
Andrew Newman
@epinewman.bsky.social
Investigating the Neuronal Epigenome in Development, Evolution, & Aging.
Junior Group Leader @ Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Junior Group Leader @ Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin
This has been a long effort, with many contributors from
Charité Berlin and a wonderful collaboration with researchers from RIKEN IMS.
full paper here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Charité Berlin and a wonderful collaboration with researchers from RIKEN IMS.
full paper here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Glial reactivity and cognitive decline follow chronic heterochromatin loss in neurons - Nature Communications
Heterochromatin loss has been linked to aging and neurodegeneration. Here, the authors show that combined loss of HP1β and HP1γ in neurons results in de-repressesion of endogenous retroviruses, i...
www.nature.com
September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
This has been a long effort, with many contributors from
Charité Berlin and a wonderful collaboration with researchers from RIKEN IMS.
full paper here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Charité Berlin and a wonderful collaboration with researchers from RIKEN IMS.
full paper here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Our study provides an invaluable insight into how heterochromatin loss with concomitant (re)activation of ERVs can drive core components of neurodegeneration by stimulation of immune pathways and the integrated stress response.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
Our study provides an invaluable insight into how heterochromatin loss with concomitant (re)activation of ERVs can drive core components of neurodegeneration by stimulation of immune pathways and the integrated stress response.
...as well as age-dependent deficits in paired-pulse inhibition and spatial memory, measured here in the barnes maze.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
...as well as age-dependent deficits in paired-pulse inhibition and spatial memory, measured here in the barnes maze.
Alongside this chronic inflammatory state we observed age-dependent reductions in dendritic complexity in the hippocampus...

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
Alongside this chronic inflammatory state we observed age-dependent reductions in dendritic complexity in the hippocampus...
However, in the chronic environment of the brain, the prolonged production of complement C3 coincided with increased number of microglia as well as increased microglial activation as measured by CD68 subcellular compartments.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
However, in the chronic environment of the brain, the prolonged production of complement C3 coincided with increased number of microglia as well as increased microglial activation as measured by CD68 subcellular compartments.
While we could not observe direct affects to complement in this acute paradigm, we could observe specific effects to CCL5 (RANTES) production and IRF7 phosphorylation and nuclear localization.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
While we could not observe direct affects to complement in this acute paradigm, we could observe specific effects to CCL5 (RANTES) production and IRF7 phosphorylation and nuclear localization.
We attempted to investigate this in an in vitro system, where we applied IAP ssRNA to mixed glial cultures, alongside pseudo-uracil (ψ) and scramble controls.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
We attempted to investigate this in an in vitro system, where we applied IAP ssRNA to mixed glial cultures, alongside pseudo-uracil (ψ) and scramble controls.
At the protein level, this is even more dramatic, where you can observe the accumulation of C3 protein in the astrocytes, and specifically their endfeet.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
At the protein level, this is even more dramatic, where you can observe the accumulation of C3 protein in the astrocytes, and specifically their endfeet.
We were shocked to find that in the IAP ERV-rich hippocampus, Complement C3 RNA production could be seen in foci we could attribute to Slc1a3 astrocytes.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
We were shocked to find that in the IAP ERV-rich hippocampus, Complement C3 RNA production could be seen in foci we could attribute to Slc1a3 astrocytes.
So HP1β & HP1γ seem to be essential for repeat silencing, but what is the consequence in the brain?
Our transcriptomic data suggested multiple pathways related to chronic inflammation, elevated integrated stress response, and notably, the complement cascade.
Our transcriptomic data suggested multiple pathways related to chronic inflammation, elevated integrated stress response, and notably, the complement cascade.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
So HP1β & HP1γ seem to be essential for repeat silencing, but what is the consequence in the brain?
Our transcriptomic data suggested multiple pathways related to chronic inflammation, elevated integrated stress response, and notably, the complement cascade.
Our transcriptomic data suggested multiple pathways related to chronic inflammation, elevated integrated stress response, and notably, the complement cascade.
The TLDR is that in the DKO brain samples we could additionally observe loss of 5mC at ERVK (IAP) elements, with corresponding increases in 5hmC. Several de novo 5mC methylation also appears to take place in HP1β cortices, suggesting that HP1β is essential for the 5mC fidelity.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
The TLDR is that in the DKO brain samples we could additionally observe loss of 5mC at ERVK (IAP) elements, with corresponding increases in 5hmC. Several de novo 5mC methylation also appears to take place in HP1β cortices, suggesting that HP1β is essential for the 5mC fidelity.
We then sought to corroborate this in the brain. Given the abundance of 5hmC in the brain, we performed oxidative RRBS (OvationRRBS system, RIP) to simultaneously profile 5mC and 5hmC from our mutant hippocampi.
September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
We then sought to corroborate this in the brain. Given the abundance of 5hmC in the brain, we performed oxidative RRBS (OvationRRBS system, RIP) to simultaneously profile 5mC and 5hmC from our mutant hippocampi.
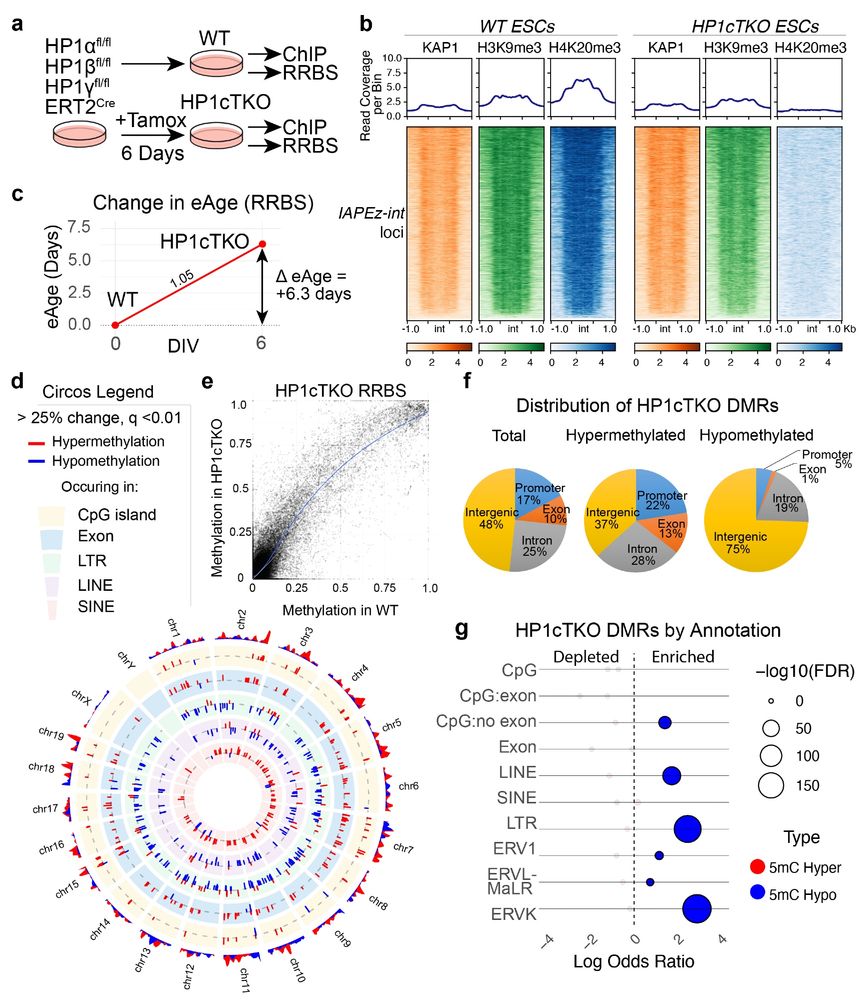
We then tested how HP1 deficiency effects DNA methylation, using an ES cell line. We could see that in stem cells triple deficient for HP1 proteins, LINE and LTR elements (including ERVK) became DNA hypomethylated.
September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
We then tested how HP1 deficiency effects DNA methylation, using an ES cell line. We could see that in stem cells triple deficient for HP1 proteins, LINE and LTR elements (including ERVK) became DNA hypomethylated.
When we re-introduced HP1γ-GFP into the DKO cortex we could recover H4K20me3 levels, albeit not to the same extent as adjacent WT interneurons.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
When we re-introduced HP1γ-GFP into the DKO cortex we could recover H4K20me3 levels, albeit not to the same extent as adjacent WT interneurons.
So why was the double loss of HP1 proteins resulting in this loss of ERV silencing? It turns out that HP1γ is necessary for secondary H4K20me3 deposition.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
So why was the double loss of HP1 proteins resulting in this loss of ERV silencing? It turns out that HP1γ is necessary for secondary H4K20me3 deposition.
And notably, while Emx1Cre results in HP1 proteins being deleted from neurons and astrocytes, IAPs are only de-repressed in neurons. Something you can appreciate here in the hippocampal formation:

