
The Groth lab
@grothlab.bsky.social
The Anja Groth group in Copenhagen studies chromatin replication, epigenetic memory and (epi)genome stability in the context of mitotic cell division
We have lift off!! 🚀 Yesterday was the official opening of EpiC! The DNRF Center for Epigenetic Cell Memory at the Danish Cancer Institute!
Our EpiC team with director Anja Groth @groth-anja.bsky.social, were joined by Jesper Fisker, CEO @cancer.dk & Niels Mejlgaar, CEO @dg.dk to celebrate 🎉
Our EpiC team with director Anja Groth @groth-anja.bsky.social, were joined by Jesper Fisker, CEO @cancer.dk & Niels Mejlgaar, CEO @dg.dk to celebrate 🎉

August 28, 2025 at 5:35 PM
We have lift off!! 🚀 Yesterday was the official opening of EpiC! The DNRF Center for Epigenetic Cell Memory at the Danish Cancer Institute!
Our EpiC team with director Anja Groth @groth-anja.bsky.social, were joined by Jesper Fisker, CEO @cancer.dk & Niels Mejlgaar, CEO @dg.dk to celebrate 🎉
Our EpiC team with director Anja Groth @groth-anja.bsky.social, were joined by Jesper Fisker, CEO @cancer.dk & Niels Mejlgaar, CEO @dg.dk to celebrate 🎉
Congratulations to Ada 🥳🍾, who very successfully defended her master's thesis today! You were an excellent student and we were super happy to have you in the lab! Wishing you all the best for the future and enjoy your well-deserved break!

June 27, 2025 at 8:10 PM
Congratulations to Ada 🥳🍾, who very successfully defended her master's thesis today! You were an excellent student and we were super happy to have you in the lab! Wishing you all the best for the future and enjoy your well-deserved break!
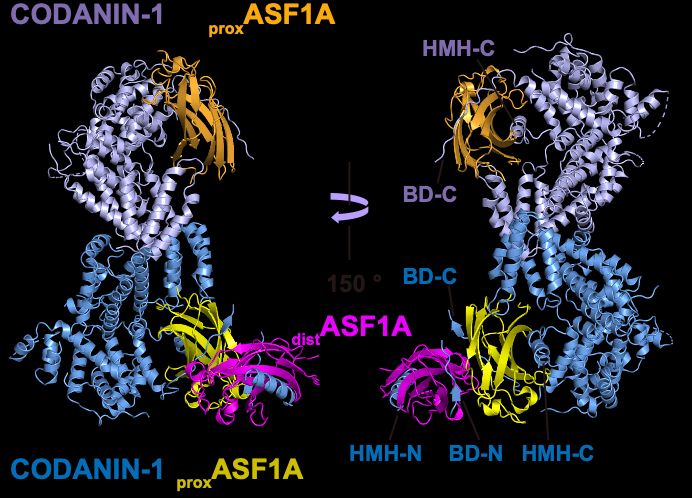
So, how does CODANIN-1 bind ASF1? Our cryo-EM structure reveals that CODANIN-1 forms a dimer, with each monomer binding two ASF1A molecules. These two ASF1As are held in proximal and distal positions by CODANIN’s N-terminal B domain (BD-N) and C-terminal histone H3 mimic helix (HMH-C), respectively.
March 6, 2025 at 12:45 PM
So, how does CODANIN-1 bind ASF1? Our cryo-EM structure reveals that CODANIN-1 forms a dimer, with each monomer binding two ASF1A molecules. These two ASF1As are held in proximal and distal positions by CODANIN’s N-terminal B domain (BD-N) and C-terminal histone H3 mimic helix (HMH-C), respectively.
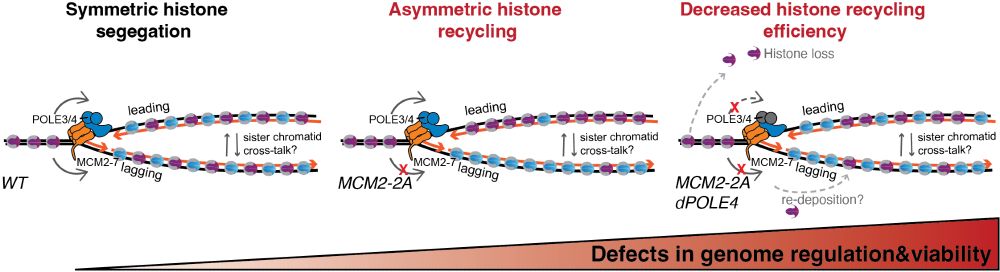
Our work highlights 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐲𝐜𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐚𝐬 𝐚 𝐤𝐞𝐲 𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐠𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐬𝐚𝐟𝐞𝐠𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐝 – histone modifications must be 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐥𝐲 transmitted to 𝐛𝐨𝐭𝐡 daughter strands for this to work! Could failures in this process contribute to developmental disorders, cancer, or aging? More to explore! 4/n
February 19, 2025 at 7:35 PM
Our work highlights 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐲𝐜𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐚𝐬 𝐚 𝐤𝐞𝐲 𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐠𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐬𝐚𝐟𝐞𝐠𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐝 – histone modifications must be 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐥𝐲 transmitted to 𝐛𝐨𝐭𝐡 daughter strands for this to work! Could failures in this process contribute to developmental disorders, cancer, or aging? More to explore! 4/n
Exciting news!🌟 Together with Alexander van Oudenaarden, @jervdberg.bsky.social and @lleonie.bsky.social, we’ve been awarded a €2M NNF Synergy grant. We're thrilled to collaborate🤝 and to develop cutting-edge single-cell and single-molecule methods for replication and chromatin research! 🚀

December 20, 2024 at 12:19 PM
Exciting news!🌟 Together with Alexander van Oudenaarden, @jervdberg.bsky.social and @lleonie.bsky.social, we’ve been awarded a €2M NNF Synergy grant. We're thrilled to collaborate🤝 and to develop cutting-edge single-cell and single-molecule methods for replication and chromatin research! 🚀


