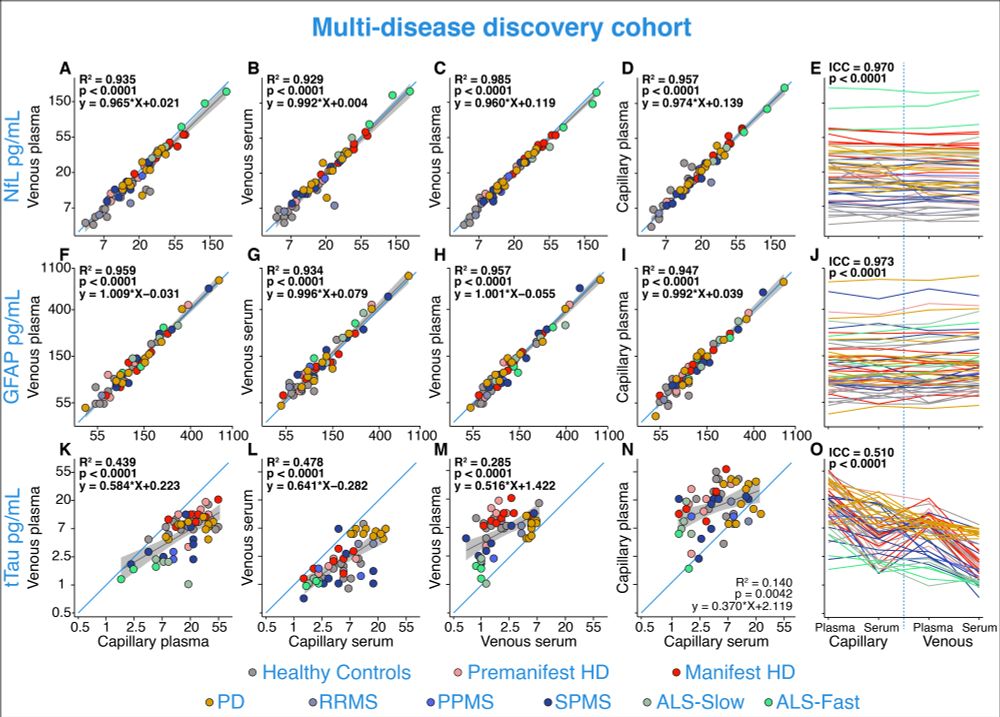
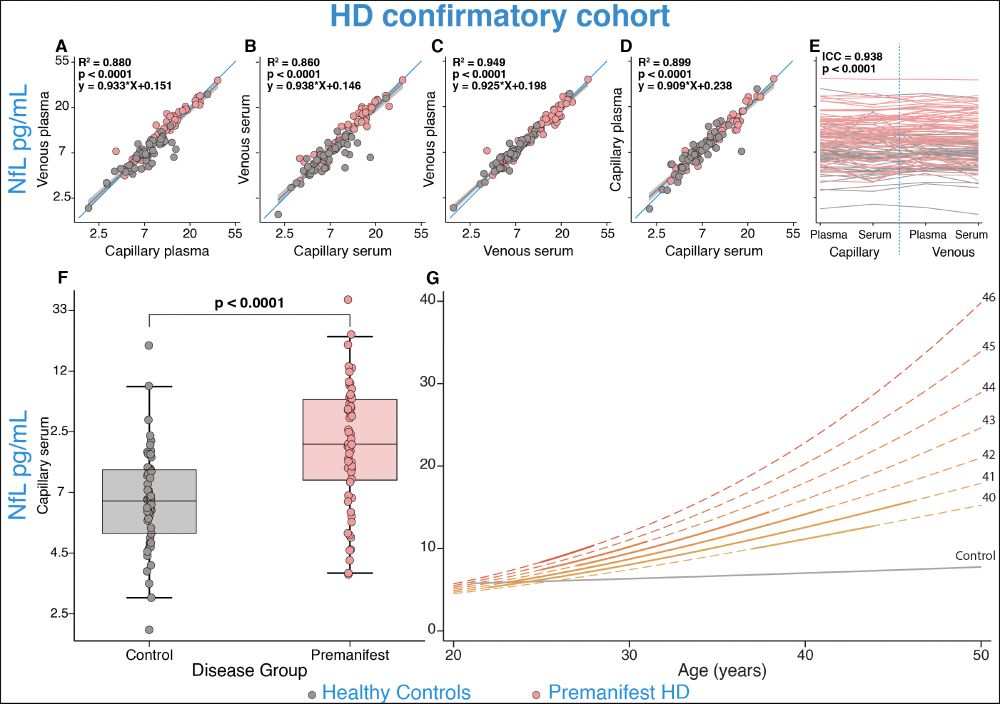
N.B. We were not powered for these group comparisons but did this to illustrate that the pattern is the same as the gold standard
