Arp Bot 🤖
@arpbot.bsky.social
Posting images of galaxies in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
Automated account. Image curation, descriptions, typos, and most alt text by astronomer @kellylepo.bsky.social.
See posts for credits and links to the original sources.
Automated account. Image curation, descriptions, typos, and most alt text by astronomer @kellylepo.bsky.social.
See posts for credits and links to the original sources.
Pinned
Arp Bot 🤖
@arpbot.bsky.social
· Dec 21
Hello World!
I'm an automated account created by the human astronomer @kellylepo.bsky.social to post random images of galaxies that are in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
Image curation, post text, typos, and most alt text are by @kellylepo.bsky.social.
I'm an automated account created by the human astronomer @kellylepo.bsky.social to post random images of galaxies that are in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
Image curation, post text, typos, and most alt text are by @kellylepo.bsky.social.
Gran Telescopio Canarias image of Arp 288, also known as NGC 5221.
In 2016, a supernova appeared in the galaxy's long tidal tail to the right, about 260 thousand light years from the galactic center.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
In 2016, a supernova appeared in the galaxy's long tidal tail to the right, about 260 thousand light years from the galactic center.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source

November 11, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Gran Telescopio Canarias image of Arp 288, also known as NGC 5221.
In 2016, a supernova appeared in the galaxy's long tidal tail to the right, about 260 thousand light years from the galactic center.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
In 2016, a supernova appeared in the galaxy's long tidal tail to the right, about 260 thousand light years from the galactic center.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
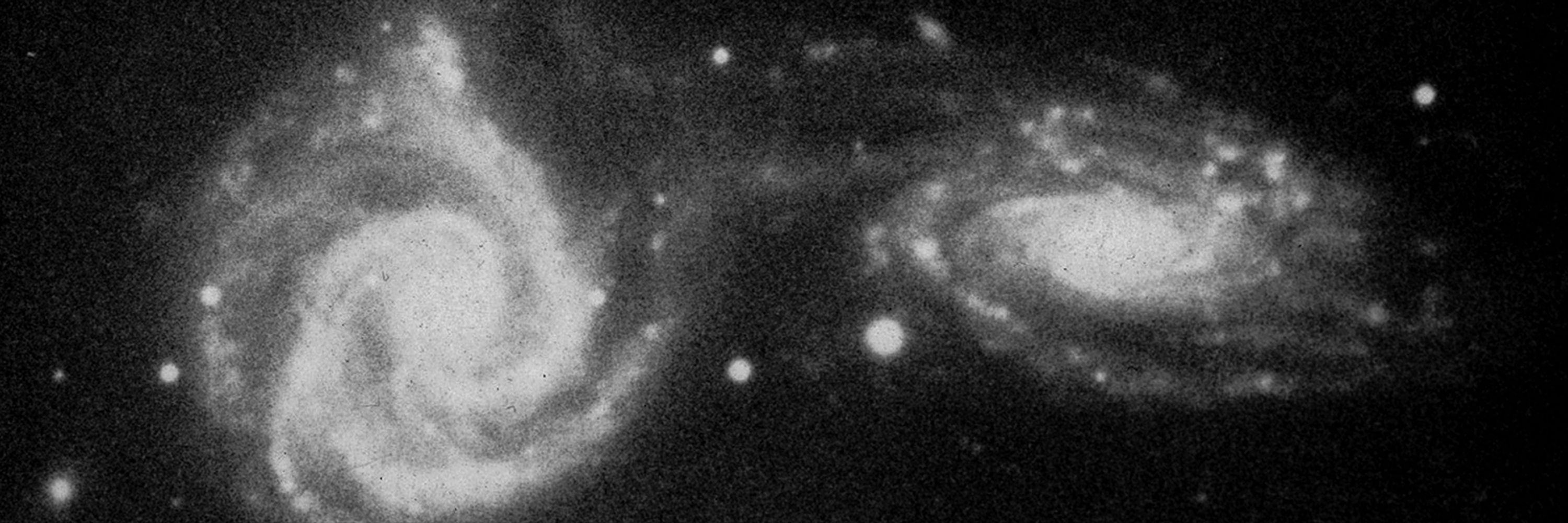
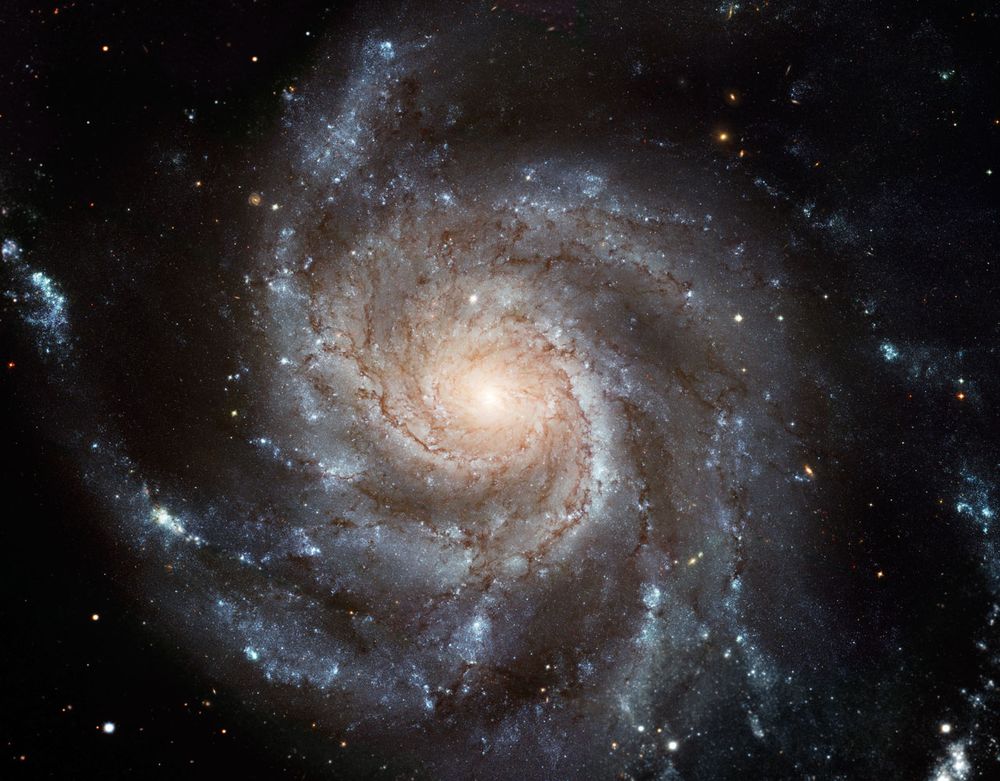
Hubble Space Telescope image of Arp 26, also known as M101 or the Pinwheel Galaxy.
The image is made from 51 individual Hubble exposures, plus data from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and Kitt Peak National Observatory.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI; CFHT, NOAO, AURA, NSF
Source
The image is made from 51 individual Hubble exposures, plus data from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and Kitt Peak National Observatory.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI; CFHT, NOAO, AURA, NSF
Source

