
12/12

12/12
10/12

10/12
Finding 5: School board members’ opinions on some high-profile education issues differ from those of the U.S. public.
9/12

Finding 5: School board members’ opinions on some high-profile education issues differ from those of the U.S. public.
9/12
8/12

8/12
7/12

7/12
6/12
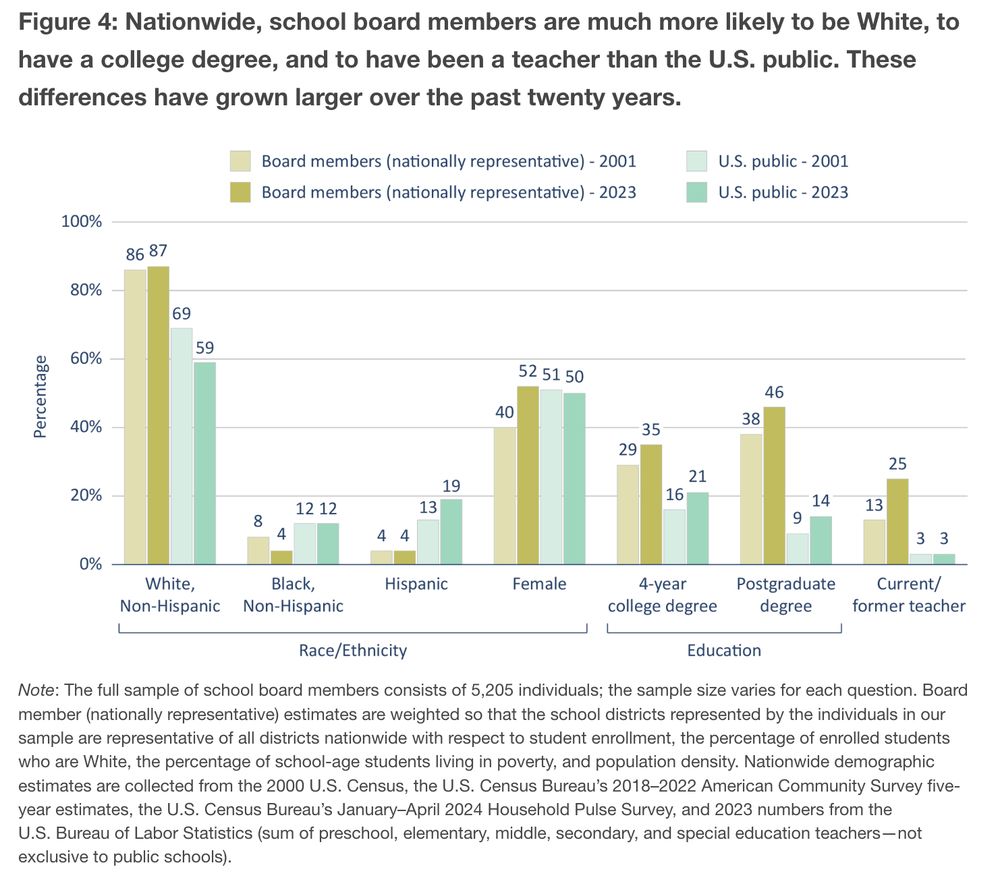
6/12
Finding 3: Two-thirds of school board members—representing seven in ten students—match the partisan lean of their districts.
4/12

Finding 3: Two-thirds of school board members—representing seven in ten students—match the partisan lean of their districts.
4/12
Finding 2: Students are disproportionately represented by school board members who are moderates, liberals, and/or Democrats.
3/12

Finding 2: Students are disproportionately represented by school board members who are moderates, liberals, and/or Democrats.
3/12
2/12

2/12
journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.3102/...
1/2

journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.3102/...
1/2
"Despite rising polarization, the data consistently show that partisan affiliation is not a primary factor in [school district superintendent] hiring decisions" @greermellon.bsky.social
journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10....

"Despite rising polarization, the data consistently show that partisan affiliation is not a primary factor in [school district superintendent] hiring decisions" @greermellon.bsky.social
journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10....
edworkingpapers.com/sites/defaul...

edworkingpapers.com/sites/defaul...
I trace the history of US K-12 school governance, focusing on institutional changes that have made the domain more exposed to partisan conflict
edworkingpapers.com/ai25-1182
1/3

I trace the history of US K-12 school governance, focusing on institutional changes that have made the domain more exposed to partisan conflict
edworkingpapers.com/ai25-1182
1/3
"We find that household voter turnout in off-cycle school bond elections is significantly lower for households with children who participate in school choice"
edworkingpapers.com/ai25-1186

