Pooja Kathail
@poojakathail.bsky.social
Computational Biology PhD student @ucberkeley
Pinned
Pooja Kathail
@poojakathail.bsky.social
· Nov 20

Leveraging genomic deep learning models for non-coding variant effect prediction
The majority of genetic variants identified in genome-wide association studies of complex traits are non-coding, and characterizing their function remains an important challenge in human genetics. Gen...
arxiv.org
Super excited to share our review on genomic deep learning models for non-coding variant effect prediction, with Ayesha Bajwa and Nilah Ioannidis. We’d like this review to be a useful resource, and welcome any feedback, comments, or questions! 1/4
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
This preprint from Helen Sakharova is one of the coolest things to come out of my lab: “Protein language models reveal evolutionary constraints on synonymous codon choice.” Codon choice is a big puzzle in how information is encoded in genomes, and we have a new angle. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Protein language models reveal evolutionary constraints on synonymous codon choice
Evolution has shaped the genetic code, with subtle pressures leading to preferences for some synonymous codons over others. Codons are translated at different speeds by the ribosome, imposing constrai...
www.biorxiv.org
August 7, 2025 at 8:29 AM
This preprint from Helen Sakharova is one of the coolest things to come out of my lab: “Protein language models reveal evolutionary constraints on synonymous codon choice.” Codon choice is a big puzzle in how information is encoded in genomes, and we have a new angle. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
Congratulations to incoming postdoc @rrastogi.bsky.social for being awarded the Warren Alpert Postdoctoral Scholarship! Look forward to having him join us in soon!
June 9, 2025 at 7:23 PM
Congratulations to incoming postdoc @rrastogi.bsky.social for being awarded the Warren Alpert Postdoctoral Scholarship! Look forward to having him join us in soon!
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
We had a bunch of requests so we're extending the #MLCB2025 deadline to June 3rd (anywhere on earth)! cmt3.research.microsoft.com/MLCB2025 to submit.
May 31, 2025 at 10:30 PM
We had a bunch of requests so we're extending the #MLCB2025 deadline to June 3rd (anywhere on earth)! cmt3.research.microsoft.com/MLCB2025 to submit.
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
Some encouraging news for cross-gene generalization of allele effects in S2F models. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Deep genomic models of allele-specific measurements
Allele-specific quantification of sequencing data, such as gene expression, allows for a causal investigation of how DNA sequence variations influence cis gene regulation. Current methods for analyzin...
www.biorxiv.org
April 16, 2025 at 1:46 AM
Some encouraging news for cross-gene generalization of allele effects in S2F models. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
Our new pre-print, investigating a few important questions when we train S2F models on different types of MPRA datasets. Congrats to Yilun and @xinmingtu.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Investigating Data Size, Sequence Diversity, and Model Complexity in MPRA-based Sequence-to-Function Prediction
We created the MPRA Dataset Collection (MDC), a curated resource of MPRA data from 12 studies comprising over 150 million labeled DNA subsequences. These datasets include both random and natural genom...
www.biorxiv.org
March 15, 2025 at 3:02 AM
Our new pre-print, investigating a few important questions when we train S2F models on different types of MPRA datasets. Congrats to Yilun and @xinmingtu.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
I have confirmation from several sources now that all T32s, many F30s and F31s, and most or all Center awards (P30, P50) have been terminated at Columbia.
This is quite damaging to research and to individuals.
This is pure terrorism and cannot be legal. But litigation will take time...
This is quite damaging to research and to individuals.
This is pure terrorism and cannot be legal. But litigation will take time...
March 11, 2025 at 2:30 PM
I have confirmation from several sources now that all T32s, many F30s and F31s, and most or all Center awards (P30, P50) have been terminated at Columbia.
This is quite damaging to research and to individuals.
This is pure terrorism and cannot be legal. But litigation will take time...
This is quite damaging to research and to individuals.
This is pure terrorism and cannot be legal. But litigation will take time...
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
Wow. "NIH" canceled my co-mentored (with Dave Sulzer) PhD student's F31 funding. His work is on understanding the genetics and neuroscience of language learning disorders. F31 provides no indirect $ to Columbia, just pays his salary. Not that it should matter, but he's an American citizen. W.T.F.
March 11, 2025 at 12:41 PM
Wow. "NIH" canceled my co-mentored (with Dave Sulzer) PhD student's F31 funding. His work is on understanding the genetics and neuroscience of language learning disorders. F31 provides no indirect $ to Columbia, just pays his salary. Not that it should matter, but he's an American citizen. W.T.F.
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
It's today, T-3h! If you're in the East Bay and care about science or education (i.e. if you care about living on this planet in any form 😃), join us, 11:45 at Upper Sproul!
And if you're elsewhere, look up a local event in your area, there's a LOT happening today!
www.standup4scienceberkeley.com
And if you're elsewhere, look up a local event in your area, there's a LOT happening today!
www.standup4scienceberkeley.com