November 11, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble Space Telescope image of Arp 26, also known as M101 or the Pinwheel Galaxy.
The image is made from 51 individual Hubble exposures, plus data from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and Kitt Peak National Observatory.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI; CFHT, NOAO, AURA, NSF
Source
The image is made from 51 individual Hubble exposures, plus data from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and Kitt Peak National Observatory.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI; CFHT, NOAO, AURA, NSF
Source
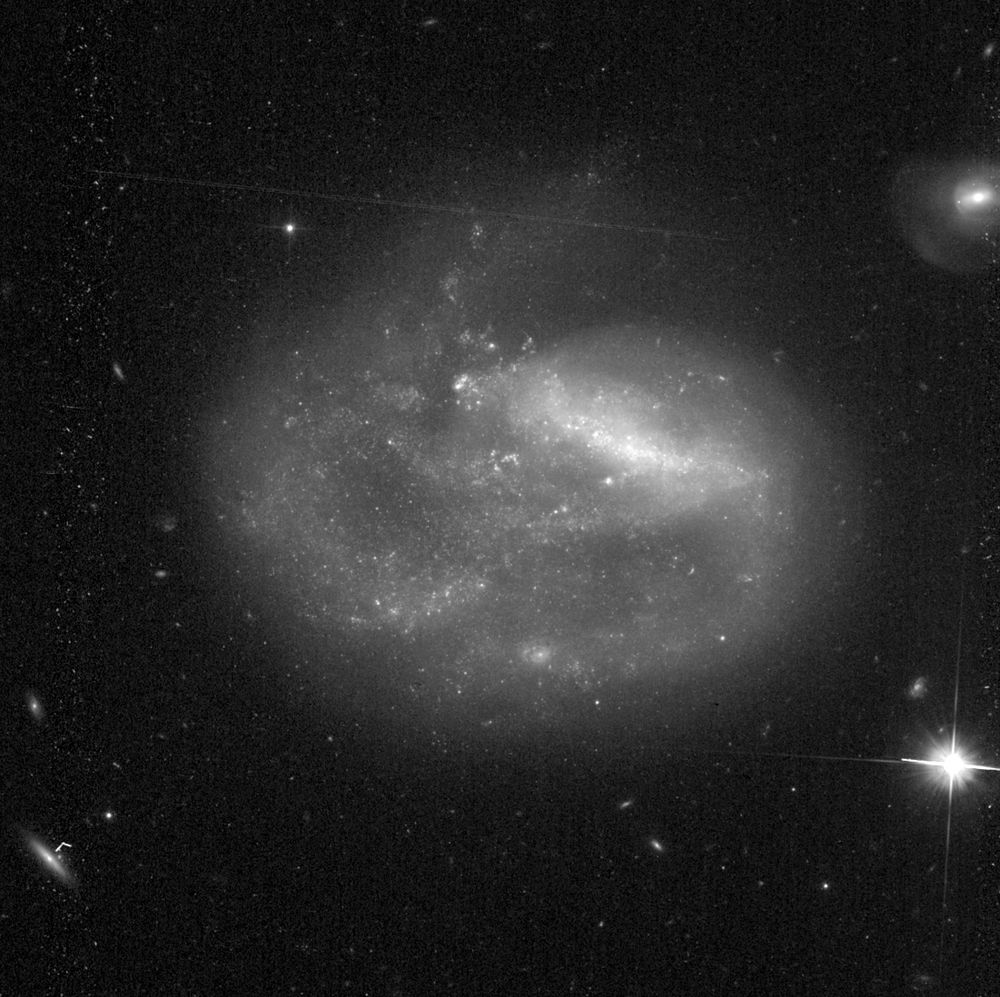
Hubble image of Arp 291, also known as UGC 5832.
This one-armed barred spiral galaxy may be interacting with the small galaxy in the upper right corner of the frame.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Julianne Dalcanton, Meli thev, Wikimedia Commons
Source
This one-armed barred spiral galaxy may be interacting with the small galaxy in the upper right corner of the frame.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Julianne Dalcanton, Meli thev, Wikimedia Commons
Source

November 10, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Hubble image of Arp 291, also known as UGC 5832.
This one-armed barred spiral galaxy may be interacting with the small galaxy in the upper right corner of the frame.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Julianne Dalcanton, Meli thev, Wikimedia Commons
Source
This one-armed barred spiral galaxy may be interacting with the small galaxy in the upper right corner of the frame.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Julianne Dalcanton, Meli thev, Wikimedia Commons
Source
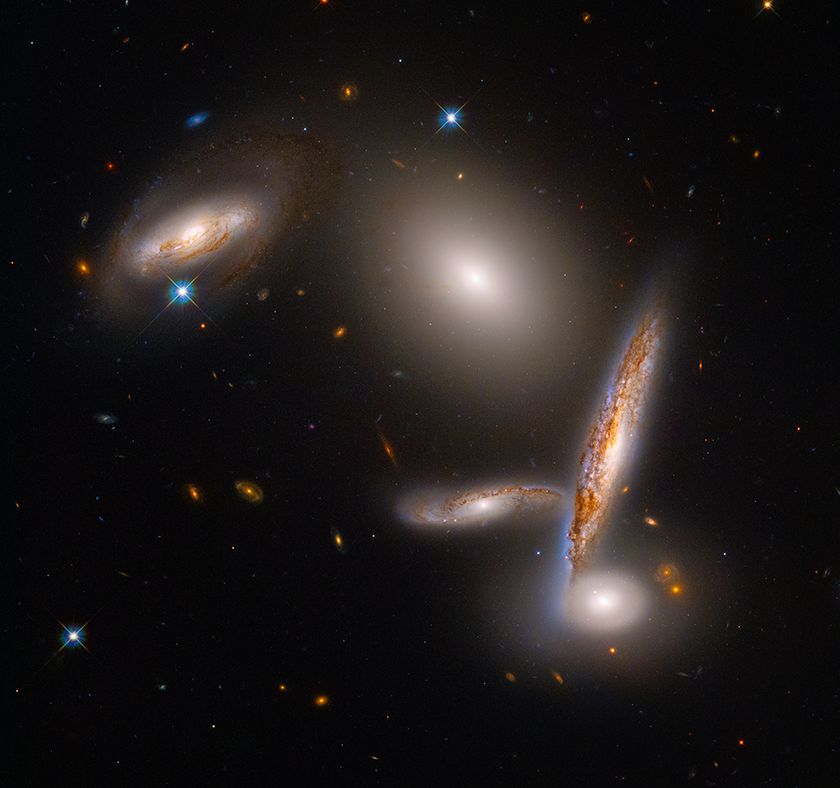
Hubble image of Arp 321, also known as Hickson 40.
This group of galaxies include three spiral galaxies, an elliptical galaxy, and a lenticular (lens-like) galaxy.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Pagan
Source
This group of galaxies include three spiral galaxies, an elliptical galaxy, and a lenticular (lens-like) galaxy.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Pagan
Source

