
https://www.nature.com/nrc/

It features #REVIEWS on:
- m6A RNA modifications
- The role of concomitant medications on ICI efficacy
- Neutrophil extracellular traps
- Transcriptomic deconvolution
👇
http://dlvr.it/TQfqS0
Mutant HSCs display broad fitness variation. Now, Agarwal et al. identify a germline noncoding variant that confers resilience to clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (#CHIP) by dampening expression of the RNA-binding protein MSI2.

Mutant HSCs display broad fitness variation. Now, Agarwal et al. identify a germline noncoding variant that confers resilience to clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (#CHIP) by dampening expression of the RNA-binding protein MSI2.
Melissa Dolan
Kendra Libby
Alison Ringel
@vangalenlab.bsky.social
#10) Ageing, immune fitness and cancer
#ageing #aging #ageingandcancer #agingandcancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Melissa Dolan
Kendra Libby
Alison Ringel
@vangalenlab.bsky.social
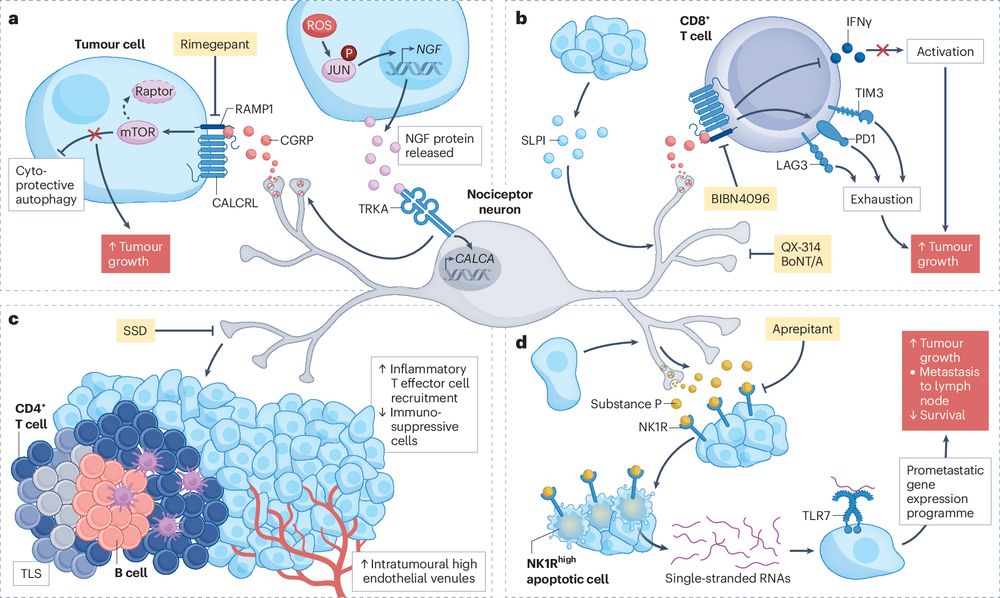
Neuro-immune cross-talk in cancer
#neuroimmune #cancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
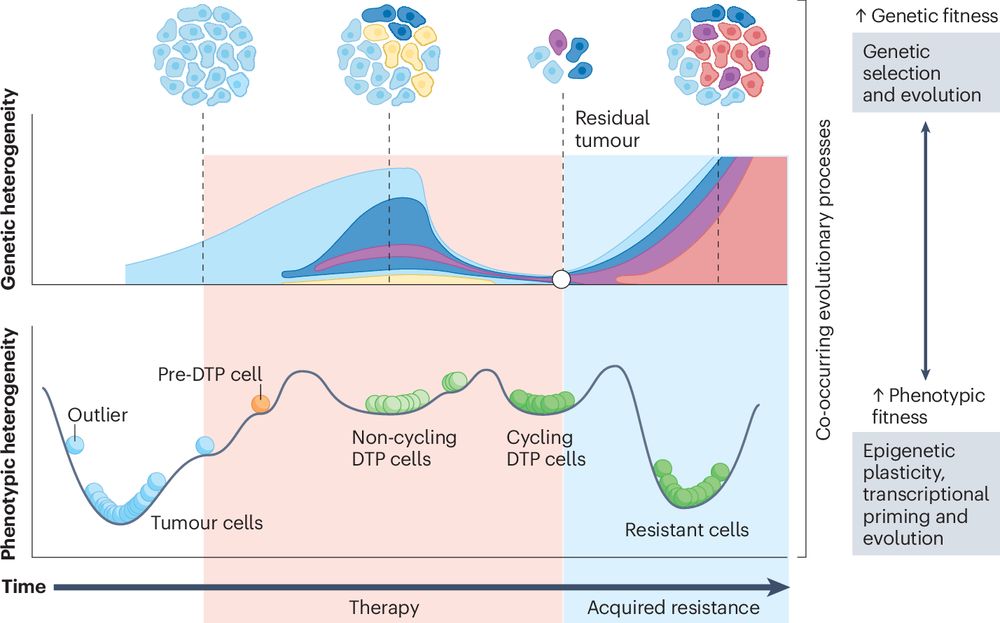
Acquired resistance in cancer: towards targeted therapeutic strategies
#therapyresistance #cancertherapy @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Our 1st most downloaded #REVIEW in 2025:
Unveiling the molecular and immunological drivers of antibody–drug conjugates in cancer treatment
#ADCs #antibodydrugconjugates @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Our 1st most downloaded #REVIEW in 2025:
Unveiling the molecular and immunological drivers of antibody–drug conjugates in cancer treatment
#ADCs #antibodydrugconjugates @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Targeted protein degradation for cancer therapy
#PROTACs #Degraders @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Targeted protein degradation for cancer therapy
#PROTACs #Degraders @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Acquired resistance in cancer: towards targeted therapeutic strategies
#therapyresistance #cancertherapy @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Acquired resistance in cancer: towards targeted therapeutic strategies
#therapyresistance #cancertherapy @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Neuro-immune cross-talk in cancer
#neuroimmune #cancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Neuro-immune cross-talk in cancer
#neuroimmune #cancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Cross-priming in cancer immunology and immunotherapy
#TME #immunotherapy
@NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Cross-priming in cancer immunology and immunotherapy
#TME #immunotherapy
@NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Dendritic cell maturation in cancer
#dendriticcells #TME @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
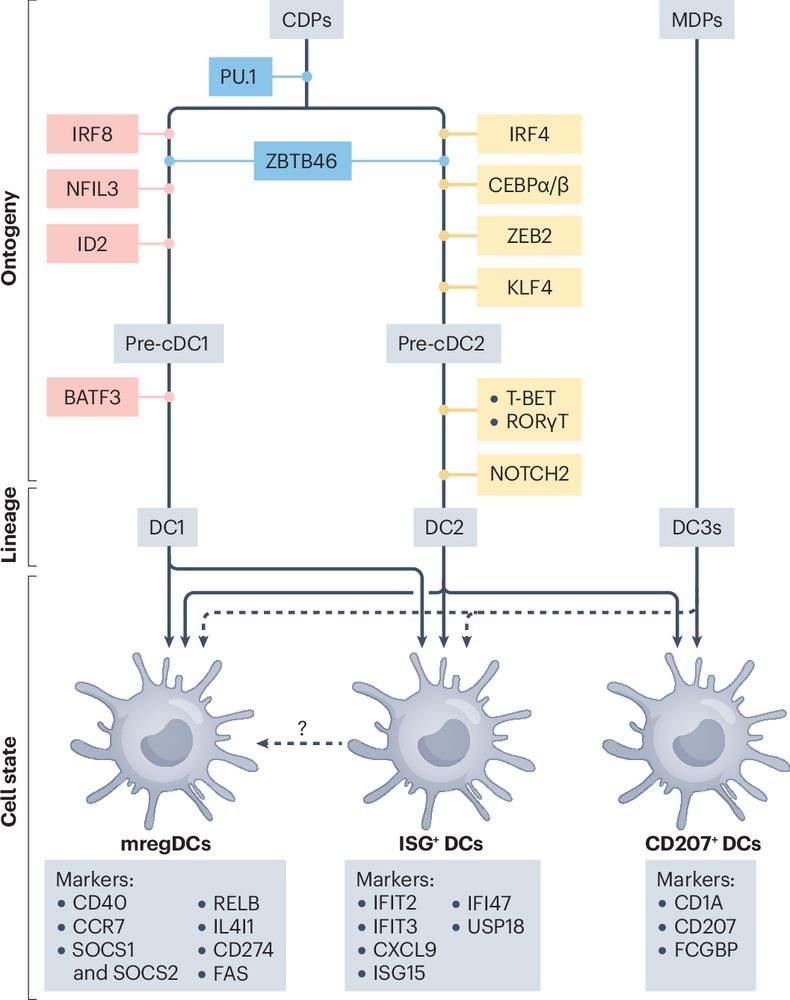
Dendritic cell maturation in cancer
#dendriticcells #TME @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Recent advances in therapeutic cancer vaccines
#cancervaccines @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Recent advances in therapeutic cancer vaccines
#cancervaccines @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