"We find that household voter turnout in off-cycle school bond elections is significantly lower for households with children who participate in school choice"
edworkingpapers.com/ai25-1186
doi.org/10.1162/edfp...
4/6
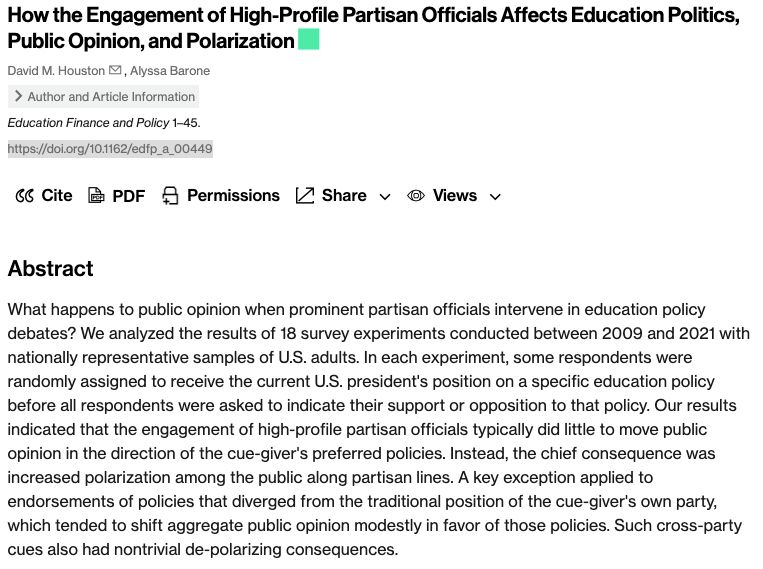
doi.org/10.1162/edfp...
4/6

Presidents with larger gaps in their approval rating between Dems and Reps, unsurprisingly, had larger polarizing effects

Presidents with larger gaps in their approval rating between Dems and Reps, unsurprisingly, had larger polarizing effects
No meaningful variation by ed attainment (proxy for how informed folks are about these issues)
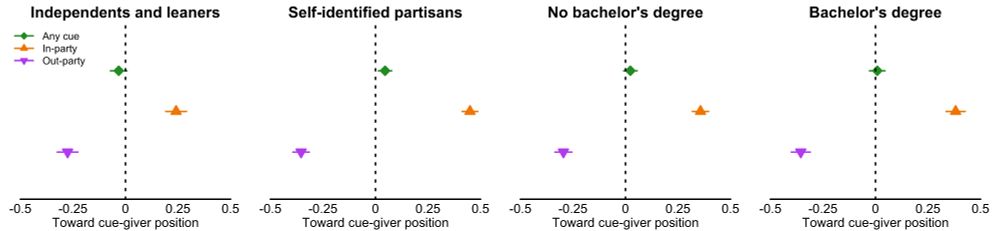
No meaningful variation by ed attainment (proxy for how informed folks are about these issues)
Instead, the chief consequence was increased polarization among the public along partisan lines
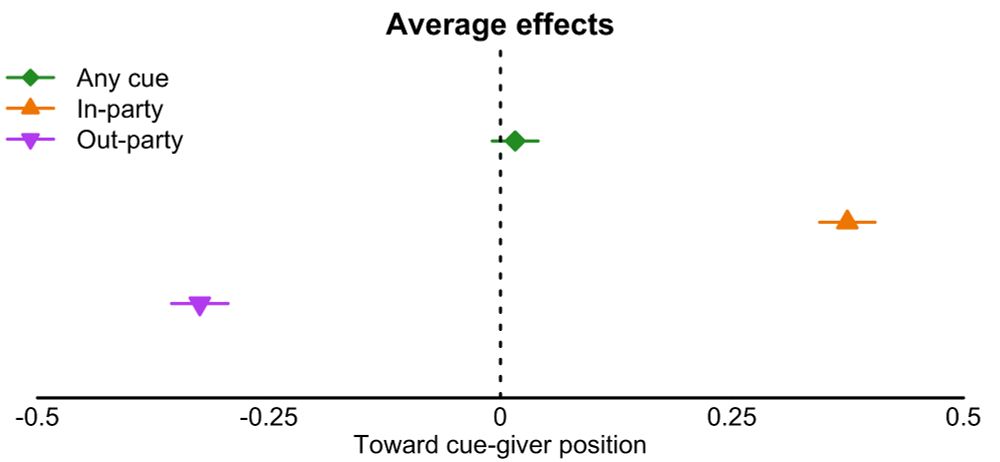
Instead, the chief consequence was increased polarization among the public along partisan lines

8/n

8/n
6/n

6/n
5/n

5/n
4/n

4/n
3/n

3/n

