go.nature.com/4nDj2di

go.nature.com/4nDj2di
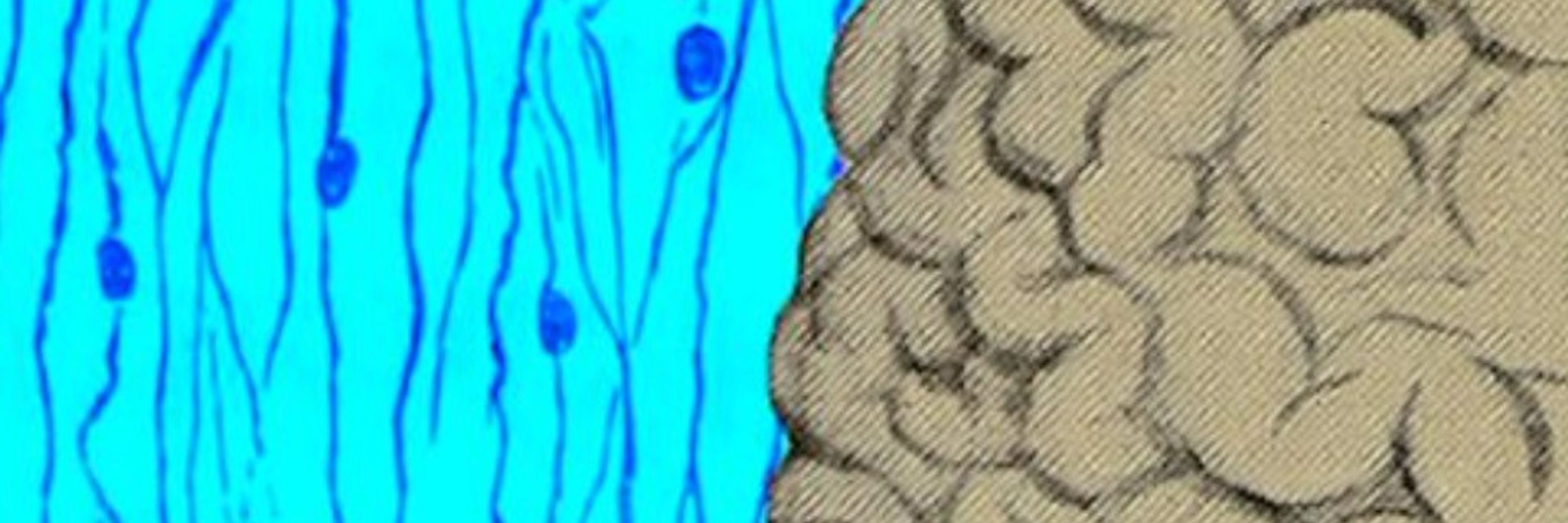
NextBrain was built using AI-powered alignment of 10,000 human post-mortem brain slices, creating a precise 3D map of 333 distinct brain regions.
🧪 #neuroskyence
www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2025/no...

NextBrain was built using AI-powered alignment of 10,000 human post-mortem brain slices, creating a precise 3D map of 333 distinct brain regions.
🧪 #neuroskyence

All publicly available. Looks like an amazing new histology-based human probabilistic atlas and parcellation tool.
#neuroskyence #mri #brainmapping
A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation | Nature share.google/5AD0iW7pxgb4...

All publicly available. Looks like an amazing new histology-based human probabilistic atlas and parcellation tool.
#neuroskyence #mri #brainmapping
A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation | Nature share.google/5AD0iW7pxgb4...
www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2025/no...

www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2025/no...
doi.org/10.1093/brai...

doi.org/10.1093/brai...

Join Prof @selinawray.bsky.social and Dr Ross Paterson for a Reddit ‘ask me anything’ (AMA) on 18 September.
You’ll have the chance to ask our experts questions about dementia research and care as part of #WorldAlzheimersMonth.
Find out more: buff.ly/Y36GExF
Join Prof @selinawray.bsky.social and Dr Ross Paterson for a Reddit ‘ask me anything’ (AMA) on 18 September.
You’ll have the chance to ask our experts questions about dementia research and care as part of #WorldAlzheimersMonth.
Find out more: buff.ly/Y36GExF
🧠 Lead pioneering imaging-informed cognitive neuroscience research
🌍 Open to international applicants | Visa sponsorship available
📍 Permanent, full-time, on-site
🔗 Apply now: www.ucl.ac.uk/work-at-ucl/...

🧠 Lead pioneering imaging-informed cognitive neuroscience research
🌍 Open to international applicants | Visa sponsorship available
📍 Permanent, full-time, on-site
🔗 Apply now: www.ucl.ac.uk/work-at-ucl/...

www.ucl.ac.uk/work-at-ucl/...

www.ucl.ac.uk/work-at-ucl/...
openstax.org/details/book...

openstax.org/details/book...
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...

onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
A next-generation, histological atlas of the human brain and its application to automated brain MRI segmentation | bioRxiv www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

A next-generation, histological atlas of the human brain and its application to automated brain MRI segmentation | bioRxiv www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