Genomic and fragmentomic landscapes of cell-free DNA for early cancer detection
#cfDNA #liquidbiopsy @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
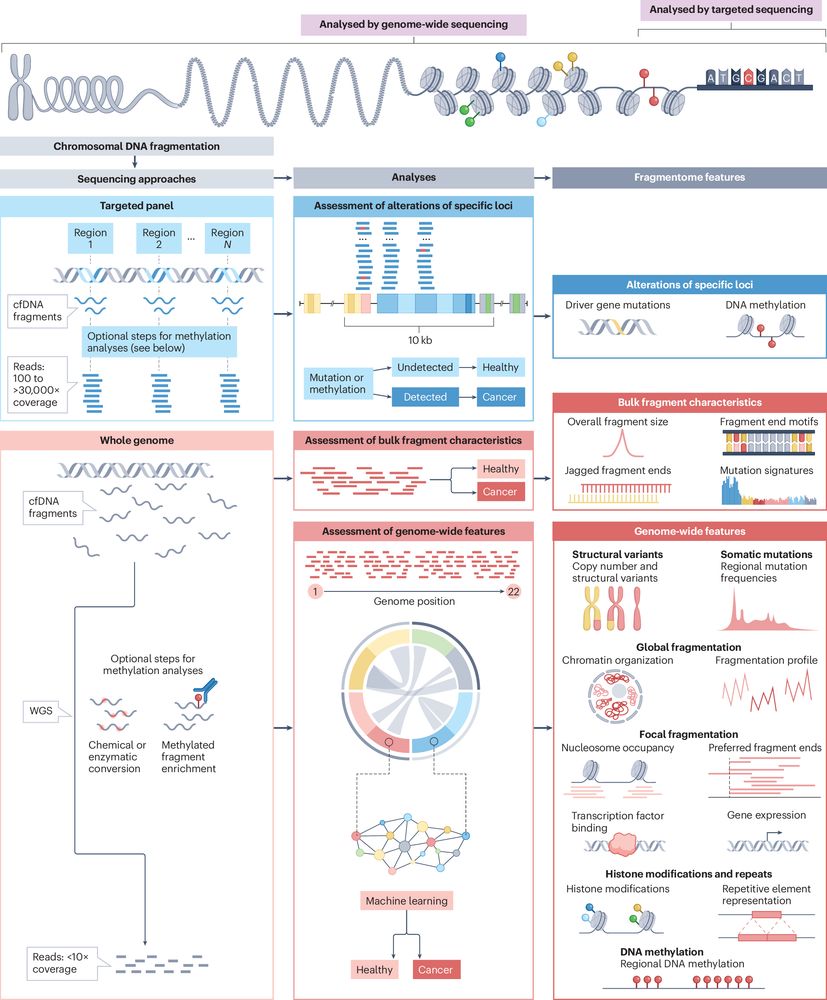
Genomic and fragmentomic landscapes of cell-free DNA for early cancer detection
#cfDNA #liquidbiopsy @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
👇 📖
http://dlvr.it/TQlvx5

