
Center for Microbial Dynamics and Infection
@cmdi.bsky.social
Our team of researchers at GeorgiaTech investigate mechanisms and consequences of microbial community dynamics both in the environment and during infection. https://sites.gatech.edu/cmdi/
Come and be our new Chair of Biological Sciences at Georgia Tech! www.biosciences.gatech.edu/chair-search
Chair Search
Chair, School of Biological Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta The School of Biological Sciences of the Georgia Institute of Technology (“Georgia Tech”) invites applications for the pos...
www.biosciences.gatech.edu
August 13, 2025 at 12:58 PM
Come and be our new Chair of Biological Sciences at Georgia Tech! www.biosciences.gatech.edu/chair-search
Peatland microbes resist warming, with stable communities and diverse carbon pathways; methanogens show metabolic flexibility but are not dominant. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Northern peatland microbial communities exhibit resistance to warming and acquire electron acceptors from soil organic matter - Nature Communications
Climate change is expected to impact microbes degrading organic matter in northern peatlands. Here, using a warming experiment, the authors show that communities remain stable after three years of war...
www.nature.com
July 28, 2025 at 2:51 PM
Peatland microbes resist warming, with stable communities and diverse carbon pathways; methanogens show metabolic flexibility but are not dominant. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Gene-specific RNA-to-protein conversion factors improve protein predictions from mRNA, enabling functional insights across diverse microbial species. #MicroSky journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

Conserved cross-domain protein-to-mRNA ratios enable proteome prediction in microbes | mBio
Deciphering the biology of natural microbial communities is limited by the lack of functional data. While transcriptomics enables gene expression profiling, mRNA levels often fail to predict protein abundance, the primary indicator of microbial function. ...
journals.asm.org
July 28, 2025 at 2:49 PM
Gene-specific RNA-to-protein conversion factors improve protein predictions from mRNA, enabling functional insights across diverse microbial species. #MicroSky journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
Alveolar macrophages limit phage therapy by clearing phages; their depletion boosts phage efficacy against P. aeruginosa in murine lung infection. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...
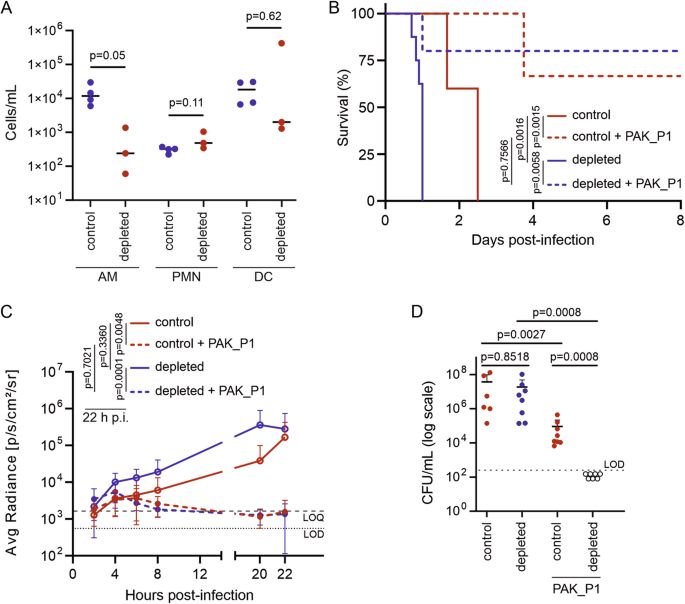
Macrophage-induced reduction of bacteriophage density limits the efficacy of in vivo pulmonary phage therapy - Nature Communications
In vivo experiments and mathematical modelling in this work, show that alveolar macrophages lower phage densities and phage-bacteria contact rates, limiting the effectiveness of synergistic treatment ...
www.nature.com
July 28, 2025 at 2:48 PM
Alveolar macrophages limit phage therapy by clearing phages; their depletion boosts phage efficacy against P. aeruginosa in murine lung infection. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...
A simple model of vertical biofilm growth arises from active fluid dynamics, linking cell decay to growth limits and unifying early and late stages. #MicroSky pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40578390/

