Constantin Anoyatis
@canopele.bsky.social
Posdoctoral researcher, candidate for weirdest E. coli mutant, at the Hugonnet Lab in Paris. From autolysin roles to (p)ppGpp-mediated resistance🧫
Pinned

Role of endopeptidases in lateral cell wall expansion in Escherichia coli
Peptidoglycan, the major constituent of bacterial cell walls, is a giant macromolecule made of glycan strands cross-linked by short peptides, which pr…
www.sciencedirect.com
Proud of our new study out in @cp-cellreports.bsky.social!
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
The stringent response does not influence ribosome pausing in Bacillus subtilis
@narjournal.bsky.social from Leendert Hamoen
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
@narjournal.bsky.social from Leendert Hamoen
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...

The stringent response does not influence ribosome pausing in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract. The stringent response represses translation and is activated when cells enter the stationary phase and intracellular amino acid levels drop. Bac
academic.oup.com
November 1, 2025 at 11:42 AM
The stringent response does not influence ribosome pausing in Bacillus subtilis
@narjournal.bsky.social from Leendert Hamoen
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
@narjournal.bsky.social from Leendert Hamoen
academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
🦠🔬🤖🧑💻 #mAIcrobe is out! With @pinholab.bsky.social's lab, we launched an open-source framework for high-throughput bacterial image analysis. By rockstars A. Brito & B. Saraiva et al, making #DeepLearning for phenotyping accessible! Easy to use, plus model training
📜 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
📜 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...



October 22, 2025 at 11:10 AM
🦠🔬🤖🧑💻 #mAIcrobe is out! With @pinholab.bsky.social's lab, we launched an open-source framework for high-throughput bacterial image analysis. By rockstars A. Brito & B. Saraiva et al, making #DeepLearning for phenotyping accessible! Easy to use, plus model training
📜 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
📜 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
A global view of morphogenetic peptidoglycan synthases across the domain Bacteria Open Access
@femsjournals.bsky.social microLife by Francisco García-del Portillo et al
academic.oup.com/microlife/ad...
@femsjournals.bsky.social microLife by Francisco García-del Portillo et al
academic.oup.com/microlife/ad...

A global view of morphogenetic peptidoglycan synthases across the domain Bacteria
Abstract. Bacteria define their heritable cell shape using membrane integral glycosyltransferases (GTases) of the shape, elongation, division and sporulati
academic.oup.com
September 27, 2025 at 6:04 PM
A global view of morphogenetic peptidoglycan synthases across the domain Bacteria Open Access
@femsjournals.bsky.social microLife by Francisco García-del Portillo et al
academic.oup.com/microlife/ad...
