
Patterns, a Cell Press journal
@cp-patterns.bsky.social
A peer-reviewed #openaccess data science journal from @cellpress.bsky.social
Editor-in-Chief: Andrew L Hufton (@alhufton.bsky.social)
Visit us online at https://www.cell.com/patterns/
Editor-in-Chief: Andrew L Hufton (@alhufton.bsky.social)
Visit us online at https://www.cell.com/patterns/
Online Now: Three-factor learning in spiking neural networks: An overview of methods and trends from a machine learning perspective #datascience

Three-factor learning in spiking neural networks: An overview of methods and trends from a machine learning perspective
This perspective surveys three-factor learning, a key mechanism for brain-inspired spiking neural networks. Adding a third, global signal, analogous to neuromodulators, allows these AI systems to learn and adapt more effectively. This overview connects recent advances in neuroscience and machine learning, outlining a path toward more powerful AI.
dlvr.it
November 10, 2025 at 4:36 PM
Online Now: Three-factor learning in spiking neural networks: An overview of methods and trends from a machine learning perspective #datascience
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
In this month’s editorial, led by our social science editor Lu Liu, we highlight the importance of social sciences for sustainability. Social science has too often been seen as a soft science, a nice-to-have element or a useful add-on rather than a fundamental pillar
www.cell.com/cell-reports...
www.cell.com/cell-reports...

Sustainability challenges demand social science insights
We live in an era of escalating sustainability challenges, such as exceeding the global
1.5°C threshold in 2024, the collapse of talks to address the widespread plastic crisis,
and increasing wildfire...
www.cell.com
October 31, 2025 at 2:11 PM
In this month’s editorial, led by our social science editor Lu Liu, we highlight the importance of social sciences for sustainability. Social science has too often been seen as a soft science, a nice-to-have element or a useful add-on rather than a fundamental pillar
www.cell.com/cell-reports...
www.cell.com/cell-reports...
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
Are individuals who are positive about artificial intelligence also more unsure?: Applications of uniform-binomial mixed densities. Patterns www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

Are individuals who are positive about artificial intelligence also more unsure?
As artificial intelligence matures, the impact it might have on how society functions
is being actively pondered. In this opinion, through uniform-binomial mixtures, the
author sheds quantitative ligh...
www.cell.com
October 13, 2025 at 2:03 PM
Are individuals who are positive about artificial intelligence also more unsure?: Applications of uniform-binomial mixed densities. Patterns www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Online Now: SIMBA: A robust and generalizable measure of data imbalance #datascience

SIMBA: A robust and generalizable measure of data imbalance
Data constitute machine learning’s fuel. Unfortunately, real-world data are often imbalanced. This poses a huge challenge to machine learning, as rare cases are hard to learn. So far, no adequate measure has been available to assess the impact of imbalance on machine learning’s performance. As a remedy for this omission, the authors introduce the status of imbalance (SIMBA), a reliable, robust, and generic imbalance measure that outperforms existing ones.
dlvr.it
October 21, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: SIMBA: A robust and generalizable measure of data imbalance #datascience
Online Now: Decoding multi-joint hand movements from brain signals by learning a synergy-based neural manifold #datascience

Decoding multi-joint hand movements from brain signals by learning a synergy-based neural manifold
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a promising avenue to restore motor function by converting neural activity into control signals for external devices. While current BCI technologies have successfully demonstrated brain-directed control of robotic arms, they still face significant limitations in dexterous hand movement control. This study proposes a novel approach called SynergyNet to decode complex hand movements directly from brain signals, facilitating high-performance BCI control with fine movements.
dlvr.it
October 20, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Decoding multi-joint hand movements from brain signals by learning a synergy-based neural manifold #datascience
New call for submissions!
To help promote critical reassessment of prior work, we are now inviting submissions that present compelling and creative reanalyses.
Learn more: www.cell.com/patterns/spe...
Submit before August 1, 2026
#openscience #datascience
To help promote critical reassessment of prior work, we are now inviting submissions that present compelling and creative reanalyses.
Learn more: www.cell.com/patterns/spe...
Submit before August 1, 2026
#openscience #datascience

