
Community ecology, ecosystem functioning, biodiversity, trophic interactions, energy dynamics, nutrient cycling

doi.org/10.1016/j.bi...
▶️Native richness limits invaders, but effect weakens at larger scales
▶️Old aliens respond to climate & disturbance🌧️
▶️Neophytes & invasives thrive with roads, urban & croplands 🚗
#sCaleGrassDiv @idiv-research.bsky.social

We present #GrasslandTraitSim.jl, a process-based simulation model that links plant traits to ecosystem processes to predict how management and climate change shape productivity and composition of plant community in temperate grasslands
doi.org/10.5194/gmd-...
Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

Submit your paper to this Special Issue of NZ Journal of Zoology, edited by me, @carlosbarreto.bsky.social & @barnesecodiv.bsky.social!
More info: www.royalsociety.org.nz/news/nzjz-so...
#SoilBiodiversity 🧪
Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

#Ecology #EcologicalNetwork #Macroecology #Biogeography



@fubcp.bsky.social, @freieuniversitaet.bsky.social
Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan




Our paper shows that multitrophic biodiversity enhances ecosystem functions, services, and ecological intensification in agriculture.
Read it here: doi.org/10.1093/jpe/...


Sampling nested plot series at multiple scales in dry grasslands 🌾 #GrassPlot #EDGG
Geat teamwork with @dariiaborovyk.bsky.social & @charly-gha.bsky.social
#FieldEcology #GrasslandScience



🌿 Identifying plants
🐾 Matching mammal fingerprints
💻 Playing with computer models
✔️ Guessing plant diversity
🦊 Exploring animal habitats at game tables
It was a blast – thanks for the curiosity and great conversations! 🧠🌼
Reposted by Elena Litchman, Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

"Deciphering the Multitrophic Consequences of Biodiversity Change Through an Energetic Lens"
Join us online Thursday 26th June 1pm AEST!
Sign up to our mailing list to receive the zoom link forms.gle/24Y557Cjeu6w...

Traditional management maintains species-rich grassland 🌼
▶️19% plant species dispersed via livestock feces💩
▶️Grassland cleaning🧹 boosts diversity
▶️Low-intensity grazing🐄 & manuring💩 shape plant composition without reducing diversity 👩🌾
doi.org/10.1016/j.bi...
Reposted by Andrew Hacket‐Pain, Sergey Rosbakh, Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan


One-size-fits-all doesn't work in restoration! Trade-offs between carbon gain, water use & nitrogen use shift with abiotic context in Mediterranean-type ecosystems. Match plant traits to place! nsojournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

by Felix Nößler, Thibault Moulin, Oksana Buzhdygan, Britta Tietjen, and Felix May doi.org/pfrn via @EgUsphere
#PlantScience
Reposted by Susanne Lachmuth, Oksana Y. Buzhdygan

Jeltsch et al.
The need for an individual-based global change ecology ibe.pensoft.net/articles.php...