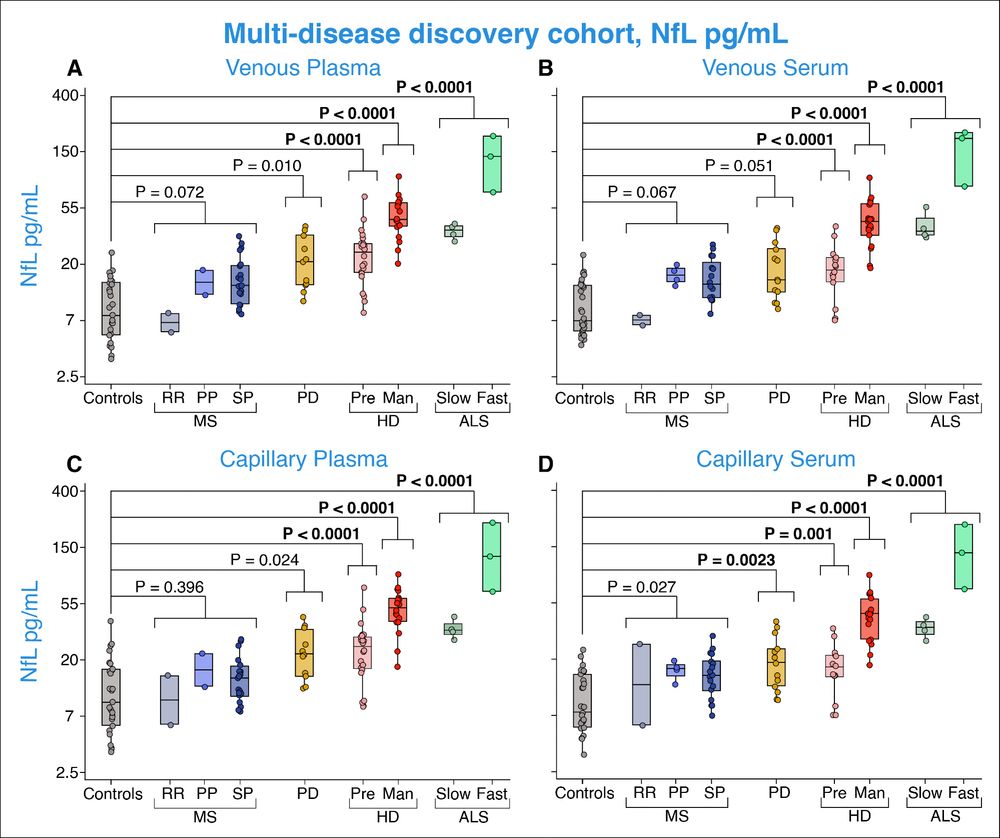
N.B. We were not powered for these group comparisons but did this to illustrate that the pattern is the same as the gold standard