Biofilm vertical growth dynamics are captured by an active fluid framework - PubMed
Bacterial biofilms, surface-attached microbial communities, grow horizontally across surfaces and vertically above them. Although a simple heuristic model for vertical growth was experimentally shown ...
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
July 28, 2025 at 2:47 PM
A simple model of vertical biofilm growth arises from active fluid dynamics, linking cell decay to growth limits and unifying early and late stages. #MicroSky pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40578390/
Spontaneous fluid flows in yeast clusters enable nutrient transport and exponential growth, aiding multicellularity before genetic adaptations evolve. #MicroSky www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
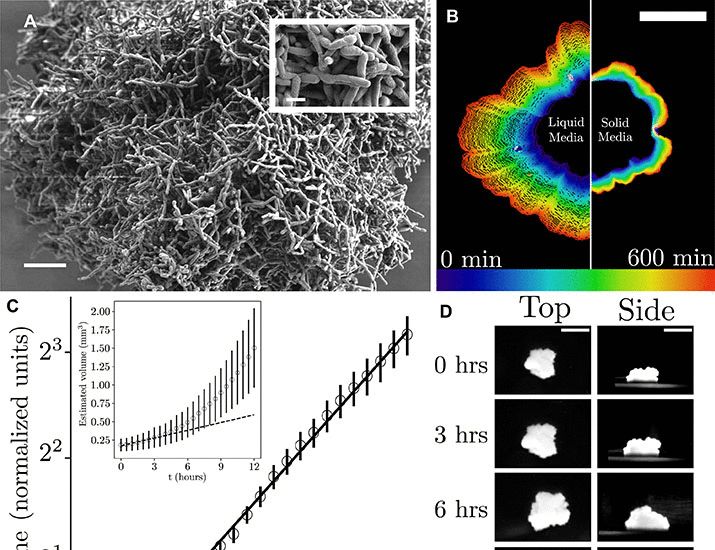
Metabolically driven flows enable exponential growth in macroscopic multicellular yeast
Metabolically generated flow is an emergent mechanism that alleviates diffusion limits in macroscopic multicellular yeast.
www.science.org
July 28, 2025 at 2:44 PM
Spontaneous fluid flows in yeast clusters enable nutrient transport and exponential growth, aiding multicellularity before genetic adaptations evolve. #MicroSky www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
This primer reviews differences between acute, chronic, mono- and polymicrobial infections, highlighting ecological and evolutionary challenges and opportunities for treatment and infection management. www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...

Microbial Primer: Challenges and opportunities in the treatment of chronic polymicrobial infections ‒ an eco-evolutionary perspective
In this primer, we will review the key distinctions between acute and chronic infections, between mono- and polymicrobial infections and how these distinctions work together to generate the growing cr...
www.microbiologyresearch.org
June 20, 2025 at 5:59 PM
This primer reviews differences between acute, chronic, mono- and polymicrobial infections, highlighting ecological and evolutionary challenges and opportunities for treatment and infection management. www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...
Mass spectrometry metabolomics methods reveal microbiome-derived natural products influencing host-microbe interactions, enabling insights into communication, immunity, and symbiosis mechanisms. pubs.rsc.org/en/content/a...

Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approaches to interrogate host–microbiome interactions in mammalian systems
Covering: 2015 to 2025Chemical crosstalk is universal to all life, niche-specific, and essential to thrive. This crosstalk is mediated by a large diversity of molecules, including metal ions, small mo...
pubs.rsc.org
June 20, 2025 at 5:57 PM
Mass spectrometry metabolomics methods reveal microbiome-derived natural products influencing host-microbe interactions, enabling insights into communication, immunity, and symbiosis mechanisms. pubs.rsc.org/en/content/a...
This review explores the ecological niches, evolutionary dynamics, pathogenic mechanisms, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, highlighting its adaptability and clinical significance. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Pseudomonas aeruginosa: ecology, evolution, pathogenesis and antimicrobial susceptibility - Nature Reviews Microbiology
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a functionally versatile bacterium, a leading opportunistic human pathogen and a model organism in microbiology. In this Review, Letizia, Diggle and Whiteley discuss P. aerug...
www.nature.com
June 3, 2025 at 3:08 PM
This review explores the ecological niches, evolutionary dynamics, pathogenic mechanisms, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, highlighting its adaptability and clinical significance. www.nature.com/articles/s41...
In Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, multicellularity evolved under predation but not settling selection. Only certain genotypes gave rise to multicellular forms, showing both deterministic and random factors shape this transition. academic.oup.com/gbe/advance-...