March 7, 2025 at 4:43 PM
It's today, T-3h! If you're in the East Bay and care about science or education (i.e. if you care about living on this planet in any form 😃), join us, 11:45 at Upper Sproul!
And if you're elsewhere, look up a local event in your area, there's a LOT happening today!
www.standup4scienceberkeley.com
And if you're elsewhere, look up a local event in your area, there's a LOT happening today!
www.standup4scienceberkeley.com
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
Our new paper describing a scalable approach for training sequence-to-function models on personal genomes ("personal genome training"), includes our observations on when this works and its limitations. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats: Anna, @xinmingtu.bsky.social , @lxsasse.bsky.social
Congrats: Anna, @xinmingtu.bsky.social , @lxsasse.bsky.social

A scalable approach to investigating sequence-to-expression prediction from personal genomes
A key promise of sequence-to-function (S2F) models is their ability to evaluate arbitrary sequence inputs, providing a robust framework for understanding genotype-phenotype relationships. However, despite strong performance across genomic loci , S2F models struggle with inter-individual variation. Training a model to make genotype-dependent predictions at a single locus-an approach we call personal genome training-offers a potential solution. We introduce SAGE-net, a scalable framework and software package for training and evaluating S2F models using personal genomes. Leveraging its scalability, we conduct extensive experiments on model and training hyperparameters, demonstrating that training on personal genomes improves predictions for held-out individuals. However, the model achieves this by identifying predictive variants rather than learning a cis-regulatory grammar that generalizes across loci. This failure to generalize persists across a range of hyperparameter settings. These findings highlight the need for further exploration to unlock the full potential of S2F models in decoding the regulatory grammar of personal genomes. Scalable software and infrastructure development will be critical to this progress. ### Competing Interest Statement The authors have declared no competing interest.
www.biorxiv.org
February 23, 2025 at 11:31 PM
Our new paper describing a scalable approach for training sequence-to-function models on personal genomes ("personal genome training"), includes our observations on when this works and its limitations. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats: Anna, @xinmingtu.bsky.social , @lxsasse.bsky.social
Congrats: Anna, @xinmingtu.bsky.social , @lxsasse.bsky.social
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
New preprint w/ @soumyakundu.bsky.social @sbmontgom.bsky.social @anshulkundaje.bsky.social !
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

Mapping the regulatory effects of common and rare non-coding variants across cellular and developmental contexts in the brain and heart
Whole genome sequencing has identified over a billion non-coding variants in humans, while GWAS has revealed the non-coding genome as a significant contributor to disease. However, prioritizing causal...
www.biorxiv.org
February 19, 2025 at 1:32 PM
New preprint w/ @soumyakundu.bsky.social @sbmontgom.bsky.social @anshulkundaje.bsky.social !
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
📣Excited to share my last postdoc paper with
@soumya-boston.bsky.social on eQTL mechanisms depending on where the RNA is in the cell! @broadinstitute.org @harvardmed.bsky.social
TL;DR:Early RNA eQTL variants in the nucleus and late RNA eQTL variants in the cytosol have distinct molecular mechanism🧵
@soumya-boston.bsky.social on eQTL mechanisms depending on where the RNA is in the cell! @broadinstitute.org @harvardmed.bsky.social
TL;DR:Early RNA eQTL variants in the nucleus and late RNA eQTL variants in the cytosol have distinct molecular mechanism🧵

