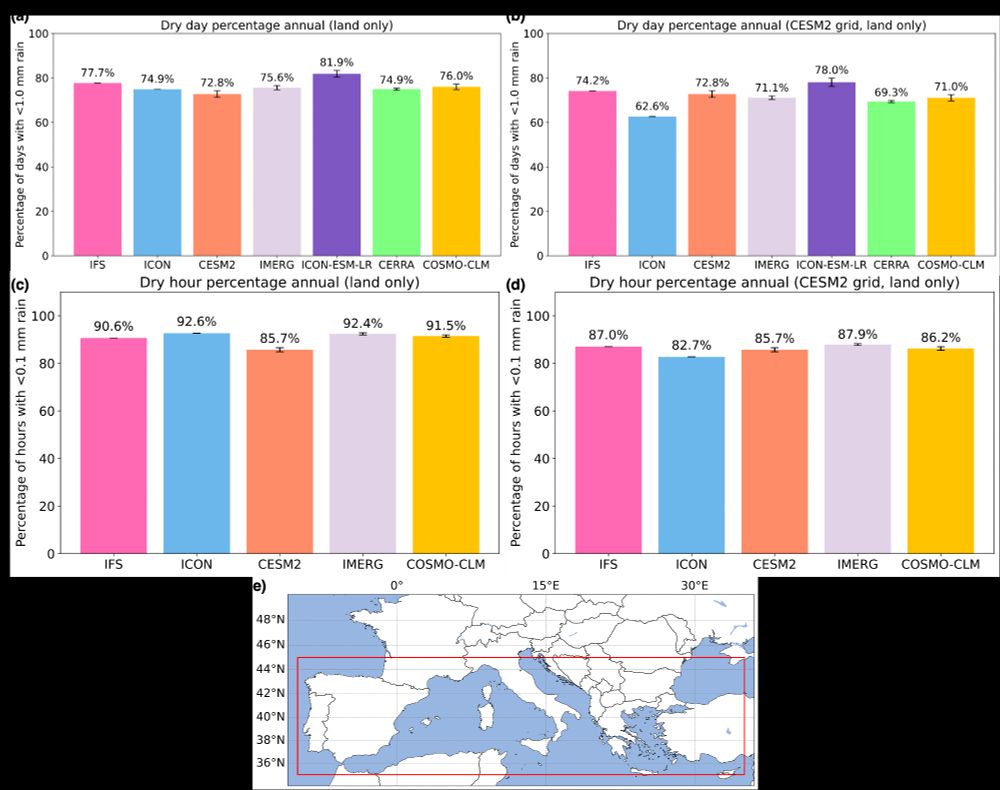
Focusing on the Mediterranean region, we test the added value of having very high resolution for depicting extreme precipitation (drought and flood). Starting with the percentage of days/hours with no rain, we find that the greatest improvements are over land. This is from the higher resolution
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
Focusing on the Mediterranean region, we test the added value of having very high resolution for depicting extreme precipitation (drought and flood). Starting with the percentage of days/hours with no rain, we find that the greatest improvements are over land. This is from the higher resolution
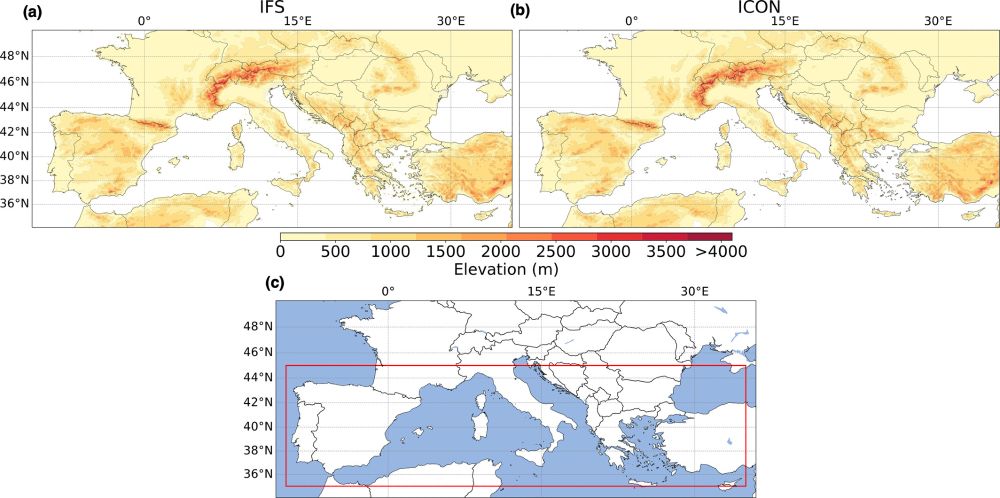
This research focused on two experimental, fully-coupled, convection permitting Earth system models designed within the nextGEMS project. The IFS model has a hybrid convection parameterization scheme and ICON has no convection parameterization. These steps help push the models to higher resolution
July 15, 2025 at 9:50 AM
This research focused on two experimental, fully-coupled, convection permitting Earth system models designed within the nextGEMS project. The IFS model has a hybrid convection parameterization scheme and ICON has no convection parameterization. These steps help push the models to higher resolution