Genetic predisposition towards multicellularity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
academic.oup.com
May 19, 2025 at 2:22 PM
In Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, multicellularity evolved under predation but not settling selection. Only certain genotypes gave rise to multicellular forms, showing both deterministic and random factors shape this transition. academic.oup.com/gbe/advance-...
Trimethoprim alters metabolite production in B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus, affecting interkingdom interactions, antifungal activity, and fungal pigmentation, revealing how therapeutics reshape microbial chemistry and virulence expression. pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...

Antimicrobial Agent Trimethoprim Influences Chemical Interactions in Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens via the ham Gene Cluster
The fungus Aspergillus fumigatus and the bacterium Burkholderia cenocepacia cause fatal respiratory infections in immunocompromised humans and patients with lung disease, such as cystic fibrosis (CF). In dual infections, antagonistic interactions contribute to increased mortality. These interactions are further altered by the presence of antimicrobial and antifungal agents. However, studies performed to date on chemical interactions between clinical B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus have focused on pathogens in isolation and do not include the most abundant chemical signal, i.e., clinically administered therapeutics, present in the lung. Here, we characterize small molecule-mediated interactions between B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus and their shift in response to trimethoprim exposure by using metabolomics and mass spectrometry imaging. Using these methods, we report that the production of several small-molecule natural products of both the bacteria and the fungus is affected by cocultivation and exposure to trimethoprim. By systematic analysis of metabolomics data, we hypothesize that the B. cenocepacia-encoded ham gene cluster plays a role in the trimethoprim-mediated alteration of bacterial–fungal interactions. We support our findings by generating a genetically modified strain lacking the ham gene cluster and querying its interaction with A. fumigatus. Using comparative analyses of the extracts of wild-type and knockout strains, we report the inactivation of a bacterially produced antifungal compound, fragin, by A. fumigatus, which was verified by the addition of purified fragin to the A. fumigatus culture. Furthermore, we report that trimethoprim does not inhibit fungal growth, but affects the biochemical pathway for DHN-melanin biosynthesis, an important antifungal drug target, altering the pigmentation of the fungal conidia and is associated with modification of ergosterol to ergosteryl-3β-O-l-valine in coculture. This study demonstrates the impact of therapeutics on shaping microbial and fungal metabolomes, which influence interkingdom interactions and the expression of virulence factors. Our findings enhance the understanding of the complexity of chemical interactions between therapeutic compounds, bacteria, and fungi and may contribute to the development of selective treatments.
pubs.acs.org
May 19, 2025 at 2:20 PM
Trimethoprim alters metabolite production in B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus, affecting interkingdom interactions, antifungal activity, and fungal pigmentation, revealing how therapeutics reshape microbial chemistry and virulence expression. pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
Sea cucumbers reshape reef sediment microbiomes by grazing, reducing microbial biomass and phototrophs, enriching anaerobic genes, and potentially supporting coral survival through disease suppression. academic.oup.com/ismej/advanc...

