Using our insilico framework, we infer dynamic GRN and identify targets to steer differentiation decisions. A nice example of how sys.bio can turn stochasticity into actionable insight.
Preprint 👉 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Using our insilico framework, we infer dynamic GRN and identify targets to steer differentiation decisions. A nice example of how sys.bio can turn stochasticity into actionable insight.
Preprint 👉 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We show that active learning + transcriptomic perturbations can guide which exps to run next, boosting phenotypic hit rates >13x. AI not just predicting bio, but designing it. 🔁

We show that active learning + transcriptomic perturbations can guide which exps to run next, boosting phenotypic hit rates >13x. AI not just predicting bio, but designing it. 🔁

To address current limitations, Jianhua Xing and his lab created GraphVelo, a machine learning framework that extends RNA velocity to multimodal data.
Read the full paper in Nature Communications: tinyurl.com/GraphVelo

To address current limitations, Jianhua Xing and his lab created GraphVelo, a machine learning framework that extends RNA velocity to multimodal data.
Read the full paper in Nature Communications: tinyurl.com/GraphVelo
Applied to neural tube patterning shows morphogen-signalling landscapes can be linearly interpolated
Connects interpretable landscape models with data
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Applied to neural tube patterning shows morphogen-signalling landscapes can be linearly interpolated
Connects interpretable landscape models with data
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
A new study from Steven Smeal and Robin E.C. Lee reveals the timing of molecular signals can change how cells respond to their environment, with implications for cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Read more: rdcu.be/ezTxF

A new study from Steven Smeal and Robin E.C. Lee reveals the timing of molecular signals can change how cells respond to their environment, with implications for cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Read more: rdcu.be/ezTxF
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
@jktgfoundation.bsky.social @itcrtraining.bsky.social @smbmathbiology.bsky.social #mathbio #mathonco @mathonco.bsky.social @deniswirtz.bsky.social
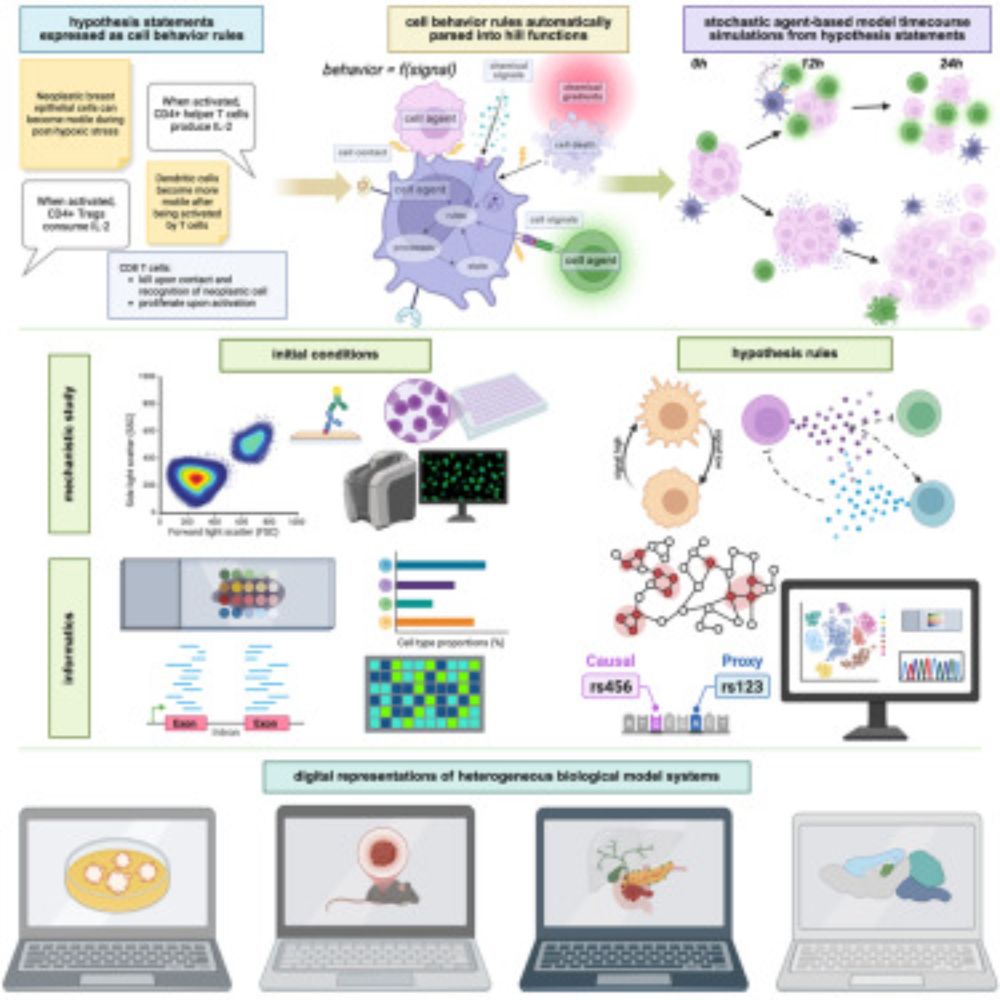
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
@jktgfoundation.bsky.social @itcrtraining.bsky.social @smbmathbiology.bsky.social #mathbio #mathonco @mathonco.bsky.social @deniswirtz.bsky.social


