
rdcu.be/eEDur

rdcu.be/eEDur
E pensar que, uma década atrás, considerava-se que as alterações no Ártico não teriam muita influência.
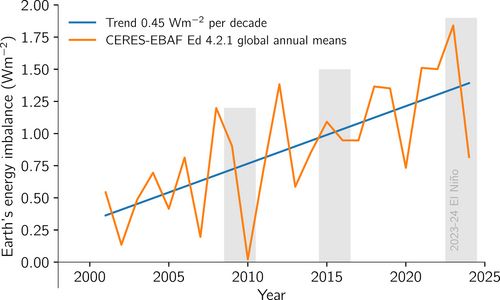
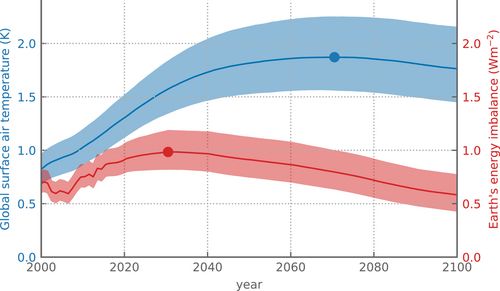
helping push CO₂ up nearly 100 ppm.
Later, peatlands soaked some of it back in.
Today, permafrost is thawing again, but there’s no new land to save us.
🧪 #SciComm
buff.ly/qDwXblR

E pensar que, uma década atrás, considerava-se que as alterações no Ártico não teriam muita influência.
A new global study shows human activity has massively increased toxic mercury in rivers since the Industrial Revolution – a key source of contamination in fish.
🔗 www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
#SciComm #Mercury #WaterPollution 🧪

doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/addb62
doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/addb62
Sim, o que estava ruim deve piorar bastante, demandando esforços muito maiores de conservação.
url:https://academic.oup.com/bioscience/article/doi/10.1093/biosci/biaf059/8127685
Sim, o que estava ruim deve piorar bastante, demandando esforços muito maiores de conservação.
url:https://academic.oup.com/bioscience/article/doi/10.1093/biosci/biaf059/8127685
A @nature.com study shows plants inhale airborne microplastics via stomata – bypassing roots.
Particles build up in leaves and food crops, raising concerns for ecosystems and human health.
🔗 doi.org/10.1038/s415...
#SciComm #Microplastics

📄 buff.ly/vMTxxvE
#climatechange #coralreefs
agencia.fapesp.br/nova-enzima-...

Como andará o humor das deusas Moirai?
Como andará o humor das deusas Moirai?