Sea cucumber grazing linked to enrichment of anaerobic microbial metabolisms in coral reef sediments
Abstract. Sea cucumbers have been overharvested world-wide, making assessments of their ecological effects challenging, but recent research demonstrated th
academic.oup.com
May 9, 2025 at 5:19 PM
Sea cucumbers reshape reef sediment microbiomes by grazing, reducing microbial biomass and phototrophs, enriching anaerobic genes, and potentially supporting coral survival through disease suppression. academic.oup.com/ismej/advanc...
In the phosphorus-limited Sargasso Sea, microbes partition phosphorus uptake by time of day—bacteria in the morning, phytoplankton by day, and cyanobacteria at dusk—revealing a temporal niche strategy. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
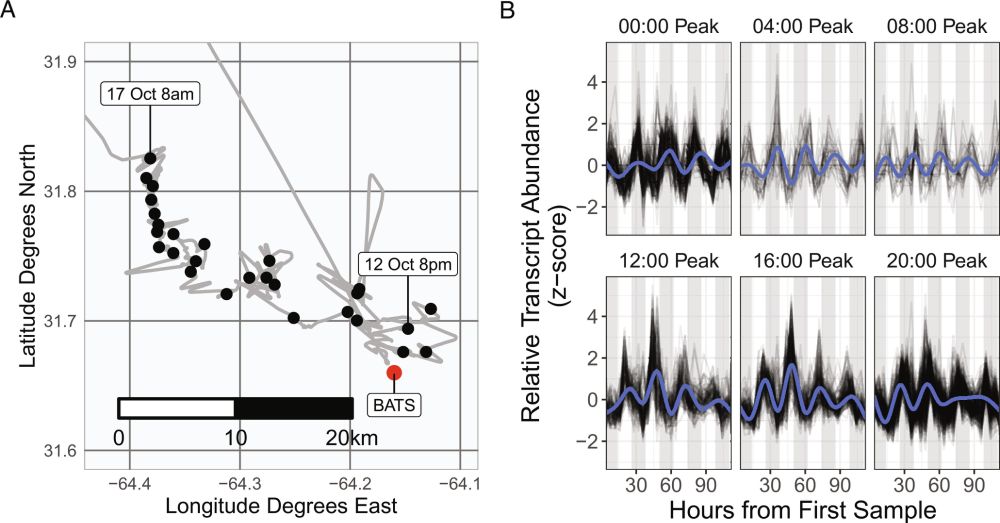
Diel partitioning in microbial phosphorus acquisition in the Sargasso Sea | PNAS
The daily cycle of photosynthetic primary production at the base of marine food webs
is often limited by the availability of scarce nutrients. Micr...
www.pnas.org
May 3, 2025 at 5:44 PM
In the phosphorus-limited Sargasso Sea, microbes partition phosphorus uptake by time of day—bacteria in the morning, phytoplankton by day, and cyanobacteria at dusk—revealing a temporal niche strategy. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
Reposted by Center for Microbial Dynamics and Infection
Mystique is here! When I started my position at @cmdi.bsky.social there were no readily available phage against my A. baumannii focal strain. The solution? Finding my own phage ofc. Mystique is a broad host range Acinetobacter phage, and I'm thrilled to see this work out today #PhageSky 🧪🦠
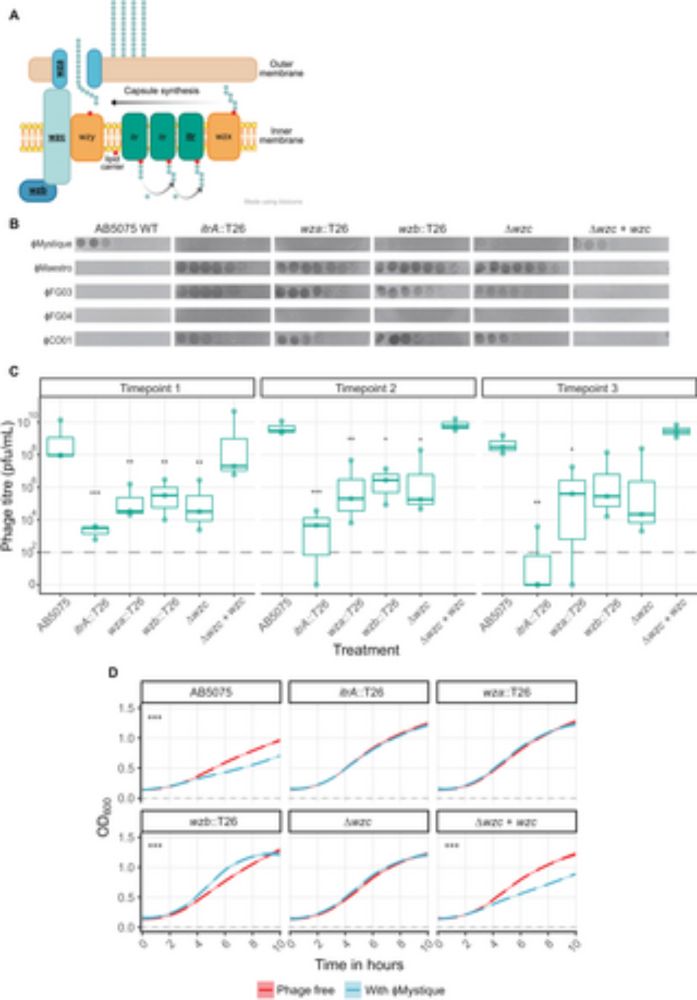
Mystique, a broad host range Acinetobacter phage, reveals the impact of culturing conditions on phage isolation and infectivity
Author summary Bacterial infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii are a major global health concern due to high antibiotic resistance, earning it a critical priority pathogen ranking by the WHO. P...
journals.plos.org
April 10, 2025 at 7:59 PM
Mystique is here! When I started my position at @cmdi.bsky.social there were no readily available phage against my A. baumannii focal strain. The solution? Finding my own phage ofc. Mystique is a broad host range Acinetobacter phage, and I'm thrilled to see this work out today #PhageSky 🧪🦠
Metaproteomics reveals bacterial peptide shifts that precede harmful algal blooms. Twelve biomarkers were consistently detected pre-bloom, offering a promising tool for early HAB forecasting and mitigation. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Harmful algal blooms are preceded by a predictable and quantifiable shift in the oceanic microbiome - Nature Communications
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) pose negative worldwide impacts that could be minimized through the development of a forecasting tool. Quantitative analysis of peptides produced by a coastal microbiome pr...
www.nature.com
May 3, 2025 at 5:41 PM
Metaproteomics reveals bacterial peptide shifts that precede harmful algal blooms. Twelve biomarkers were consistently detected pre-bloom, offering a promising tool for early HAB forecasting and mitigation. www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Across 209 infection models, death risk increases exponentially over time, challenging assumptions of constant mortality and highlighting gaps in linking within-host dynamics to population outcomes. journals.asm.org/doi/full/10....