Start of sampling in the #BlühenderCampus of the @freieuniversitaet.bsky.social to assess the effects of management intensity on biodiversity 🌼🐛🐞🐿️ & functioning ♻️ of campus green spaces. Stay tuned for more 😉
by @dariiaborovyk.bsky.social
Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan
Reiht sich gut ein in den Artikel von @christianschwaegerl.mastodon.social.ap.brid.gy letztens
www.faz.net/aktuell/wiss...
with @anyameadow.bsky.social, @dariiaborovyk.bsky.social, and #sCaleGrassDiv group
Reposted by Nick M. Haddad, Irena Šímová, Oksana Y. Buzhdygan
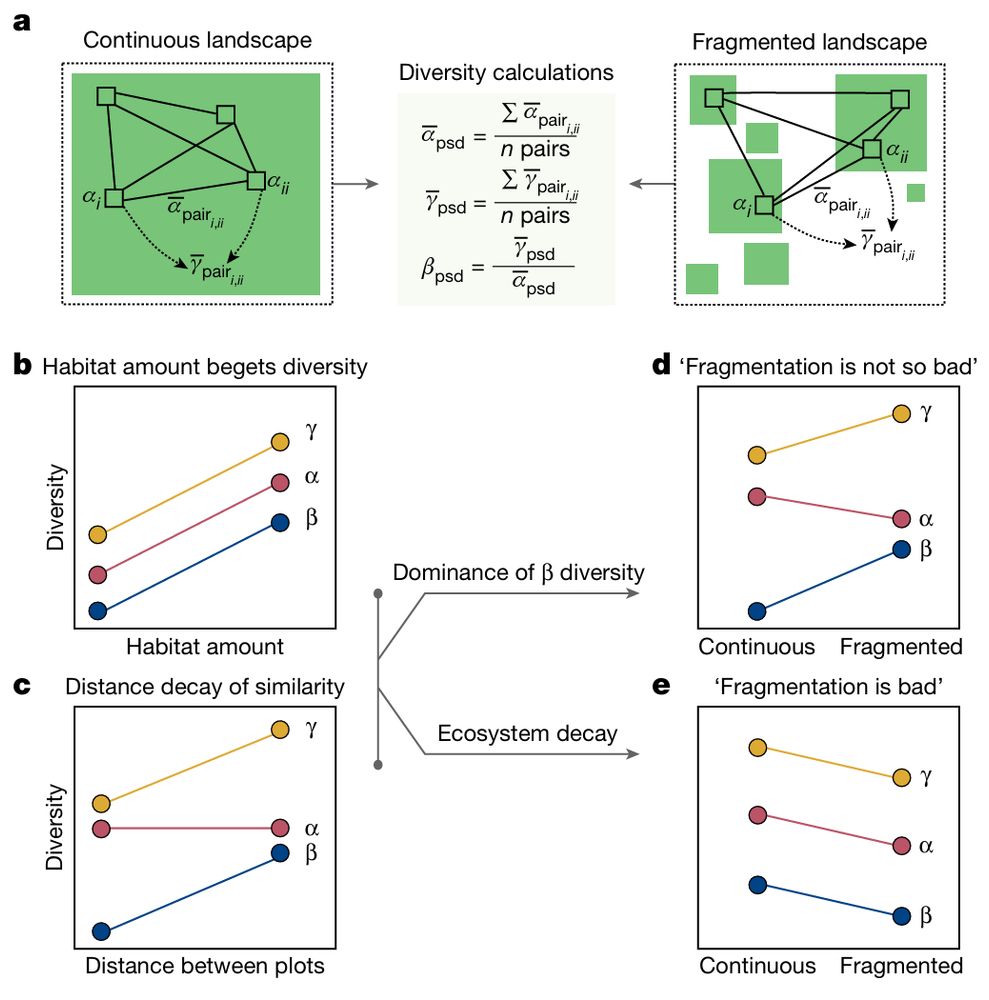
Landscapes of fragmented habitat have lower diversity, at all scales, than do unfragmented landscapes.
Habitat fragmentation does not compensate for the loss of local (alpha) diversity by increasing the diversity among fragments (beta diversity).
www.nature.com/articles/s41...


Reposted by Karl Andraczek

Scale-Dependent Effects of Plant Diversity Drivers Across Different Grassland Habitats in Ukraine doi.org/10.1002/ece3...
result of #sDiv synthesis working #sCaleGrassDiv in @iDiv www.idiv.de/research/sdi...

Reposted by Oksana Y. Buzhdygan
Different facets of plant diversity differentially affect energy dynamics across trophic levels and below- or aboveground compartements. 🌱🍃🪲🪱
doi.org/10.1002/ecm....
##BEassembly2025 #Biodiversityexploratories #forest #grassland #snow


Looking forward to ##BEassembly2026
Reposted by Malte Jochum, Oksana Y. Buzhdygan


##BEassembly2025 #Biodiversityexploratories #forest #grassland #snow