October 20, 2025 at 12:02 PM
New call for submissions!
To help promote critical reassessment of prior work, we are now inviting submissions that present compelling and creative reanalyses.
Learn more: www.cell.com/patterns/spe...
Submit before August 1, 2026
#openscience #datascience
To help promote critical reassessment of prior work, we are now inviting submissions that present compelling and creative reanalyses.
Learn more: www.cell.com/patterns/spe...
Submit before August 1, 2026
#openscience #datascience
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
In this paper in @cp-patterns.bsky.social, Core Faculty member George Church, Postdoc Li Li, and their colleagues outline how LLMs are becoming crucial tools at every stage of drug development to dramatically reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new therapeutics to patients.
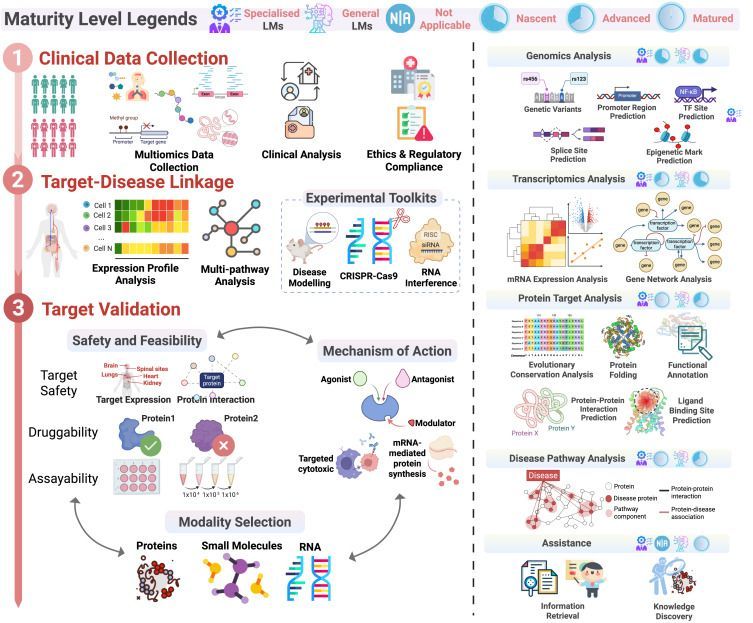
Large language models for drug discovery and development
In this review, the authors explore the transformative impact of large language models (LLMs) on drug discovery and development. They detail how LLMs can potentially accelerate our understanding of…
buff.ly
September 30, 2025 at 3:05 PM
In this paper in @cp-patterns.bsky.social, Core Faculty member George Church, Postdoc Li Li, and their colleagues outline how LLMs are becoming crucial tools at every stage of drug development to dramatically reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new therapeutics to patients.
Online Now: Computational workflows for natural and biomedical image processing based on hypercomplex algebras #datascience

Computational workflows for natural and biomedical image processing based on hypercomplex algebras
Quaternions, a type of hypercomplex number, are particularly useful in handling three-dimensional data, i.e., color images. Within the feature-rich hypercomplex setting, image-processing workflows can be realized for natural and biomedical images enabling alternative visual representations, offering effective solutions to current problems in computer vision and digital pathology, and generally expanding the scope and impact of hypercomplex image processing across a wide range of applications.
dlvr.it
October 15, 2025 at 3:36 PM
Online Now: Computational workflows for natural and biomedical image processing based on hypercomplex algebras #datascience
Online Now: Unraveling learning characteristics of transformer models for molecular design #datascience

Unraveling learning characteristics of transformer models for molecular design
Transformer models are adaptable to off-the-beaten-path molecular design tasks, such as protein-sequence-based compound design. The authors use these predictions as a model system to unravel the learning characteristics of transformers. The analysis reveals that the transformer predictions are statistically driven and that the models do not learn protein-ligand interactions or other biologically relevant information. Instead, compound memorization plays an important role. These findings caution against over-interpretation of sequence-based generative compound design using transformer models.
dlvr.it
October 14, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Unraveling learning characteristics of transformer models for molecular design #datascience
Our October issue is now live!
www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
Featured on the cover this month is a paper presenting LigUnity, a foundation model for predicting small molecule binding affinity for drug discovery and optimization applications www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
Featured on the cover this month is a paper presenting LigUnity, a foundation model for predicting small molecule binding affinity for drug discovery and optimization applications www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

October 10, 2025 at 4:34 PM
Our October issue is now live!
www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
Featured on the cover this month is a paper presenting LigUnity, a foundation model for predicting small molecule binding affinity for drug discovery and optimization applications www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
Featured on the cover this month is a paper presenting LigUnity, a foundation model for predicting small molecule binding affinity for drug discovery and optimization applications www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
Very nice article co-authored by one of my former students, Mihai Codreanu, discovering how much of many documents eg press releases, job postings, have been written using LLMs (10-20% depending on type of document but it might have stabilised in late 2024) www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

