
Using health data to learn what works.
Making #causalinference less casual.
Director, @causalab.bsky.social
Professor, @hsph.harvard.edu
Methods Editor, Annals of Internal Medicine @annalsofim.bsky.social

A revision of our book "Causal Inference: What If" is available at miguelhernan.org/whatifbook
Thanks to everyone who suggested improvements, reported typos, and proposed new citations and material.
Enjoy the #WhatIfBook plus code and data. Also, it's free.
See our review of procedures to align eligibility and treatment assignment in observational emulations. We use 3 target trials of increasing complexity and provide a decision diagram
www.bmj.com/content/392/...

See our review of procedures to align eligibility and treatment assignment in observational emulations. We use 3 target trials of increasing complexity and provide a decision diagram
www.bmj.com/content/392/...
Hospitalization risk very low in unvaccinated, lower in vaccinated.
6-11 years old: no myocarditis cases
12-17 years old: myocarditis risk very low in vaccinated, lower in unvaccinated
journals.lww.com/pidj/fulltex...

Hospitalization risk very low in unvaccinated, lower in vaccinated.
6-11 years old: no myocarditis cases
12-17 years old: myocarditis risk very low in vaccinated, lower in unvaccinated
journals.lww.com/pidj/fulltex...
20th Kolokotrones Symposium: “Acetaminophen During Pregnancy and Autism: What Does Causal Inference Take?"
Details in comments. In-person limited to Harvard ID holders due to space restrictions. Online attendance free & public.
Register:
www.eventbrite.com/e/acetaminop...

20th Kolokotrones Symposium: “Acetaminophen During Pregnancy and Autism: What Does Causal Inference Take?"
Details in comments. In-person limited to Harvard ID holders due to space restrictions. Online attendance free & public.
Register:
www.eventbrite.com/e/acetaminop...
Take advantage of expert advice for your research projects. Learn more and help spread the word! :)
Free #causalinference consulting open to Boston-based, junior clinical investigators. Postdoc fellows provide guidance pertaining to #studydesign, data analysis and results for works in progress.
Learn more & apply:
hsph.harvard.edu/research/cau...

Take advantage of expert advice for your research projects. Learn more and help spread the word! :)
For those who prefer to be explicit about what they do, we have developed the TARGET Statement 👇
TARGET is a reporting guideline for observational studies of interventions that use the target trial framework.
Over 3 years the @TARGETGuideline was rigorously developed and was co-published today in @jama.com & @bmj.com
doi.org/10.1001/jama.2025.13350
#episky


For those who prefer to be explicit about what they do, we have developed the TARGET Statement 👇
"Celebrating James M. Robins Contributions to Epidemiology" explored Robins' impact, including his landmark 1986 paper. It concluded with his comments on progress still to come in #causalinference research.

"Celebrating James M. Robins Contributions to Epidemiology" explored Robins' impact, including his landmark 1986 paper. It concluded with his comments on progress still to come in #causalinference research.
➡️ Read here: link.springer.com/article/10.1...
#cancer #screening #colorectal

➡️ Read here: link.springer.com/article/10.1...
#cancer #screening #colorectal
CAUSALab is partnering w/ @cemfi.es for the course, Causal Inference for Health and Social Scientists.
📆 Aug 25-29, 2025
Taught by @miguelhernan.org, CEMFI course introduces 2 step causal framework for experimental & non-experimental data.
www.cemfi.es/programs/css...

CAUSALab is partnering w/ @cemfi.es for the course, Causal Inference for Health and Social Scientists.
📆 Aug 25-29, 2025
Taught by @miguelhernan.org, CEMFI course introduces 2 step causal framework for experimental & non-experimental data.
www.cemfi.es/programs/css...
privately-funded research in for-profit companies, watch this:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ar0z...
The topic is the "de-extinction of the dire wolf", but the message applies beyond it. (Think "AI".)

privately-funded research in for-profit companies, watch this:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ar0z...
The topic is the "de-extinction of the dire wolf", but the message applies beyond it. (Think "AI".)
A must if you are considering CAUSALab's "Advanced Confounding Adjustment" course for time-varying treatments in the Summer.
⭐ Fundamentals of Confounding Adjustment (FCA)
Learn confounding adjustment in time-fixed settings & build a foundation for advanced methods. Self-paced course w/ video lectures & hands-on exercises.
Ready to join our FCA classroom? Register now:
causalab.hsph.harvard.edu/courses/
A must if you are considering CAUSALab's "Advanced Confounding Adjustment" course for time-varying treatments in the Summer.
➡️ Go to event page to register: hsph.harvard.edu/epidemiology...