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
And notably, while Emx1Cre results in HP1 proteins being deleted from neurons and astrocytes, IAPs are only de-repressed in neurons. Something you can appreciate here in the hippocampal formation:
A large proportion of what is de-repressed are IAP (Intracisternal Alpha Particle) elements, mouse specific ERVK family members, which are the closest functional analogs to human HERV-K.
With a consensus RNA probe, we can visualise locations of IAP transcripts in situ.
With a consensus RNA probe, we can visualise locations of IAP transcripts in situ.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
A large proportion of what is de-repressed are IAP (Intracisternal Alpha Particle) elements, mouse specific ERVK family members, which are the closest functional analogs to human HERV-K.
With a consensus RNA probe, we can visualise locations of IAP transcripts in situ.
With a consensus RNA probe, we can visualise locations of IAP transcripts in situ.
Using bulk RNAseq, we found that deletion of these two genes in combination resulted in derepression of ERV elements (here listed as green under LTR Class) across the genome, primarily those with a smaller Kimura distances, corresponding to evolutionarily younger sequences.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
Using bulk RNAseq, we found that deletion of these two genes in combination resulted in derepression of ERV elements (here listed as green under LTR Class) across the genome, primarily those with a smaller Kimura distances, corresponding to evolutionarily younger sequences.
We asked if we could mimic age-related heterochromatin loss by deleting two members of the HP1 family, HP1β and HP1γ, and observe the consequences in the Cortex of a living mouse using Emx1Cre.
September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
We asked if we could mimic age-related heterochromatin loss by deleting two members of the HP1 family, HP1β and HP1γ, and observe the consequences in the Cortex of a living mouse using Emx1Cre.
Heterochromatin formation is dependent on Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1), a protein that dimerises and binds strongly to K9me3 on histone 3 (H3K9me3) initiating condensate formation and phase separation.

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
Heterochromatin formation is dependent on Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1), a protein that dimerises and binds strongly to K9me3 on histone 3 (H3K9me3) initiating condensate formation and phase separation.
One way ERVs are silenced is by the KAP1 repressor complex, where the element is recognised by a KRAB-containing Zinc finger and the result is silencing via H3K9me3, H4K20me3 histone methylation and 5mC DNA methylation.
royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10....
royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10....

September 1, 2025 at 12:42 PM
One way ERVs are silenced is by the KAP1 repressor complex, where the element is recognised by a KRAB-containing Zinc finger and the result is silencing via H3K9me3, H4K20me3 histone methylation and 5mC DNA methylation.
royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10....
royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10....