February 27, 2025 at 2:21 AM
📣Excited to share my last postdoc paper with
@soumya-boston.bsky.social on eQTL mechanisms depending on where the RNA is in the cell! @broadinstitute.org @harvardmed.bsky.social
TL;DR:Early RNA eQTL variants in the nucleus and late RNA eQTL variants in the cytosol have distinct molecular mechanism🧵
@soumya-boston.bsky.social on eQTL mechanisms depending on where the RNA is in the cell! @broadinstitute.org @harvardmed.bsky.social
TL;DR:Early RNA eQTL variants in the nucleus and late RNA eQTL variants in the cytosol have distinct molecular mechanism🧵
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
[SAVE THE DATE] MLCB 2025 is happening Sept 10-11 at the NY Genome Center in NYC!
Attend the premier conference at the intersection of ML & Bio, share your research and make lasting connections!
Submission deadline: June 1
More details: mlcb.github.io
Help spread the word—please RT! #MLCB2025
Attend the premier conference at the intersection of ML & Bio, share your research and make lasting connections!
Submission deadline: June 1
More details: mlcb.github.io
Help spread the word—please RT! #MLCB2025
February 5, 2025 at 2:50 AM
[SAVE THE DATE] MLCB 2025 is happening Sept 10-11 at the NY Genome Center in NYC!
Attend the premier conference at the intersection of ML & Bio, share your research and make lasting connections!
Submission deadline: June 1
More details: mlcb.github.io
Help spread the word—please RT! #MLCB2025
Attend the premier conference at the intersection of ML & Bio, share your research and make lasting connections!
Submission deadline: June 1
More details: mlcb.github.io
Help spread the word—please RT! #MLCB2025
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
#MLCB2025 will be Sept 10-11 at @nygenome.org in NYC! Paper deadline June 1st & in-person registration will open in May. Please sign up for our mailing list groups.google.com/g/mlcb/ for future announcements. More details at mlcb.github.io. Please RP!
January 27, 2025 at 6:40 PM
#MLCB2025 will be Sept 10-11 at @nygenome.org in NYC! Paper deadline June 1st & in-person registration will open in May. Please sign up for our mailing list groups.google.com/g/mlcb/ for future announcements. More details at mlcb.github.io. Please RP!
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
(1/10) Excited to announce our latest work! @arpita-s.bsky.social, @amanpatel100.bsky.social , and I will be presenting DART-Eval, a rigorous suite of evals for DNA Language Models on transcriptional regulatory DNA at #NeurIPS2024. Check it out! arxiv.org/abs/2412.05430

DART-Eval: A Comprehensive DNA Language Model Evaluation Benchmark on Regulatory DNA
Recent advances in self-supervised models for natural language, vision, and protein sequences have inspired the development of large genomic DNA language models (DNALMs). These models aim to learn gen...
arxiv.org
December 11, 2024 at 2:30 AM
(1/10) Excited to announce our latest work! @arpita-s.bsky.social, @amanpatel100.bsky.social , and I will be presenting DART-Eval, a rigorous suite of evals for DNA Language Models on transcriptional regulatory DNA at #NeurIPS2024. Check it out! arxiv.org/abs/2412.05430
Reposted by Pooja Kathail
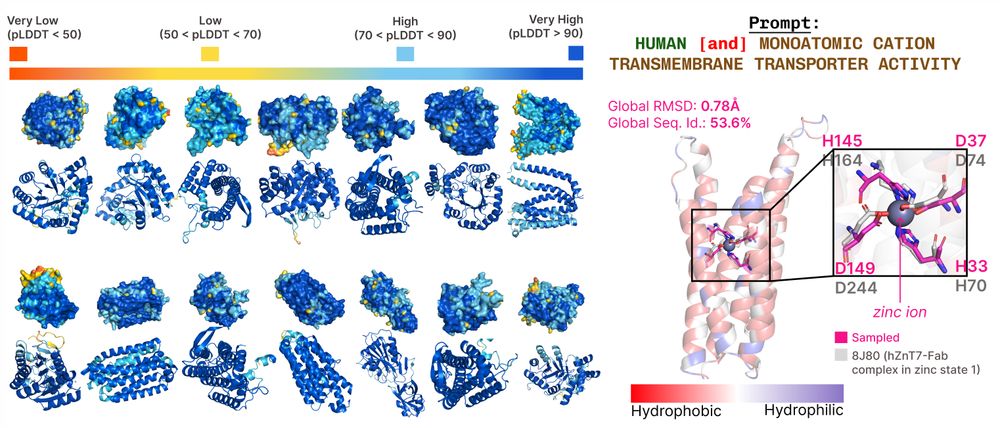
1/🧬 Excited to share PLAID, our new approach for co-generating sequence and all-atom protein structures by sampling from the latent space of ESMFold. This requires only sequences during training, which unlocks more data and annotations:
bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
December 6, 2024 at 5:44 PM
1/🧬 Excited to share PLAID, our new approach for co-generating sequence and all-atom protein structures by sampling from the latent space of ESMFold. This requires only sequences during training, which unlocks more data and annotations:
bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
bit.ly/plaid-proteins
🧵
Super excited to share our review on genomic deep learning models for non-coding variant effect prediction, with Ayesha Bajwa and Nilah Ioannidis. We’d like this review to be a useful resource, and welcome any feedback, comments, or questions! 1/4
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158

Leveraging genomic deep learning models for non-coding variant effect prediction
The majority of genetic variants identified in genome-wide association studies of complex traits are non-coding, and characterizing their function remains an important challenge in human genetics. Gen...
arxiv.org
November 20, 2024 at 1:31 AM
Super excited to share our review on genomic deep learning models for non-coding variant effect prediction, with Ayesha Bajwa and Nilah Ioannidis. We’d like this review to be a useful resource, and welcome any feedback, comments, or questions! 1/4
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158