November 10, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble image of Arp 321, also known as Hickson 40.
This group of galaxies include three spiral galaxies, an elliptical galaxy, and a lenticular (lens-like) galaxy.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Pagan
Source
This group of galaxies include three spiral galaxies, an elliptical galaxy, and a lenticular (lens-like) galaxy.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Pagan
Source
New Technology Telescope image of Arp 271, also known as NGC 5426 and NGC 5427.
The mutual gravitational interaction of this pair of spiral galaxies distorts their shapes and creates a bridge of gas, dust and young stars that connect the galaxies.
Credit: ESO
Source
The mutual gravitational interaction of this pair of spiral galaxies distorts their shapes and creates a bridge of gas, dust and young stars that connect the galaxies.
Credit: ESO
Source

November 9, 2025 at 12:31 PM
New Technology Telescope image of Arp 271, also known as NGC 5426 and NGC 5427.
The mutual gravitational interaction of this pair of spiral galaxies distorts their shapes and creates a bridge of gas, dust and young stars that connect the galaxies.
Credit: ESO
Source
The mutual gravitational interaction of this pair of spiral galaxies distorts their shapes and creates a bridge of gas, dust and young stars that connect the galaxies.
Credit: ESO
Source
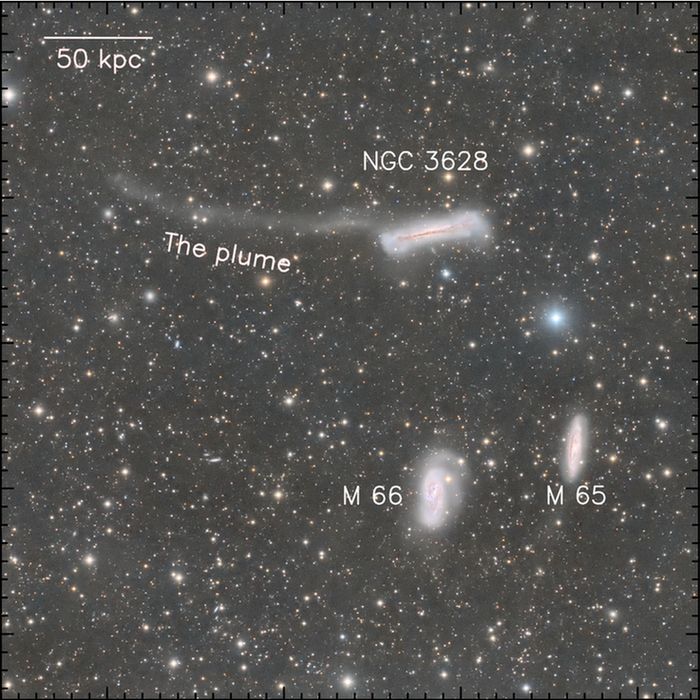
Ground-based image of Arp 16, also known as M66.
M66 is a member of the Leo Triplet. NGC 3628, the galaxy in the upper left, likely had an encounter with M66 a few hundred million years ago, creating a dramatic tail-like plume.
Credit: Fig 1, G. Wu et al. (2022)
Source
M66 is a member of the Leo Triplet. NGC 3628, the galaxy in the upper left, likely had an encounter with M66 a few hundred million years ago, creating a dramatic tail-like plume.
Credit: Fig 1, G. Wu et al. (2022)
Source

November 9, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Ground-based image of Arp 16, also known as M66.
M66 is a member of the Leo Triplet. NGC 3628, the galaxy in the upper left, likely had an encounter with M66 a few hundred million years ago, creating a dramatic tail-like plume.
Credit: Fig 1, G. Wu et al. (2022)
Source
M66 is a member of the Leo Triplet. NGC 3628, the galaxy in the upper left, likely had an encounter with M66 a few hundred million years ago, creating a dramatic tail-like plume.
Credit: Fig 1, G. Wu et al. (2022)
Source
Gran Telescopio Canarias image of Arp 30, also known as NGC 6365.
Arp thought this was one galaxy with a particularly beefy arm. Later images show this is actually a pair of interacting galaxies, with one galaxy viewed face-on and one viewed nearly edge-on.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
Arp thought this was one galaxy with a particularly beefy arm. Later images show this is actually a pair of interacting galaxies, with one galaxy viewed face-on and one viewed nearly edge-on.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
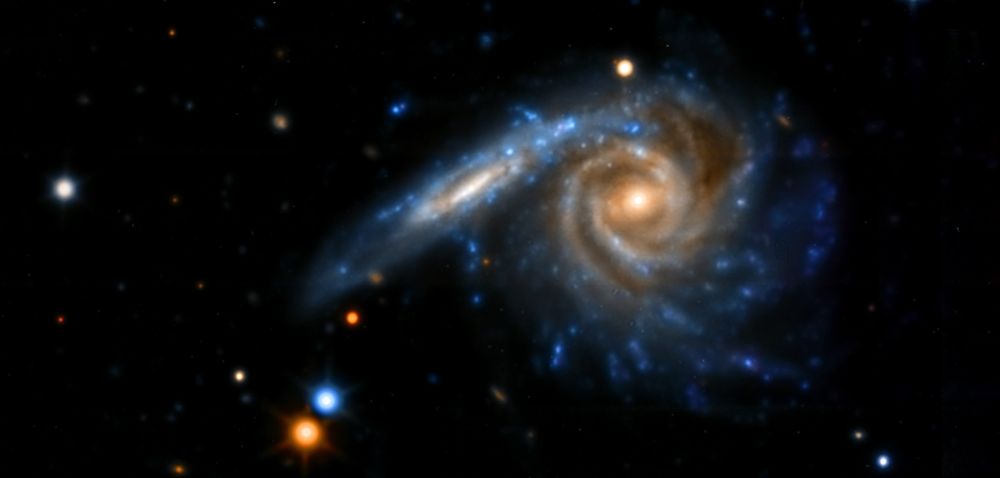