Risk of death during acute infection is accelerating across diverse host-pathogen systems and consistent with multiple models of host-pathogen interaction | mSphere
Here, we ask a simple question: what are the dynamics of pathogen-induced death? Death
is a central phenotype in both biomedical and epidemiological infectious disease biology,
yet very little work ha...
journals.asm.org
May 3, 2025 at 5:39 PM
Across 209 infection models, death risk increases exponentially over time, challenging assumptions of constant mortality and highlighting gaps in linking within-host dynamics to population outcomes. journals.asm.org/doi/full/10....
Metaproteomics offers powerful insights into microbiome function across health and the environment. This Viewpoint calls for overcoming key challenges to make it a mainstream tool in multiomics, sparking cross-disciplinary collaboration and discovery. #Microbiome pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40289407/

A Non‐Metaproteomics Researchers’ View on Metaproteomics in Microbiome Research
Metaproteomics, an emerging field among the omic techniques, holds great promise for unraveling the function of microbiomes in host health and our environment. Metaproteomics can also be a valuable a...
analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
May 3, 2025 at 5:33 PM
Metaproteomics offers powerful insights into microbiome function across health and the environment. This Viewpoint calls for overcoming key challenges to make it a mainstream tool in multiomics, sparking cross-disciplinary collaboration and discovery. #Microbiome pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40289407/
Long-term studies have transformed our understanding of evolution by tracking real-time dynamics, revealing trends, and exposing rare events. Despite funding challenges, they remain vital in a rapidly changing world. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Long-term studies provide unique insights into evolution - Nature
Long-term studies provide insights into the complex interplay between evolutionary process and pattern across multiple systems and timescales.
www.nature.com
March 20, 2025 at 7:24 PM
Long-term studies have transformed our understanding of evolution by tracking real-time dynamics, revealing trends, and exposing rare events. Despite funding challenges, they remain vital in a rapidly changing world. www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Whole genome duplication in S. cerevisiae enables rapid tetraploidy under selection for larger size, persists for 5,000 generations, and drives adaptive evolution. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Genome duplication in a long-term multicellularity evolution experiment - Nature
In the Multicellularity Long Term Evolution Experiment, diploid yeast evolve to be tetraploid under selection for larger multicellular size, revealing how whole-genome duplication can arise due to its...
www.nature.com
March 15, 2025 at 4:35 PM
Whole genome duplication in S. cerevisiae enables rapid tetraploidy under selection for larger size, persists for 5,000 generations, and drives adaptive evolution. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s41...
This review explores the structural, mechanistic, and therapeutic aspects of R-pyocins produced by P. aeruginosa, including their potential for infection management. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s44...
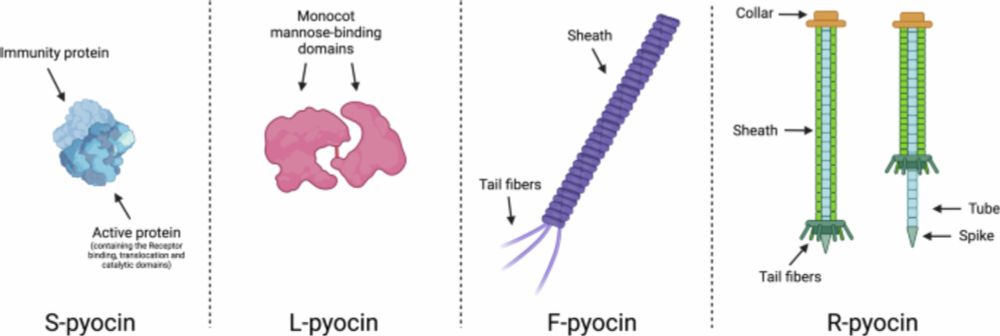
R-pyocins as targeted antimicrobials against Pseudomonas aeruginosa - npj Antimicrobials and Resistance
npj Antimicrobials and Resistance - R-pyocins as targeted antimicrobials against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
www.nature.com
March 3, 2025 at 2:50 PM
This review explores the structural, mechanistic, and therapeutic aspects of R-pyocins produced by P. aeruginosa, including their potential for infection management. #MicroSky www.nature.com/articles/s44...
Overusing AI in job applications may hurt candidates. Personal authenticity matters more than polished, generic responses. #AI #JobSearch www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