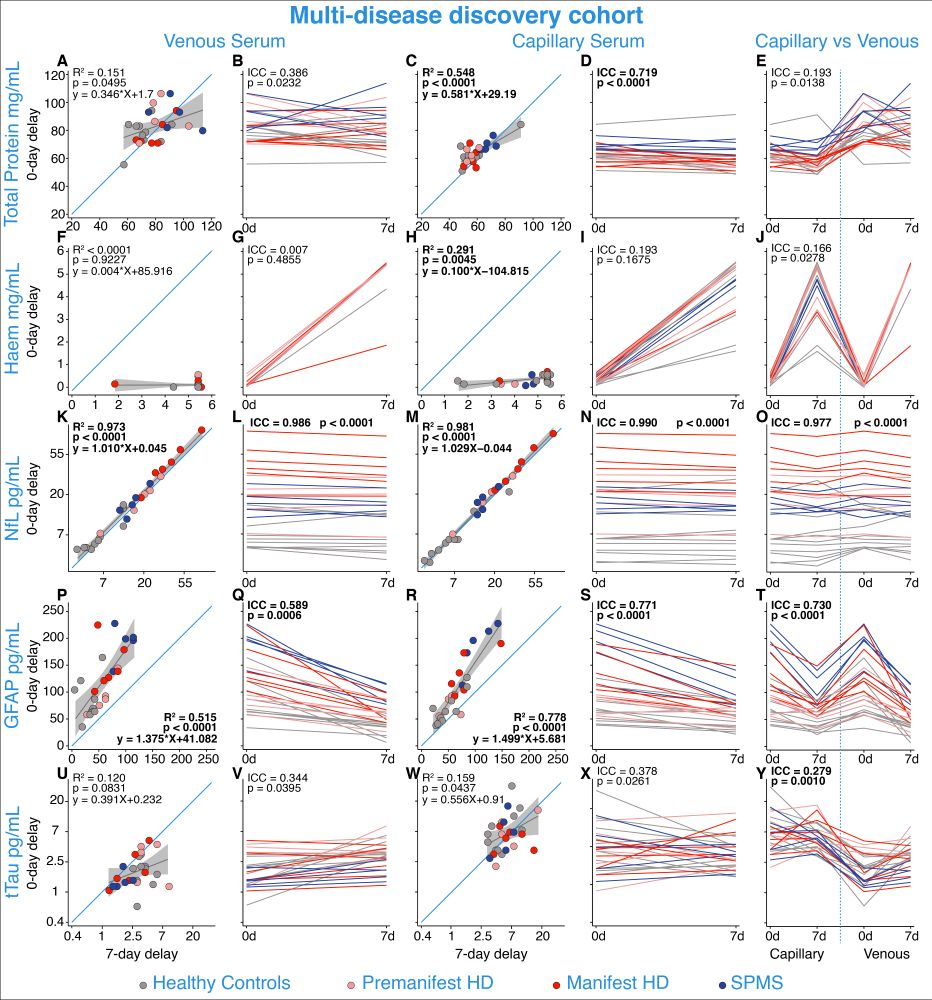
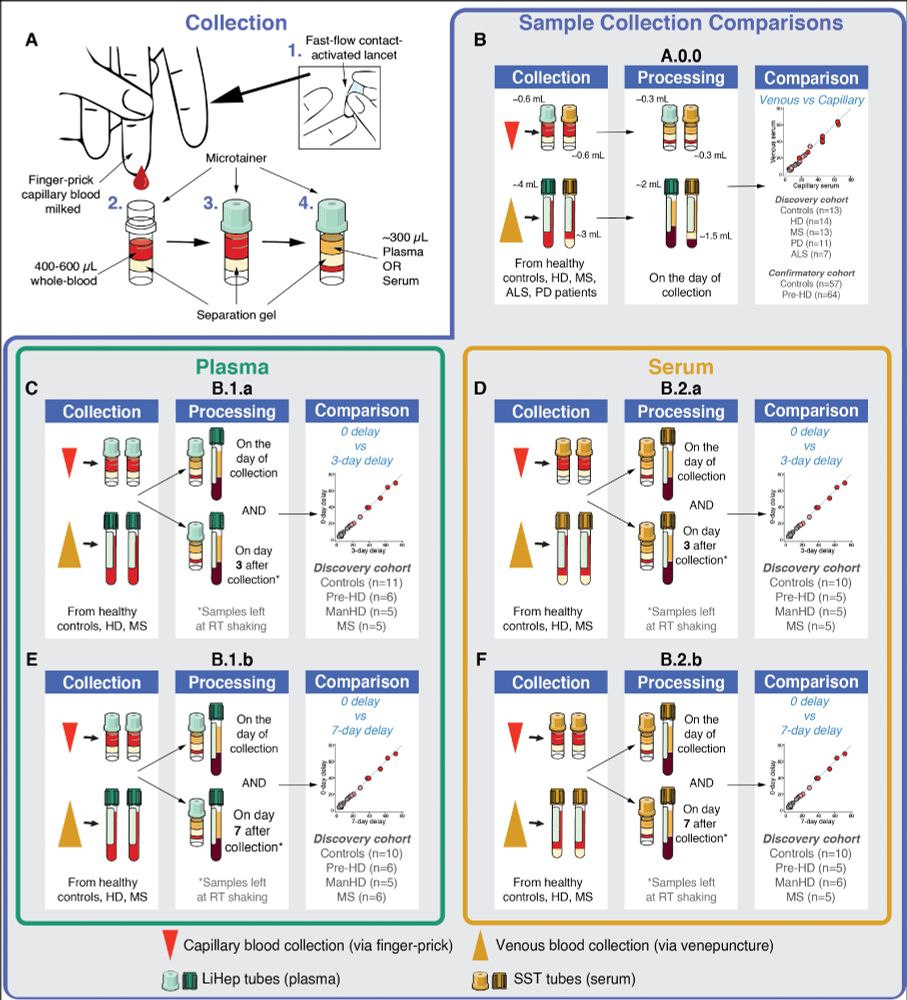
Total protein and haemoglobin were included to the impact of delayed process on the average protein.