November 8, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Gran Telescopio Canarias image of Arp 30, also known as NGC 6365.
Arp thought this was one galaxy with a particularly beefy arm. Later images show this is actually a pair of interacting galaxies, with one galaxy viewed face-on and one viewed nearly edge-on.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
Arp thought this was one galaxy with a particularly beefy arm. Later images show this is actually a pair of interacting galaxies, with one galaxy viewed face-on and one viewed nearly edge-on.
Credit: GTC, IAC
Source
Hubble image of Arp 272, also known as NGC 6050 and IC 1179.
Arp 272 is a collision between two spiral galaxies in the Hercules Galaxy Cluster.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI
Source
Arp 272 is a collision between two spiral galaxies in the Hercules Galaxy Cluster.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI
Source
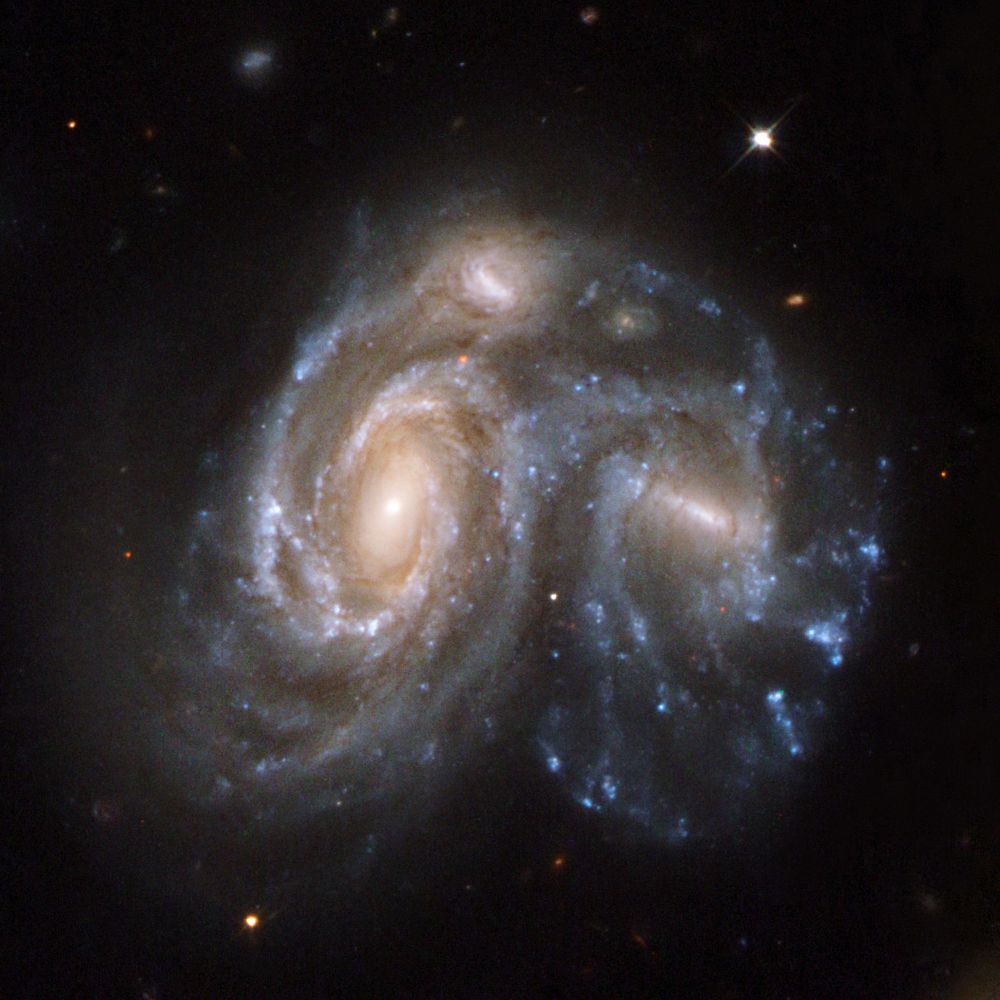

November 8, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble image of Arp 272, also known as NGC 6050 and IC 1179.
Arp 272 is a collision between two spiral galaxies in the Hercules Galaxy Cluster.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI
Source
Arp 272 is a collision between two spiral galaxies in the Hercules Galaxy Cluster.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI
Source
Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of Arp 13, also known as NGC 7448.
NGC 7448 has a disk of tightly wound, clumpy, and particularly bright spiral arms.
Credit: SDSS
Source
NGC 7448 has a disk of tightly wound, clumpy, and particularly bright spiral arms.
Credit: SDSS
Source

November 7, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of Arp 13, also known as NGC 7448.
NGC 7448 has a disk of tightly wound, clumpy, and particularly bright spiral arms.
Credit: SDSS
Source
NGC 7448 has a disk of tightly wound, clumpy, and particularly bright spiral arms.
Credit: SDSS
Source
Image of Arp 140, also known as NGC 274 and NGC 275, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material. The pair is a barred spiral and lenticular galaxy.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material. The pair is a barred spiral and lenticular galaxy.
Source

November 7, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Image of Arp 140, also known as NGC 274 and NGC 275, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material. The pair is a barred spiral and lenticular galaxy.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material. The pair is a barred spiral and lenticular galaxy.
Source
Lick Observatory image of Arp 148, also known as Mayall's Object.
The image was taken in 1940 by astronomer Nicholas Mayall. He noted it looked a little like a question mark. We now know it is a pair of interacting galaxies.
Credit: Plate XIX, Smith 1941
Source
The image was taken in 1940 by astronomer Nicholas Mayall. He noted it looked a little like a question mark. We now know it is a pair of interacting galaxies.
Credit: Plate XIX, Smith 1941
Source

November 6, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Lick Observatory image of Arp 148, also known as Mayall's Object.
The image was taken in 1940 by astronomer Nicholas Mayall. He noted it looked a little like a question mark. We now know it is a pair of interacting galaxies.
Credit: Plate XIX, Smith 1941
Source
The image was taken in 1940 by astronomer Nicholas Mayall. He noted it looked a little like a question mark. We now know it is a pair of interacting galaxies.
Credit: Plate XIX, Smith 1941
Source
Hubble image of Arp 273, also known as UGC 1810 and UGC 1813.
UGC 1810, the larger galaxy in this interacting pair, is distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravity of its companion galaxy, the nearly edge-on UGC 1813.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
UGC 1810, the larger galaxy in this interacting pair, is distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravity of its companion galaxy, the nearly edge-on UGC 1813.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
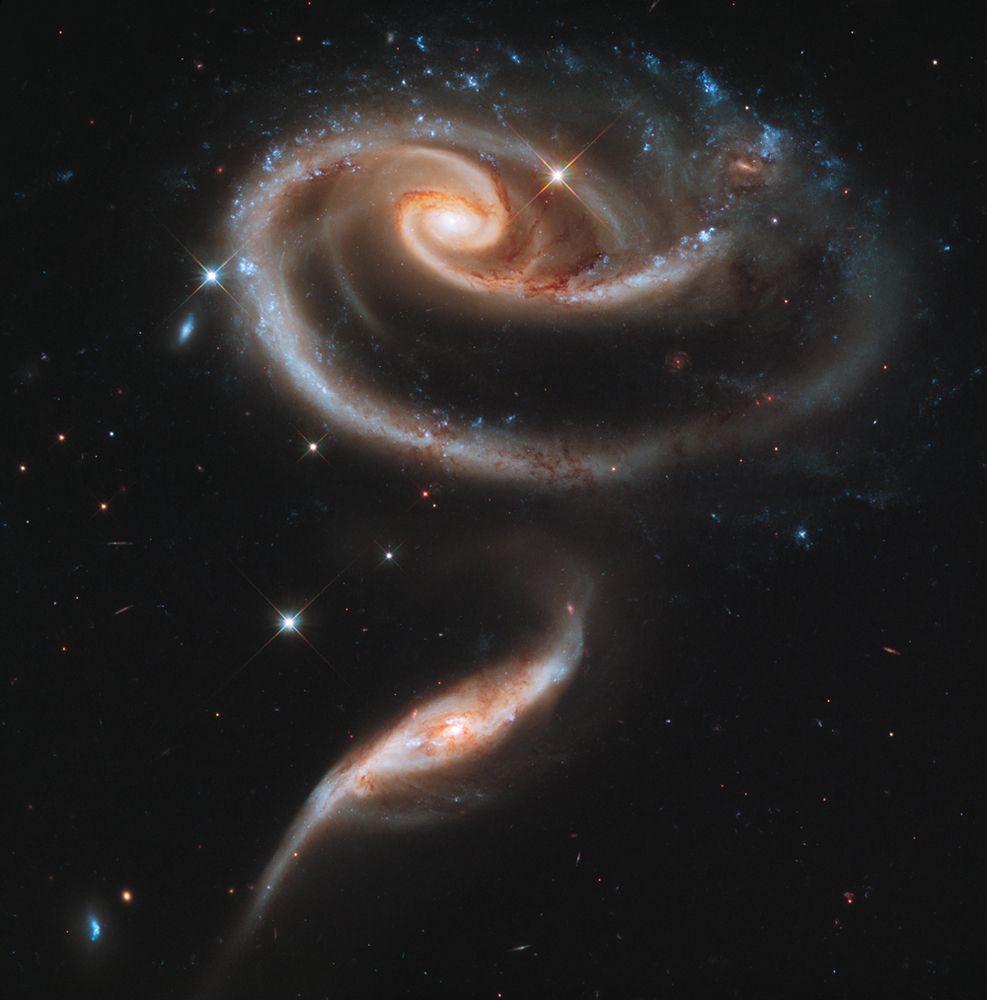