The widespread adoption of large language model-assisted writing across society
This study explores AI-generated writing adoption across consumer complaints, corporate
press releases, job postings, and international organization communications, revealing
widespread use following ...
www.cell.com
October 3, 2025 at 7:51 AM
Very nice article co-authored by one of my former students, Mihai Codreanu, discovering how much of many documents eg press releases, job postings, have been written using LLMs (10-20% depending on type of document but it might have stabilised in late 2024) www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Online Now: The widespread adoption of large language model-assisted writing across society #datascience

The widespread adoption of large language model-assisted writing across society
This study explores AI-generated writing adoption across consumer complaints, corporate press releases, job postings, and international organization communications, revealing widespread use following ChatGPT’s release. Findings highlight significant generative AI integration by small firms, corporations, and global institutions, emphasizing its transformative impact on communication practices, business strategies, and public policy.
dlvr.it
October 2, 2025 at 3:36 PM
Online Now: The widespread adoption of large language model-assisted writing across society #datascience
Online Now: Neural mechanisms of visual quality perception and adaptability in the visual pathway #datascience

Neural mechanisms of visual quality perception and adaptability in the visual pathway
Visual quality assessment is crucial for both human perception and artificial vision systems. This study reveals how the human brain naturally perceives image quality through distinct neural pathways. Functional magnetic resonance imaging results show that while low-level visual areas are highly sensitive to distortions, higher-level regions compensate to maintain recognition, much like how AI systems might “fill in” missing details. These findings not only deepen our understanding of human vision but also provide biological inspiration for developing more robust image-processing algorithms.
dlvr.it
October 1, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Neural mechanisms of visual quality perception and adaptability in the visual pathway #datascience
Online Now: Pan-microalgal dark proteome mapping via interpretable deep learning and synthetic chimeras #datascience
Pan-microalgal dark proteome mapping via interpretable deep learning and synthetic chimeras
The vast microbial “dark proteome” remains largely uncharacterized. Nelson et al. present LA4SR, a transformer framework that classifies algal sequences 10,000× faster than traditional methods with near-perfect recall. Trained on 77 million sequences including synthetic chimeras, the system can robustly classify unknown sequences with natural or scrambled start and stop information. They also developed an accompanying suite of explainability software to reveal biologically meaningful patterns linking amino acid patterns to evolutionary affiliations.
dlvr.it
September 24, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Pan-microalgal dark proteome mapping via interpretable deep learning and synthetic chimeras #datascience
Online Now: Automating quantum computing laboratory experiments with an agent-based AI framework #datascience

Automating quantum computing laboratory experiments with an agent-based AI framework
This study introduces a language-model-driven agent system that captures and applies laboratory knowledge to autonomously plan, execute, and analyze experiments. When the agent system was demonstrated on quantum computing tasks, the agents achieved performance on par with expert researchers. By enabling intelligent coordination and decision-making in complex lab settings, this approach paves the way for more flexible, scalable automation in experimental science.
dlvr.it
September 23, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Automating quantum computing laboratory experiments with an agent-based AI framework #datascience
How can AI benefit communities, particularly in low-resource settings? In our latest People of Data interview, Edith Luhanga from @cmu.edu Africa shares her journey in human-centric AI, discussing topics such as digital health, financial inclusion, and digital equity.
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

September 18, 2025 at 10:44 AM
How can AI benefit communities, particularly in low-resource settings? In our latest People of Data interview, Edith Luhanga from @cmu.edu Africa shares her journey in human-centric AI, discussing topics such as digital health, financial inclusion, and digital equity.
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
Reposting my 2024 #PeerReviewWeek editorial as it is particularly fitting to this year's theme, "Rethinking Peer Review in the AI Era": www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
September 18, 2025 at 7:50 AM
Reposting my 2024 #PeerReviewWeek editorial as it is particularly fitting to this year's theme, "Rethinking Peer Review in the AI Era": www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
September 17, 2025 at 6:58 PM
Online Now: Hierarchical affinity landscape navigation through learning a shared pocket-ligand space #datascience

Hierarchical affinity landscape navigation through learning a shared pocket-ligand space
LigUnity is a protein-ligand affinity foundation model, enabling both rapid virtual screening and precise hit-to-lead optimization. LigUnity learns a shared “language” for protein pockets and ligands, outperforming docking in screening and approaching FEP+ accuracy at far lower cost. It generalizes to new targets and new chemical scaffolds and achieves 106 times the speedup compared to Glide-SP, offering a practical foundation for early-stage drug discovery.
dlvr.it
September 17, 2025 at 3:36 PM
Online Now: Hierarchical affinity landscape navigation through learning a shared pocket-ligand space #datascience
Online Now: AISleep: Automated and interpretable sleep staging from single-channel EEG data #datascience