@femsjournals.bsky.social microLife by Francisco García-del Portillo et al
academic.oup.com/microlife/ad...
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
This work is finally published! 🥳🧬
Plasmids are associated with very variable fitness costs in their different bacterial hosts. But, what is the contribution of each of the plasmid-genes in these host-specific effects? Study led by
@jorgesastred.bsky.social, @sanmillan.bsky.social and myself! 1/14
Plasmids are associated with very variable fitness costs in their different bacterial hosts. But, what is the contribution of each of the plasmid-genes in these host-specific effects? Study led by
@jorgesastred.bsky.social, @sanmillan.bsky.social and myself! 1/14
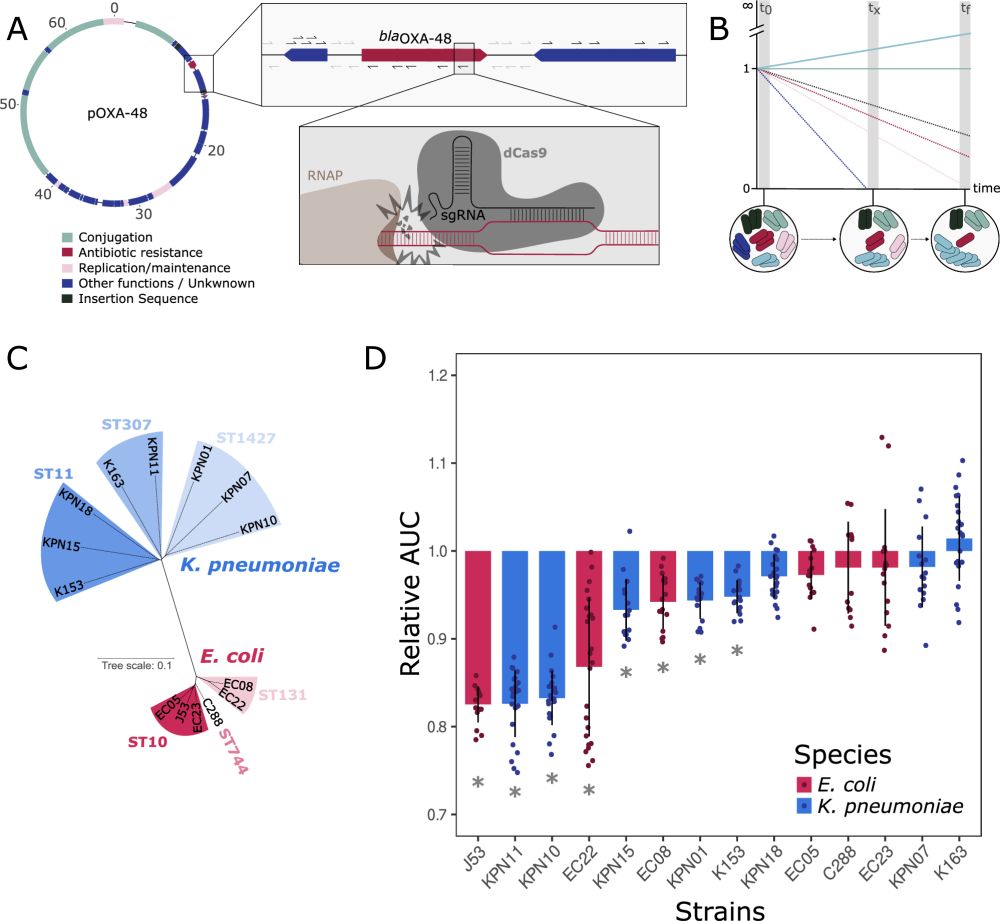
Dissecting pOXA-48 fitness effects in clinical Enterobacterales using plasmid-wide CRISPRi screens
Nature Communications - This study investigates the effects of the carbapenem resistance plasmid pOXA-48 in clinical enterobacteria. Using CRISPRi screens, the authors revealed that the...
rdcu.be
August 20, 2025 at 1:25 PM
This work is finally published! 🥳🧬
Plasmids are associated with very variable fitness costs in their different bacterial hosts. But, what is the contribution of each of the plasmid-genes in these host-specific effects? Study led by
@jorgesastred.bsky.social, @sanmillan.bsky.social and myself! 1/14
Plasmids are associated with very variable fitness costs in their different bacterial hosts. But, what is the contribution of each of the plasmid-genes in these host-specific effects? Study led by
@jorgesastred.bsky.social, @sanmillan.bsky.social and myself! 1/14
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
Our paper on the Bacteroidota BAM complex is out in @natmicrobiol.nature.com! With @madejmar.bsky.social
We found that BAM in Bacteroides and Porphyromonas gingivalis has a distinct architecture from BAM in Proteobacteria.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
We found that BAM in Bacteroides and Porphyromonas gingivalis has a distinct architecture from BAM in Proteobacteria.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...

Structure of a distinct β-barrel assembly machinery complex in the Bacteroidota - Nature Microbiology
Structural and functional characterization of the β-barrel assembly machinery complex in Bacteroidota reveals a distinct, seven-component complex with a large extracellular domain that may enable β-barrel–surface lipoprotein complex assembly.
doi.org
October 2, 2025 at 6:20 AM
Our paper on the Bacteroidota BAM complex is out in @natmicrobiol.nature.com! With @madejmar.bsky.social
We found that BAM in Bacteroides and Porphyromonas gingivalis has a distinct architecture from BAM in Proteobacteria.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
We found that BAM in Bacteroides and Porphyromonas gingivalis has a distinct architecture from BAM in Proteobacteria.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
Proud of our new study out in @cp-cellreports.bsky.social!