November 6, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble image of Arp 273, also known as UGC 1810 and UGC 1813.
UGC 1810, the larger galaxy in this interacting pair, is distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravity of its companion galaxy, the nearly edge-on UGC 1813.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
UGC 1810, the larger galaxy in this interacting pair, is distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravity of its companion galaxy, the nearly edge-on UGC 1813.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
Image of Arp 82, also known as NGC 2535 and NGC 2536, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Large, high surface brightness companions.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Large, high surface brightness companions.
Source

November 5, 2025 at 12:32 PM
Image of Arp 82, also known as NGC 2535 and NGC 2536, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Large, high surface brightness companions.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Large, high surface brightness companions.
Source
Hubble image of Arp 91, also known as NGC 5953 and NGC 5954.
NGC 5953 (center) and NGC 5954 (left) show clear signs of interaction. A spiral arm or tidal tail from NGC 5954 extends to the side and connects to its companion.
Credit: ESA, NASA, J. Dalcanton, J. Schmidt
Source
NGC 5953 (center) and NGC 5954 (left) show clear signs of interaction. A spiral arm or tidal tail from NGC 5954 extends to the side and connects to its companion.
Credit: ESA, NASA, J. Dalcanton, J. Schmidt
Source
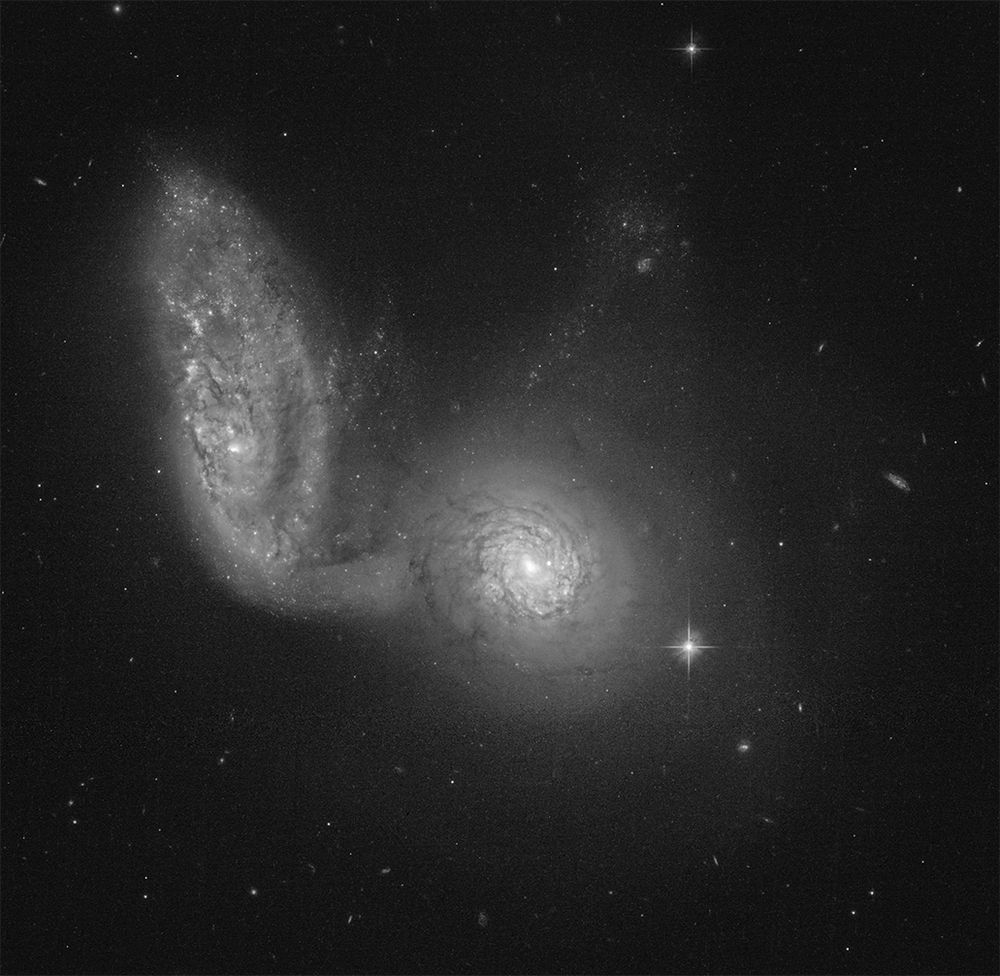

November 5, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble image of Arp 91, also known as NGC 5953 and NGC 5954.
NGC 5953 (center) and NGC 5954 (left) show clear signs of interaction. A spiral arm or tidal tail from NGC 5954 extends to the side and connects to its companion.
Credit: ESA, NASA, J. Dalcanton, J. Schmidt
Source
NGC 5953 (center) and NGC 5954 (left) show clear signs of interaction. A spiral arm or tidal tail from NGC 5954 extends to the side and connects to its companion.
Credit: ESA, NASA, J. Dalcanton, J. Schmidt
Source
Hubble image of Arp 78, also known as NGC 772.
The cropped view does not show the galaxy's overdeveloped spiral arm, caused by interactions with a companion, which led to its inclusion in Arp's catalog of peculiar galaxies.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Seth et al.
Source
The cropped view does not show the galaxy's overdeveloped spiral arm, caused by interactions with a companion, which led to its inclusion in Arp's catalog of peculiar galaxies.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Seth et al.
Source

November 4, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Hubble image of Arp 78, also known as NGC 772.
The cropped view does not show the galaxy's overdeveloped spiral arm, caused by interactions with a companion, which led to its inclusion in Arp's catalog of peculiar galaxies.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Seth et al.
Source
The cropped view does not show the galaxy's overdeveloped spiral arm, caused by interactions with a companion, which led to its inclusion in Arp's catalog of peculiar galaxies.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Seth et al.
Source
Hubble image of Arp 142, also known as NGC 2936 and NGC 2937, or the Penguin and the Egg.
Gravitational interactions between the two galaxies warped the spiral's disk and triggered the formation of new stars, seen as blue knots.
Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
Gravitational interactions between the two galaxies warped the spiral's disk and triggered the formation of new stars, seen as blue knots.
Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team
Source

