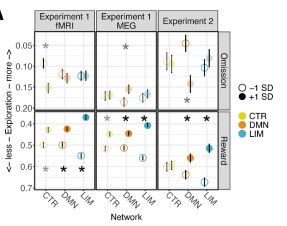
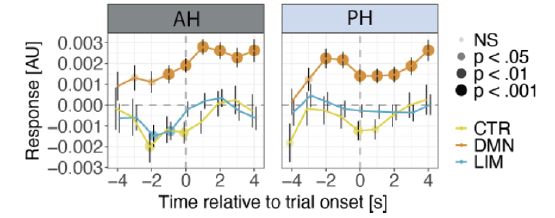
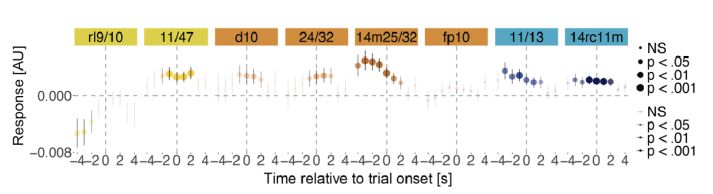
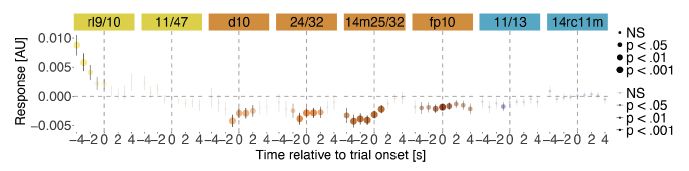
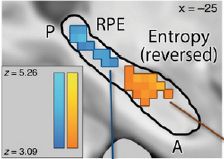
Physics and math enthusiast. Friendly with R, Matlab, and Python.


Works just like the mobile app.
Install this app on your iPhone: tap the share button and then Add to Home Screen.
Tap the Share button
in Safari's toolbar
Select "Add to Home Screen"
from the menu
Tap "Add"
The app will appear on your home screen




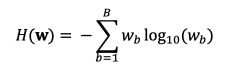








Enter your Bluesky handle and app password to unlock posting, likes, and your Following feed.
Need an app password? Open Bluesky, go to Settings > App passwords, and create a new one.


Sign in with your Bluesky account to unlock posting, likes, and your Following feed.