AISleep: Automated and interpretable sleep staging from single-channel EEG data
Sleep staging is vital for understanding sleep physiology and diagnosing sleep disorders, yet manual scoring is time-consuming and unscalable. The authors introduce AISleep, an unsupervised sleep staging algorithm based on feature-weighted kernel density estimation, using only a single EEG channel. AISleep outperforms SOTA unsupervised methods, generalizes better than supervised models, and uncovers age-related EEG feature decline impacting staging accuracy. Its lightweight design enables integration into portable devices, providing a practical, scalable solution for accurate and accessible home-based sleep monitoring.
dlvr.it
September 15, 2025 at 7:47 PM
Online Now: AISleep: Automated and interpretable sleep staging from single-channel EEG data #datascience
Our September issue is now live! www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
This month's awesome cover image highlights a paper from a team of researchers at @uniulm.bsky.social who present a #quantum algorithm for gene regulatory network discovery
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
This month's awesome cover image highlights a paper from a team of researchers at @uniulm.bsky.social who present a #quantum algorithm for gene regulatory network discovery
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

September 12, 2025 at 3:04 PM
Our September issue is now live! www.cell.com/patterns/iss...
This month's awesome cover image highlights a paper from a team of researchers at @uniulm.bsky.social who present a #quantum algorithm for gene regulatory network discovery
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
This month's awesome cover image highlights a paper from a team of researchers at @uniulm.bsky.social who present a #quantum algorithm for gene regulatory network discovery
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Reposted by Patterns, a Cell Press journal
From @cp-patterns.bsky.social | #Bioconductor: Planning a third decade of comprehensive support for genomic data science | #Bioinformatics #Genomics #OpenScience #OpenSource 🧬 🖥️ 🧪 🔓
⬇️
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
⬇️
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...

Bioconductor: Planning a third decade of comprehensive support for genomic data science
This opinion piece discusses the Bioconductor project for open-source bioinformatics
and the engineering concepts underlying its effectiveness to date. Since the inception
of Bioconductor in 2002 with...
www.cell.com
September 11, 2025 at 12:58 PM
From @cp-patterns.bsky.social | #Bioconductor: Planning a third decade of comprehensive support for genomic data science | #Bioinformatics #Genomics #OpenScience #OpenSource 🧬 🖥️ 🧪 🔓
⬇️
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
⬇️
www.cell.com/patterns/ful...
Online Now: A multimodal LLM-agent framework for personalized clinical decision-making in hepatocellular carcinoma #datascience
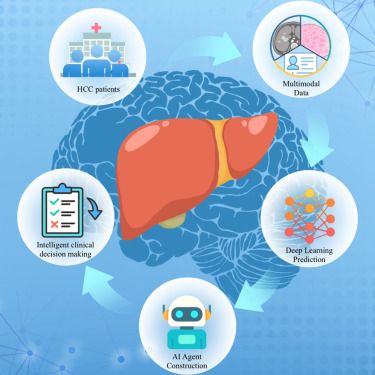
A multimodal LLM-agent framework for personalized clinical decision-making in hepatocellular carcinoma
The authors present an integrated radiomics-deep learning-LLM agent framework for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) management. A multimodal fusion model accurately predicts key pathological features from MRI, while LLM agents generate personalized treatment strategies. Expert evaluation confirms strong clinical alignment. This work demonstrates the promise of AI-powered decision systems in precision oncology.
dlvr.it
September 8, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: A multimodal LLM-agent framework for personalized clinical decision-making in hepatocellular carcinoma #datascience
Online Now: Large language models for drug discovery and development #datascience

Large language models for drug discovery and development
In this review, the authors explore the transformative impact of large language models (LLMs) on drug discovery and development. They detail how LLMs can potentially accelerate our understanding of disease mechanisms, facilitate de novo drug discovery, and optimize clinical trial processes, including patient matching and outcome prediction. They also assess the current maturity of LLM applications and outline future directions for integrating these advanced computational models into the pharmaceutical pipeline.
dlvr.it
September 2, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Large language models for drug discovery and development #datascience
Online Now: Current progress and open challenges for applying artificial intelligence across the in vitro fertilization cycle #datascience

Current progress and open challenges for applying artificial intelligence across the in vitro fertilization cycle
This review explains how artificial intelligence is reshaping in vitro fertilization, from forecasting embryo health to tailoring hormone therapy. By combining images, health records, and molecular clues, these tools promise safer, more effective fertility treatments for patients worldwide.
dlvr.it
August 29, 2025 at 3:35 PM
Online Now: Current progress and open challenges for applying artificial intelligence across the in vitro fertilization cycle #datascience