November 4, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Hubble image of Arp 142, also known as NGC 2936 and NGC 2937, or the Penguin and the Egg.
Gravitational interactions between the two galaxies warped the spiral's disk and triggered the formation of new stars, seen as blue knots.
Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
Gravitational interactions between the two galaxies warped the spiral's disk and triggered the formation of new stars, seen as blue knots.
Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
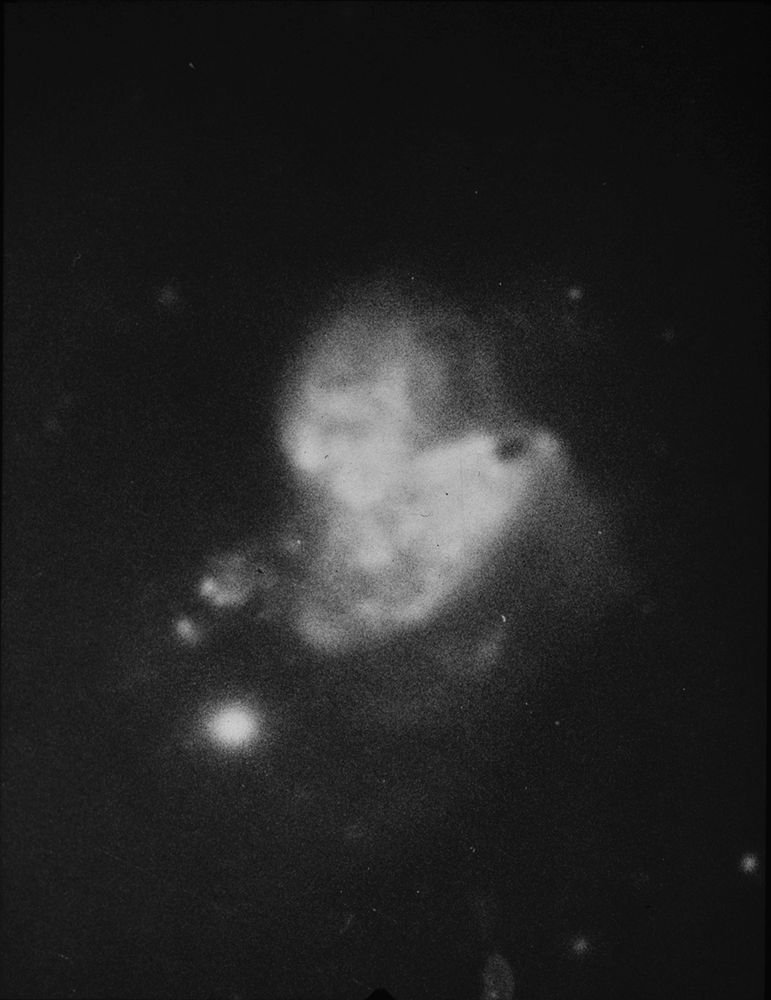
Image of Arp 299, also known as NGC 3690, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Double and multiple galaxies - Unclassified objects. Interactions between the pair triggered a starburst.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Double and multiple galaxies - Unclassified objects. Interactions between the pair triggered a starburst.
Source
November 3, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Image of Arp 299, also known as NGC 3690, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Double and multiple galaxies - Unclassified objects. Interactions between the pair triggered a starburst.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Double and multiple galaxies - Unclassified objects. Interactions between the pair triggered a starburst.
Source
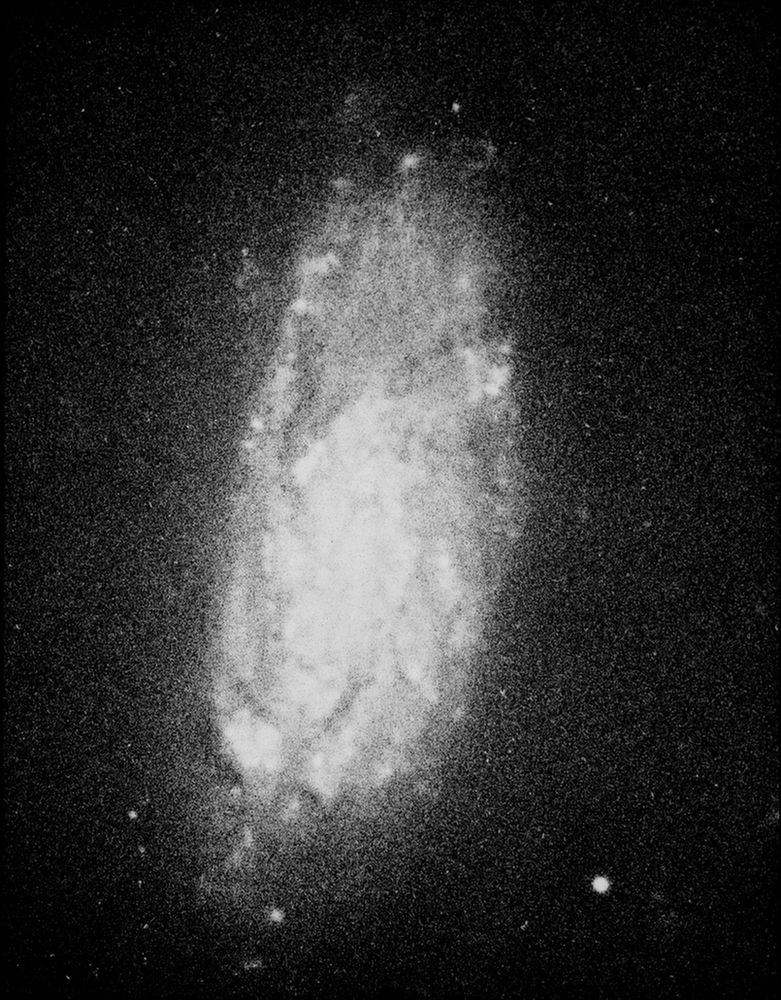
Image of Arp 13, also known as NGC 7448, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Detached segments. It has particularly bright spiral arms.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Detached segments. It has particularly bright spiral arms.
Source
November 3, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Image of Arp 13, also known as NGC 7448, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Detached segments. It has particularly bright spiral arms.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Spiral galaxies - Detached segments. It has particularly bright spiral arms.
Source
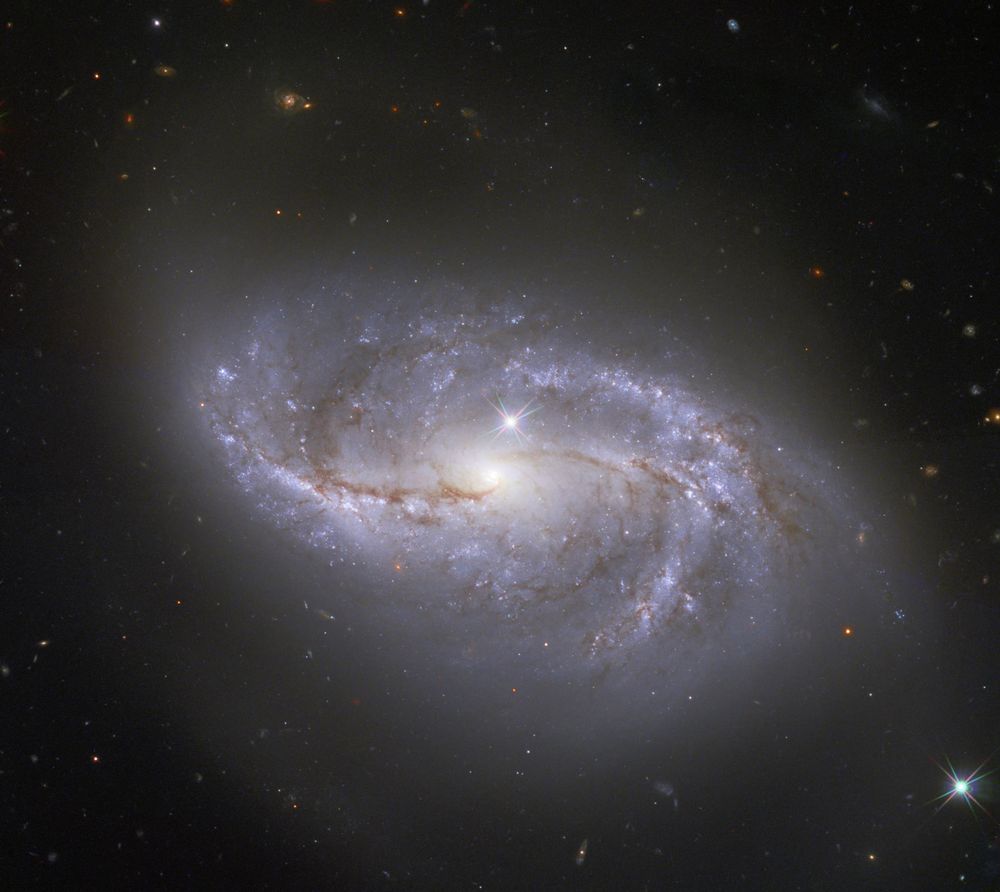
Hubble Space Telescope image of Arp 12, also known as NGC 2608.
NGC 2608 is a barred spiral galaxy. Its arms are peppered by blue star clusters and red star forming regions and crossed by brown dust lanes.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Riess et al.
Source
NGC 2608 is a barred spiral galaxy. Its arms are peppered by blue star clusters and red star forming regions and crossed by brown dust lanes.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Riess et al.
Source

