
Here's my deep dive into the naming debate with citations from 15+ recent papers (link in thread)
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.16746
data: huggingface.co/datasets/mul...

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.16746
data: huggingface.co/datasets/mul...
Dataset for vision-language reasoning where the model *generates images during the CoT*. Example: for geometry problems, it's helpful to draw lines in image space.
182K CoT labels: math, visual search, robot planning, and more.
Only downside: cc-by-nc license :(

Dataset for vision-language reasoning where the model *generates images during the CoT*. Example: for geometry problems, it's helpful to draw lines in image space.
182K CoT labels: math, visual search, robot planning, and more.
Only downside: cc-by-nc license :(
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.14137
code: github.com/valeoai/Franca

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.14137
code: github.com/valeoai/Franca


Fully open vision encoder. Masks image, encodes patches, then trains student to match teacher's clusters. Key advance: Matryoshka clustering. Each slice of the embedding gets its own projection head and clustering objective. Fewer features == fewer clusters to match.

Fully open vision encoder. Masks image, encodes patches, then trains student to match teacher's clusters. Key advance: Matryoshka clustering. Each slice of the embedding gets its own projection head and clustering objective. Fewer features == fewer clusters to match.
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.098...
project: vru-accident.github.io

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.098...
project: vru-accident.github.io
New benchmark of 1K videos, 1K captions, and 6K MCQs from accidents involving VRUs. Example: "why did the accident happen?" "(B): pedestrian moves or stays on the road."
Current VLMs get ~50-65% accuracy, much worse than humans (95%).

New benchmark of 1K videos, 1K captions, and 6K MCQs from accidents involving VRUs. Example: "why did the accident happen?" "(B): pedestrian moves or stays on the road."
Current VLMs get ~50-65% accuracy, much worse than humans (95%).
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.090...

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.090...


AMD paper: they find attention heads often have stereotyped sparsity patterns (e.g. only attending within an image, not across). They generate sparse attention variants for each prompt. Theoretically saves ~35% FLOPs for 1-2% worse on benches.

AMD paper: they find attention heads often have stereotyped sparsity patterns (e.g. only attending within an image, not across). They generate sparse attention variants for each prompt. Theoretically saves ~35% FLOPs for 1-2% worse on benches.
Nvidia paper scaling RL to long videos. First trains with SFT on a synthetic long CoT dataset, then does GRPO with up to 512 video frames. Uses cached image embeddings + sequence parallelism, speeding up rollouts >2X.
Bonus: code is already up!

Nvidia paper scaling RL to long videos. First trains with SFT on a synthetic long CoT dataset, then does GRPO with up to 512 video frames. Uses cached image embeddings + sequence parallelism, speeding up rollouts >2X.
Bonus: code is already up!


GRPO is pretty standard, interesting that they just did math instead of math, grounding, other possible RLVR tasks. Qwen-2.5-Instruct 32B to judges the accuracy of the answer in addition to rule-based verification.

GRPO is pretty standard, interesting that they just did math instead of math, grounding, other possible RLVR tasks. Qwen-2.5-Instruct 32B to judges the accuracy of the answer in addition to rule-based verification.
InternViT-6B stitched with QwQ-32B. SFT warmup, GRPO on math, then a small SFT fine-tune at the end.
Good benches, actual ablations, and interesting discussion.
Details: 🧵

InternViT-6B stitched with QwQ-32B. SFT warmup, GRPO on math, then a small SFT fine-tune at the end.
Good benches, actual ablations, and interesting discussion.
Details: 🧵
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.05920
code: github.com/EvolvingLMMs...

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.05920
code: github.com/EvolvingLMMs...
Results: +18 points better on V* compared to Qwen2.5-VL, and +5 points better than GRPO alone.

Results: +18 points better on V* compared to Qwen2.5-VL, and +5 points better than GRPO alone.
Data: training subset of MME-RealWorld. Evaluate on V*.

Data: training subset of MME-RealWorld. Evaluate on V*.
They use a SFT warm-start, as the VLMs struggled to output good grounding coordinates. They constructed two-turn samples for this.
They use a SFT warm-start, as the VLMs struggled to output good grounding coordinates. They constructed two-turn samples for this.
I've been waiting for a paper like this! Trains the LLM to iteratively crop regions of interest to answer a question, and the only reward is the final answer.
Details in thread 👇

I've been waiting for a paper like this! Trains the LLM to iteratively crop regions of interest to answer a question, and the only reward is the final answer.
Details in thread 👇
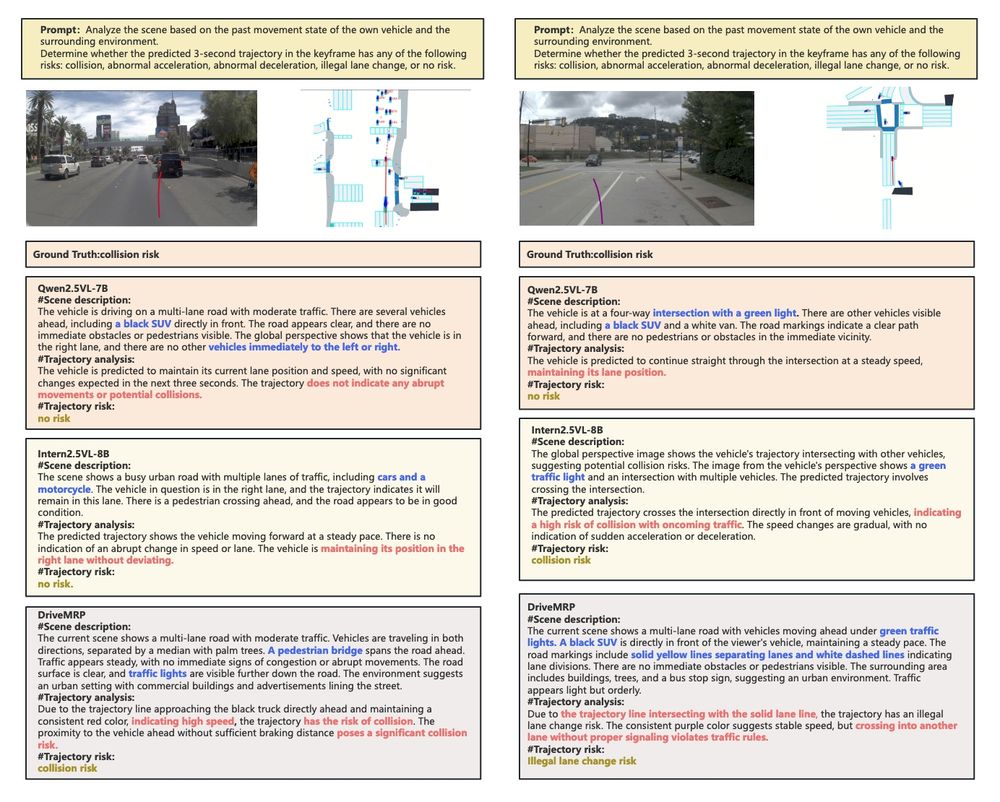
arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.02948
code: github.com/hzy138/Drive...

arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2507.02948
code: github.com/hzy138/Drive...