👇 📖
http://dlvr.it/TQlvx5
The immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer
#TME #colorectalcancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

The immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer
#TME #colorectalcancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
Fucosylation—the attachment of the dietary sugar L‑fucose to glycoproteins & glycolipids—is frequently altered in cancer. Bitaraf et al. outline its role in tumour progression and therapeutic response.
📖 👇

#10) Ageing, immune fitness and cancer
#ageing #aging #ageingandcancer #agingandcancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025

#10) Ageing, immune fitness and cancer
#ageing #aging #ageingandcancer #agingandcancer @NatResCancer
#NRCtop10of2025
🚨 Starting Monday, we're counting down the top 10 most downloaded #REVIEW articles of 2025! 🚨
Don't miss it! 🎉
#NRCtop10of2025

🚨 Starting Monday, we're counting down the top 10 most downloaded #REVIEW articles of 2025! 🚨
Don't miss it! 🎉
#NRCtop10of2025
It features #REVIEWS on:
- m6A RNA modifications
- The role of concomitant medications on ICI efficacy
- Neutrophil extracellular traps
- Transcriptomic deconvolution
👇
http://dlvr.it/TQfqS0

It features #REVIEWS on:
- m6A RNA modifications
- The role of concomitant medications on ICI efficacy
- Neutrophil extracellular traps
- Transcriptomic deconvolution
👇
http://dlvr.it/TQfqS0
Pablo Siliceo & Alfredo Rodríguez discuss histoCAT, a method that offers interactive spatial analysis to reveal tumour tissue architecture and cell–cell interactions, highlighting the growing power of #SpatialBiology.
📖⬇️
http://dlvr.it/TQfjPk

Pablo Siliceo & Alfredo Rodríguez discuss histoCAT, a method that offers interactive spatial analysis to reveal tumour tissue architecture and cell–cell interactions, highlighting the growing power of #SpatialBiology.
📖⬇️
http://dlvr.it/TQfjPk
Cat tumour viruses mirror human oncogenic viruses. Beatty & Tu argue that comparative oncology in cats could accelerate prevention and treatment strategies for viral cancers.
📖⬇️
http://dlvr.it/TQdk2t

Cat tumour viruses mirror human oncogenic viruses. Beatty & Tu argue that comparative oncology in cats could accelerate prevention and treatment strategies for viral cancers.
📖⬇️
http://dlvr.it/TQdk2t
To preserve tumour architecture, cellular heterogeneity & the dynamic crosstalk that influences cancer, Fong and colleagues advocate for coordinated, cross-disciplinary and sustained efforts to promote the widespread adoption of tumour explants.
👇 📖
http://dlvr.it/TQZPW7

To preserve tumour architecture, cellular heterogeneity & the dynamic crosstalk that influences cancer, Fong and colleagues advocate for coordinated, cross-disciplinary and sustained efforts to promote the widespread adoption of tumour explants.
👇 📖
http://dlvr.it/TQZPW7