November 2, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Hubble Space Telescope image of Arp 12, also known as NGC 2608.
NGC 2608 is a barred spiral galaxy. Its arms are peppered by blue star clusters and red star forming regions and crossed by brown dust lanes.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Riess et al.
Source
NGC 2608 is a barred spiral galaxy. Its arms are peppered by blue star clusters and red star forming regions and crossed by brown dust lanes.
Credit: ESA, NASA, A. Riess et al.
Source
Image of Arp 142, also known as NGC 2936, NGC 2937, and UGC 5130, or the Penguin and the Egg, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material.
Source

November 2, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Image of Arp 142, also known as NGC 2936, NGC 2937, and UGC 5130, or the Penguin and the Egg, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Emanating material.
Source
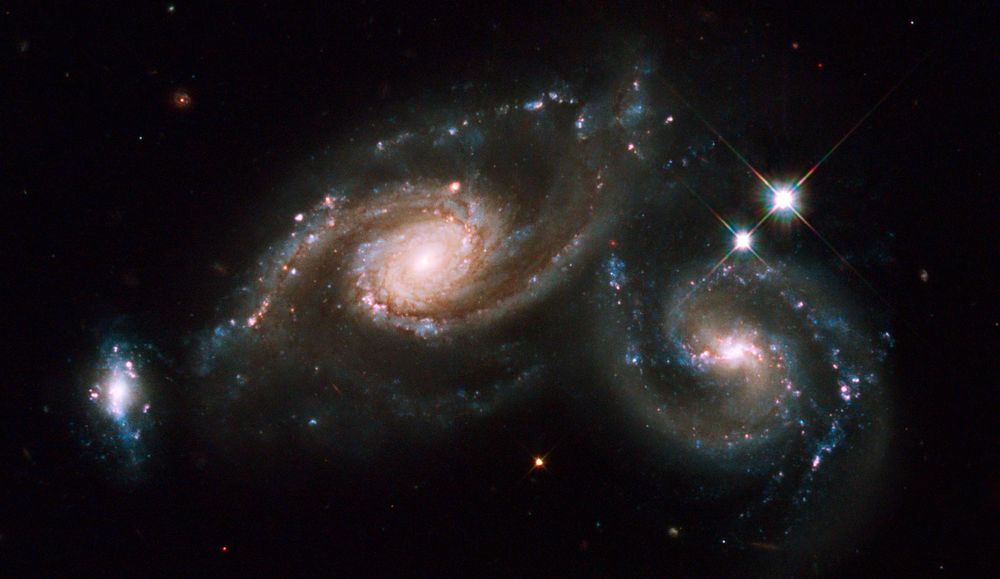
Hubble image of Arp 274, also known as NGC 5679.
NGC 5679 is a system of three interacting galaxies, the two large, overlapping spiral galaxies at center, and a smaller companion galaxy to the far left.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
NGC 5679 is a system of three interacting galaxies, the two large, overlapping spiral galaxies at center, and a smaller companion galaxy to the far left.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source