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky

Role of endopeptidases in lateral cell wall expansion in Escherichia coli
Peptidoglycan, the major constituent of bacterial cell walls, is a giant macromolecule made of glycan strands cross-linked by short peptides, which pr…
www.sciencedirect.com
October 8, 2025 at 2:54 PM
Proud of our new study out in @cp-cellreports.bsky.social!
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky
Using E. coli lacking all 8 endopeptidases, we provide direct evidence that peptidoglycan expansion during elongation requires ED-mediated insertion of one glycan strand at a time. This can be performed by MepS, MepM, MepH and PBP7 #microsky
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation | mBio
Bacteria often experience nutrient limitation and, in response, attenuate energetically costly metabolic processes like protein synthesis. At the same time, however, they stimulate the expression of a subset of proteins that facilitate survival under ...
journals.asm.org
August 19, 2025 at 1:29 PM
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
Congrats @herailquentin.bsky.social
Thrilled to announce our new paper with M. Ethève-Quelquejeu's lab @upcite.bsky.social published @chemistryeurope.bsky.social! We report on the synthesis, and testing by HRMS, of new β-lactam prodrugs, a proof of concept for designing drugs targetting specifically β-lactamase-producing pathogens.
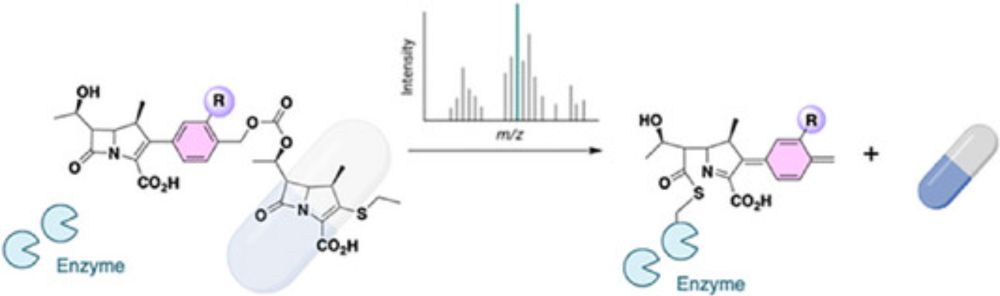
Optimization of Prodrug Activation by Enzymatic Cleavage of the β‐lactam Ring of Carbapenems
We report synthetic routes that yield prodrugs consisting of two carbapenems connected by benzyl carbonate linkers. A mass spectrometry assay was elaborated to monitor, in a single kinetic experiment...
doi.org
July 29, 2025 at 1:21 PM
Congrats @herailquentin.bsky.social
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
Excited to present our new study on the mechanism of lateral peptidoglycan expansion in B. subtilis. We combined microscopy visualisation with clickable D-Ala-D-Ala analogues and stable-isotope peptidoglycan labelling to describe an inside-to-outside expansion model @natcomms.nature.com.
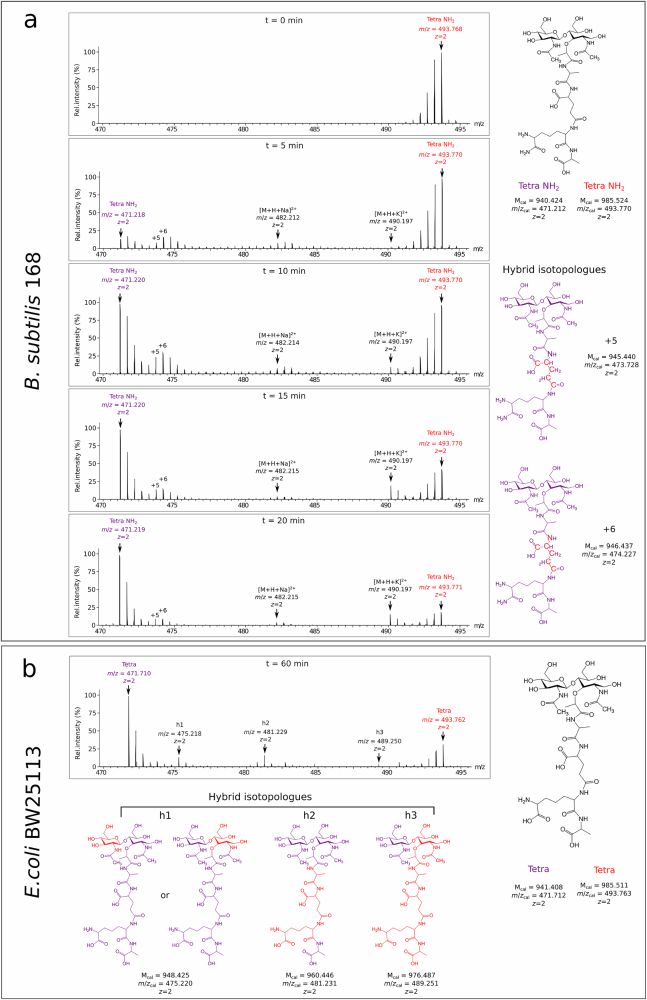
Mechanism of lateral cell-wall expansion at a constant diameter in Bacillus subtilis
Nature Communications - In Escherichia coli, lateral cell-wall expansion during growth occurs by crosslinking of new glycan chains to the existing peptidoglycan network. Here, Liang et al. show a...