➡️ Go to event page to register: hsph.harvard.edu/epidemiology...
In a new paper, we explain why and when the #TargetTrial framework is helpful.
www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/...
Joint work with my colleagues @causalab.bsky.social
In a new paper, we explain why and when the #TargetTrial framework is helpful.
www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/...
Joint work with my colleagues @causalab.bsky.social
If you were taught to test for proportional hazards, talk to your teacher.
The proportional hazards assumption is implausible in most #randomized and #observational studies because the hazard ratios aren't expected to be constant during the follow-up. So "testing" is futile.
But there is more 👇
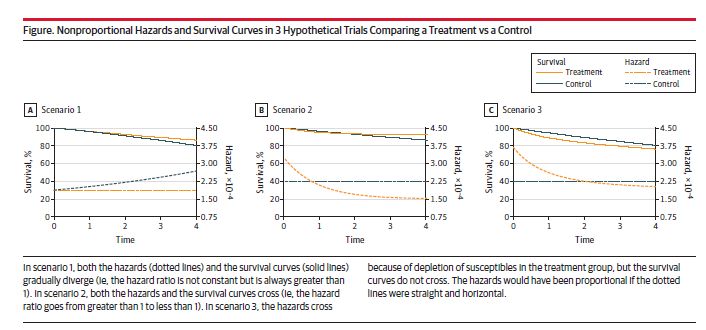
If you were taught to test for proportional hazards, talk to your teacher.
The proportional hazards assumption is implausible in most #randomized and #observational studies because the hazard ratios aren't expected to be constant during the follow-up. So "testing" is futile.
But there is more 👇
That "immortal time" is so frequent in survival analyses for #causalinference is fascinating.
Because "immortal time" doesn't exist in the data, *we* create it when misanalyzing the data.
Our new paper pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39494894/ summarizes why immortal time arises & how to prevent it.

That "immortal time" is so frequent in survival analyses for #causalinference is fascinating.
Because "immortal time" doesn't exist in the data, *we* create it when misanalyzing the data.
Our new paper pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39494894/ summarizes why immortal time arises & how to prevent it.
A revision of our book "Causal Inference: What If" is available at miguelhernan.org/whatifbook
Thanks to everyone who suggested improvements, reported typos, and proposed new citations and material.
Enjoy the #WhatIfBook plus code and data. Also, it's free.

A revision of our book "Causal Inference: What If" is available at miguelhernan.org/whatifbook
Thanks to everyone who suggested improvements, reported typos, and proposed new citations and material.
Enjoy the #WhatIfBook plus code and data. Also, it's free.
In Denmark 860 individuals were randomly allocated to either intervention or control. Individuals were unaware of their allocation. No intervention took place. Mortality was higher in the intervention group (p=0.003)

In Denmark 860 individuals were randomly allocated to either intervention or control. Individuals were unaware of their allocation. No intervention took place. Mortality was higher in the intervention group (p=0.003)
@ziobrando.bsky.social

@ziobrando.bsky.social
This month's topic - #causalinference & #suicideprevention.
Attend in-person: bit.ly/SRCsession6
Attend online: bit.ly/src_zoom

journals.lww.com/epidem/fullt...

journals.lww.com/epidem/fullt...
Roger has worked as a CAUSALab Senior Research Scientist @harvardchanschool.bsky.social for 23 years. He has been a valuable team member & made major contributions to #causalinference research.
Wishing Roger all the best in this new chapter! #publichealth

Roger has worked as a CAUSALab Senior Research Scientist @harvardchanschool.bsky.social for 23 years. He has been a valuable team member & made major contributions to #causalinference research.
Wishing Roger all the best in this new chapter! #publichealth
A fair and critical dose of reality that the wider health research sphere desparately needs to hear!
#EpiSky

A fair and critical dose of reality that the wider health research sphere desparately needs to hear!
#EpiSky
CAUSALab collaborator Yu-Han Chiu identified no increased risk for childbirth with major birth defects when compared w/ women who discontinued the drug.
CNN article: www.cnn.com/2024/06/17/h...

CAUSALab collaborator Yu-Han Chiu identified no increased risk for childbirth with major birth defects when compared w/ women who discontinued the drug.
CNN article: www.cnn.com/2024/06/17/h...
"Observational data (#RWD) can often be used to emulate a #TargetTrial, but we need more research to characterize questions that can only be answered by randomized trials."
Let's learn the limits of #RWE.

"Observational data (#RWD) can often be used to emulate a #TargetTrial, but we need more research to characterize questions that can only be answered by randomized trials."
Let's learn the limits of #RWE.
Imbens & Angrist in Econometrica
and
Baker & Lindeman in Statistics in Medicine?
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
A delightful historical overview of LATE is now available www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....

Imbens & Angrist in Econometrica
and
Baker & Lindeman in Statistics in Medicine?
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
A delightful historical overview of LATE is now available www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....