Using AI to prepare for academic interviews – don’t trade authenticity for polish | EMBO reports
EMBO Press is an editorially independent publishing platform for the development of EMBO scientific publications.
www.embopress.org
February 25, 2025 at 3:18 PM
Overusing AI in job applications may hurt candidates. Personal authenticity matters more than polished, generic responses. #AI #JobSearch www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
Sphagnum moss relies on its microbiome for growth and thermal acclimation. Matched host-microbiome pairs boost growth, aiding peatland resilience. #ClimateChange #Microbiome #MicroSky onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...

Host Species–Microbiome Interactions Contribute to Sphagnum Moss Growth Acclimation to Warming
Sphagnum mosses are vital for storing carbon in northern peatlands but are sensitive to climate warming. They host microbes that help with nutrient uptake and carbon cycling, and recent studies sugge....
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
February 25, 2025 at 3:16 PM
Sphagnum moss relies on its microbiome for growth and thermal acclimation. Matched host-microbiome pairs boost growth, aiding peatland resilience. #ClimateChange #Microbiome #MicroSky onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
Multicellularity evolved via cell attachment. Yeast formed cuboidal clusters, showing key traits of individuality, driven by ace2 mutations. #Evolution #MicroSky academic.oup.com/evlett/artic...

Experimental evolution of multicellularity via cuboidal cell packing in fission yeast
Abstract. The evolution of multicellularity represents a major transition in life’s history, enabling the rise of complex organisms. Multicellular groups c
academic.oup.com
February 25, 2025 at 3:15 PM
Multicellularity evolved via cell attachment. Yeast formed cuboidal clusters, showing key traits of individuality, driven by ace2 mutations. #Evolution #MicroSky academic.oup.com/evlett/artic...
Virus decay is often non-exponential. Optimized sampling reveals multiphasic decay in phage ΦD9, with 94% decaying 16x faster than the slowest subpopulation, highlighting viral decay heterogeneity. #MicroSky www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

Design, optimization, and inference of biphasic decay of infectious virus particles
Virus population dynamics are driven by counter-balancing forces of production and loss. Whereas viral production arises from complex interactions wit…
www.sciencedirect.com
February 10, 2025 at 2:55 PM
Virus decay is often non-exponential. Optimized sampling reveals multiphasic decay in phage ΦD9, with 94% decaying 16x faster than the slowest subpopulation, highlighting viral decay heterogeneity. #MicroSky www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
Oxygen-binding proteins like myoglobin improve oxygen diffusion and fitness in multicellular models, suggesting their role in enabling complex metazoan evolution in oxygen-rich environments. #MicroSky journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...

Oxygen-binding proteins aid oxygen diffusion to enhance fitness of a yeast model of multicellularity
How did early multicellular organisms manage to exploit rising oxygen levels? By modeling facilitated diffusion and expressing animal oxygen-binding proteins in snowflake yeast, this study shows that ...
journals.plos.org
February 10, 2025 at 2:47 PM
Oxygen-binding proteins like myoglobin improve oxygen diffusion and fitness in multicellular models, suggesting their role in enabling complex metazoan evolution in oxygen-rich environments. #MicroSky journals.plos.org/plosbiology/...

