https://norwichctu.uea.ac.uk/inhale/
https://norwichctu.uea.ac.uk/inhale-pdg/
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
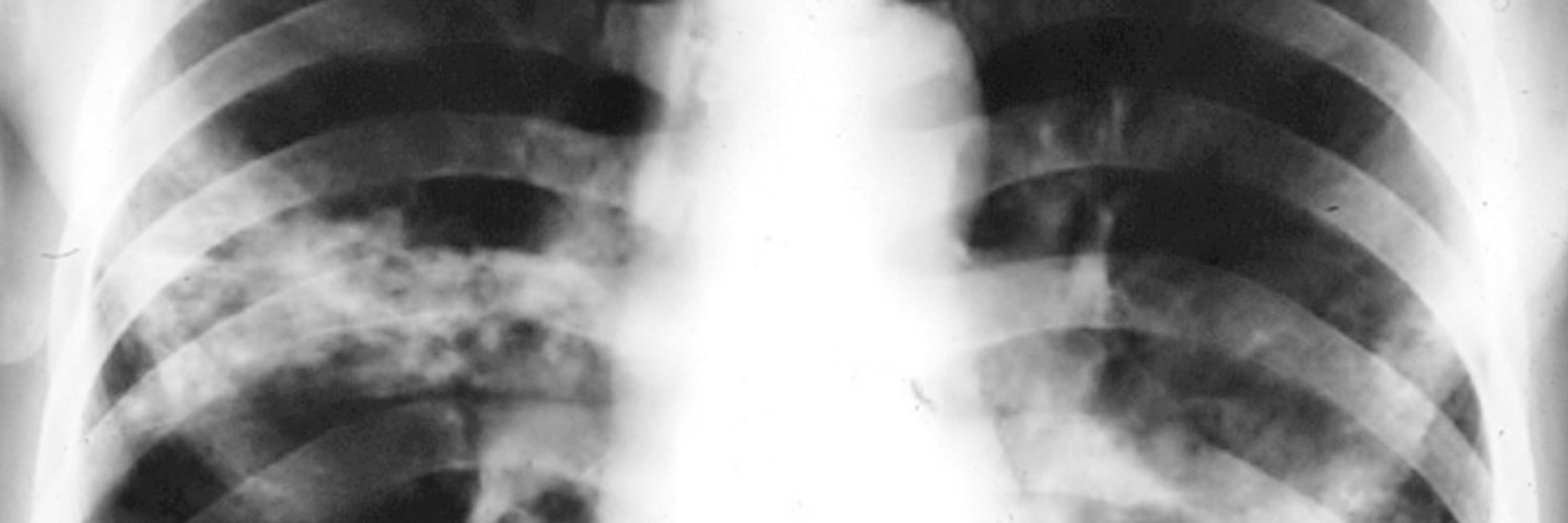
Findings underscore the challenge of changing prescribing decisions based on technical results or guidelines, highlighting factors such as clinicians’ previous experience, and ‘knowledge in practice, to be more proximal drivers of decisions.
Findings underscore the challenge of changing prescribing decisions based on technical results or guidelines, highlighting factors such as clinicians’ previous experience, and ‘knowledge in practice, to be more proximal drivers of decisions.