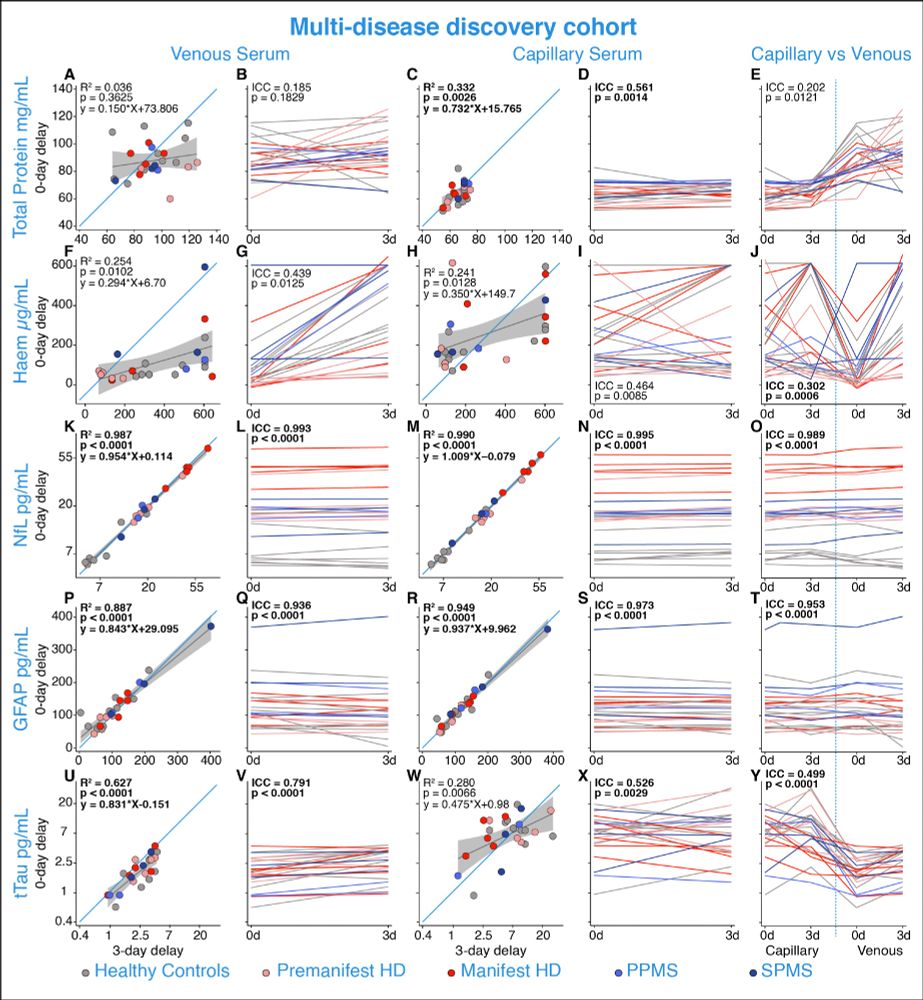
Total protein and haemoglobin were included to the impact of delayed process on the average protein.