
This work was a true collaboration with my co-authors
Xuemin Wang and @drtracy.bsky.social @qimrb.bsky.social
Science advances through teamwork and shared expertise. 12/x
This work was a true collaboration with my co-authors
Xuemin Wang and @drtracy.bsky.social @qimrb.bsky.social
Science advances through teamwork and shared expertise. 12/x
Are their specific immune pathways linking thyroid dysfunction to cancer protection?
How can we translate these insights into clinical applications? 11/x
Are their specific immune pathways linking thyroid dysfunction to cancer protection?
How can we translate these insights into clinical applications? 11/x

Thyroid hormone pathways may influence cancer biology, although we found no evidence of this our study.
Immune mechanisms (especially in Hashimoto's) warrant investigation. 8/x
Thyroid hormone pathways may influence cancer biology, although we found no evidence of this our study.
Immune mechanisms (especially in Hashimoto's) warrant investigation. 8/x
Overall EC: (OR = 0.93, 95% CI: 0.89-0.97) 4/x
Overall EC: (OR = 0.93, 95% CI: 0.89-0.97) 4/x


@NatureComms
paper (doi.org/10.1038/s414...) was designed to identify causal genes for CRC risk and prioritise genes with therapeutic potential. 2/7
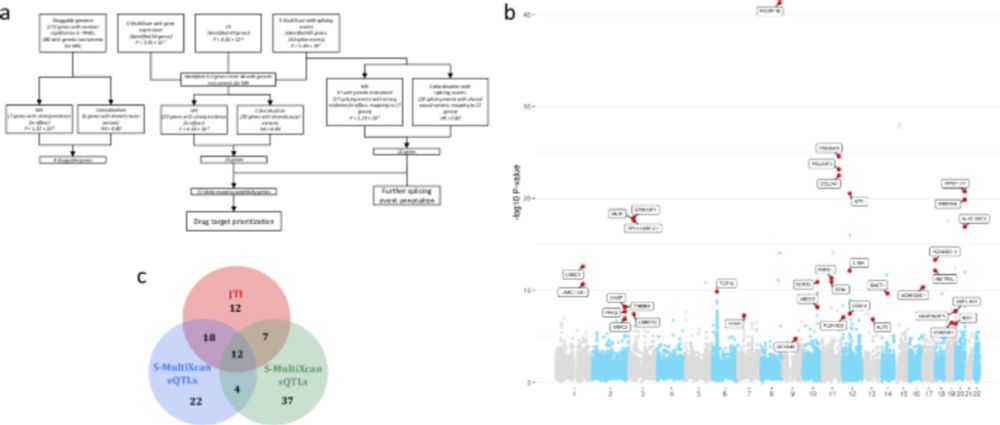
@NatureComms
paper (doi.org/10.1038/s414...) was designed to identify causal genes for CRC risk and prioritise genes with therapeutic potential. 2/7

