https://norwichctu.uea.ac.uk/inhale/
https://norwichctu.uea.ac.uk/inhale-pdg/
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains one of the biggest threats to global health - demanding innovation, collaboration, & better understanding of how we use antibiotics in clinical care.
Read more tinyurl.com/yw792han

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains one of the biggest threats to global health - demanding innovation, collaboration, & better understanding of how we use antibiotics in clinical care.
Read more tinyurl.com/yw792han
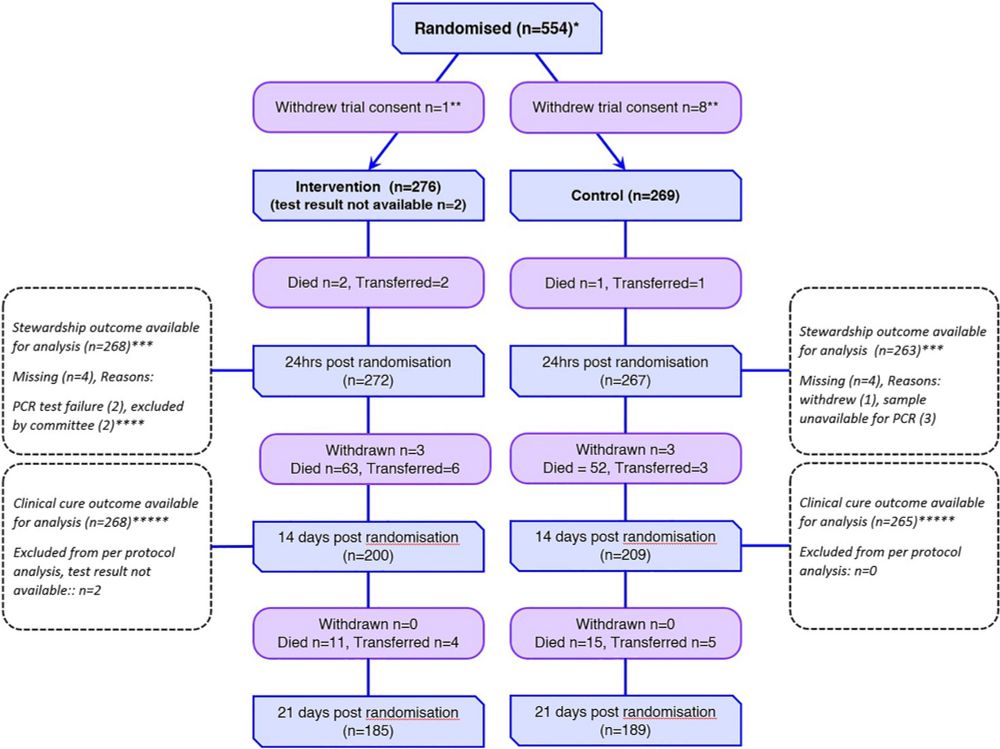
The Pneumonia Panel PCR had lower average ICU costs and was cost effective for antimicrobial stewardship, but not clinical cure.
Read in full at: rdcu.be/eAmSD
The Pneumonia Panel PCR had lower average ICU costs and was cost effective for antimicrobial stewardship, but not clinical cure.
Read in full at: rdcu.be/eAmSD
This poem was written and performed by Amander Wellings, of the INHALE Patient, Carer and Public Involvement (PPI) group.
youtu.be/-UUBzbSmEo0?...

This poem was written and performed by Amander Wellings, of the INHALE Patient, Carer and Public Involvement (PPI) group.
youtu.be/-UUBzbSmEo0?...
Visual abstract below and full paper available online at rdcu.be/ehlAu

Visual abstract below and full paper available online at rdcu.be/ehlAu
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S119...
www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S119...

“Guidelines vs Mindlines” published in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

“Guidelines vs Mindlines” published in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...