rdcu.be
July 25, 2025 at 10:40 AM
Excited to present our new study on the mechanism of lateral peptidoglycan expansion in B. subtilis. We combined microscopy visualisation with clickable D-Ala-D-Ala analogues and stable-isotope peptidoglycan labelling to describe an inside-to-outside expansion model @natcomms.nature.com.
Reposted by Constantin Anoyatis
Very excited to share our work on (p)ppGpp-mediated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics published in Nature Microbiology!! A great outcome for a project we started working on 5 years ago. A big thank you to all authors that participated in this study!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
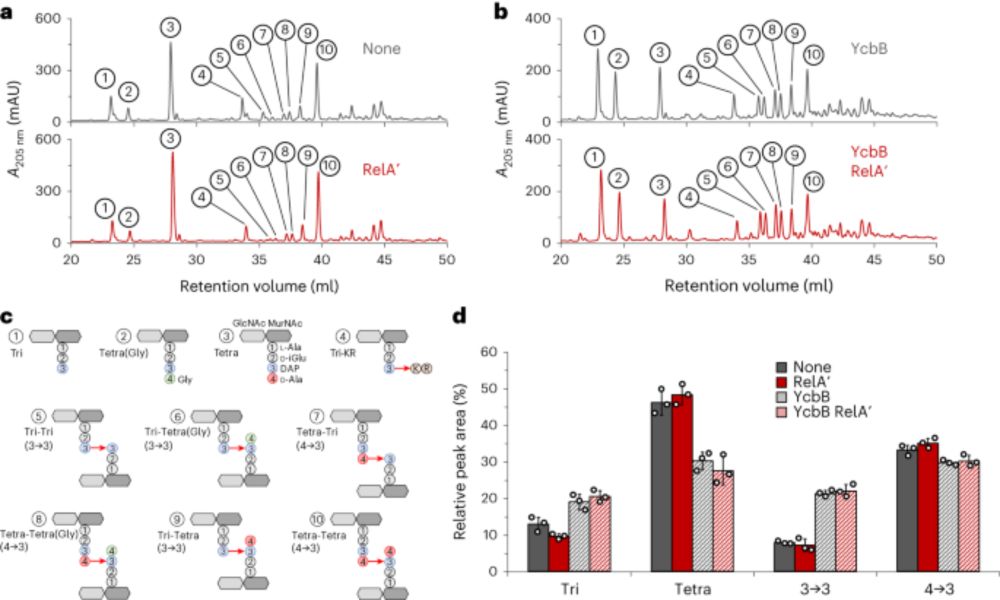
(p)ppGpp modifies RNAP function to confer β-lactam resistance in a peptidoglycan-independent manner - Nature Microbiology
The bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp induces β-lactam resistance through modification of RNA polymerase and ribosome function rather than regulation of peptidoglycan metabolism in Escherichia coli.
www.nature.com
January 21, 2025 at 3:05 PM
Very excited to share our work on (p)ppGpp-mediated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics published in Nature Microbiology!! A great outcome for a project we started working on 5 years ago. A big thank you to all authors that participated in this study!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