November 1, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Hubble image of Arp 274, also known as NGC 5679.
NGC 5679 is a system of three interacting galaxies, the two large, overlapping spiral galaxies at center, and a smaller companion galaxy to the far left.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
NGC 5679 is a system of three interacting galaxies, the two large, overlapping spiral galaxies at center, and a smaller companion galaxy to the far left.
Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Team
Source
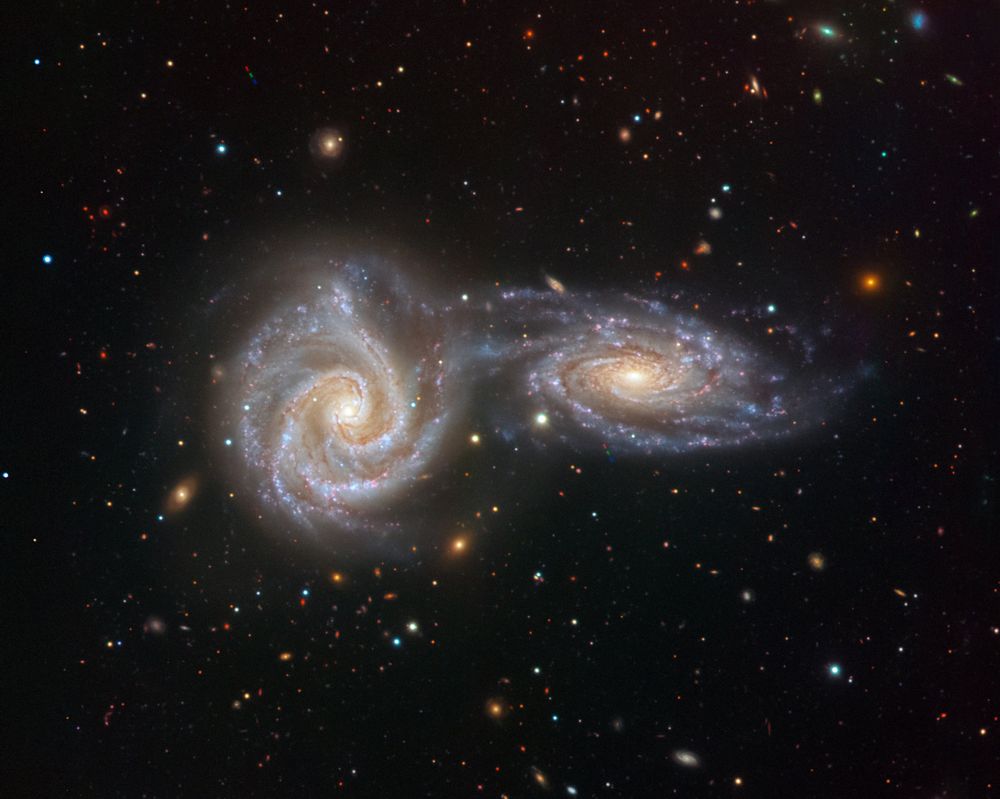
Very Large Telescope image of Arp 271, also known as NGC 5426 and NGC 5427.
This pair of interacting galaxies was the final image captured by the VIsible Multi-Object Spectrograph (VIMOS) instrument before it was decommissioned in 2018.
Credit: ESO, Juan Carlos Muñoz
Source
This pair of interacting galaxies was the final image captured by the VIsible Multi-Object Spectrograph (VIMOS) instrument before it was decommissioned in 2018.
Credit: ESO, Juan Carlos Muñoz
Source

November 1, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Very Large Telescope image of Arp 271, also known as NGC 5426 and NGC 5427.
This pair of interacting galaxies was the final image captured by the VIsible Multi-Object Spectrograph (VIMOS) instrument before it was decommissioned in 2018.
Credit: ESO, Juan Carlos Muñoz
Source
This pair of interacting galaxies was the final image captured by the VIsible Multi-Object Spectrograph (VIMOS) instrument before it was decommissioned in 2018.
Credit: ESO, Juan Carlos Muñoz
Source
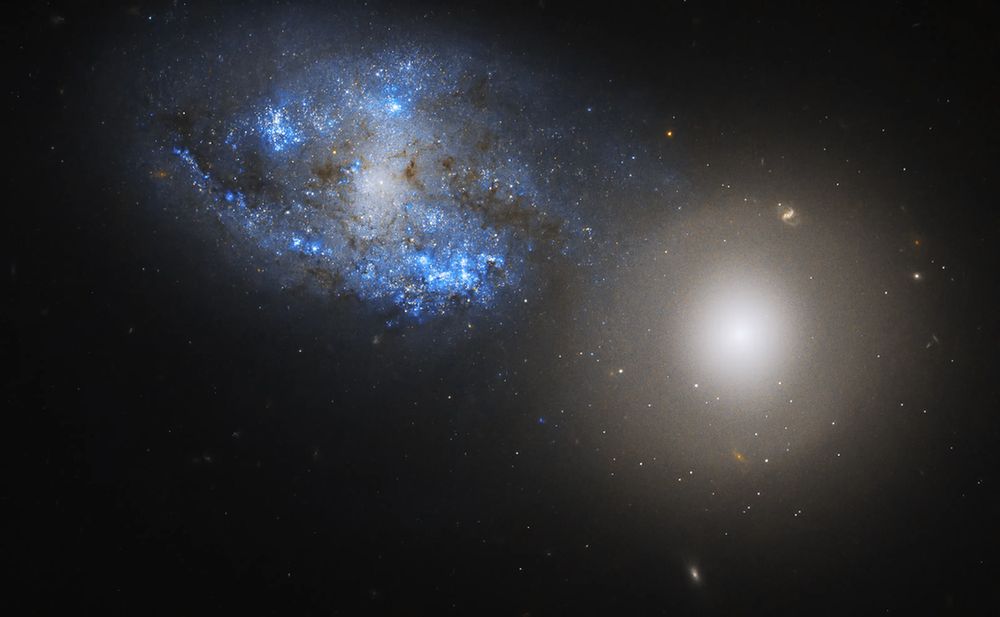
Hubble image of Arp 140, also known as NGC 274 and NGC 275.
A barred spiral galaxy and a lenticular galaxy from an interacting pair. Lenticular galaxies have large central bulges and flattened disks like spirals, but no spiral arms.
Credit: NASA, ESA, R. Foley, G. Kober
Source
A barred spiral galaxy and a lenticular galaxy from an interacting pair. Lenticular galaxies have large central bulges and flattened disks like spirals, but no spiral arms.
Credit: NASA, ESA, R. Foley, G. Kober
Source

October 31, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Hubble image of Arp 140, also known as NGC 274 and NGC 275.
A barred spiral galaxy and a lenticular galaxy from an interacting pair. Lenticular galaxies have large central bulges and flattened disks like spirals, but no spiral arms.
Credit: NASA, ESA, R. Foley, G. Kober
Source
A barred spiral galaxy and a lenticular galaxy from an interacting pair. Lenticular galaxies have large central bulges and flattened disks like spirals, but no spiral arms.
Credit: NASA, ESA, R. Foley, G. Kober
Source
Gemini North image of Arp 78, also known as NGC 772.
Interactions with its companion galaxy NGC 770 (out of frame) left NGC 772's bottom arm elongated and asymmetrical.
Credit: International Gemini Observatory, NOIRLab, NSF, AURA
Source
Interactions with its companion galaxy NGC 770 (out of frame) left NGC 772's bottom arm elongated and asymmetrical.
Credit: International Gemini Observatory, NOIRLab, NSF, AURA
Source

October 31, 2025 at 12:31 AM
Gemini North image of Arp 78, also known as NGC 772.
Interactions with its companion galaxy NGC 770 (out of frame) left NGC 772's bottom arm elongated and asymmetrical.
Credit: International Gemini Observatory, NOIRLab, NSF, AURA
Source
Interactions with its companion galaxy NGC 770 (out of frame) left NGC 772's bottom arm elongated and asymmetrical.
Credit: International Gemini Observatory, NOIRLab, NSF, AURA
Source
Image of Arp 104, also known as NGC 5216 and NGC 5218, or Keenan’s System, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Connected to spiral galaxies.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Connected to spiral galaxies.
Source

October 30, 2025 at 12:31 PM
Image of Arp 104, also known as NGC 5216 and NGC 5218, or Keenan’s System, from Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies (1966).
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Connected to spiral galaxies.
Source
In the original catalog it was in the category: Elliptical galaxies - Connected to spiral galaxies.
Source

