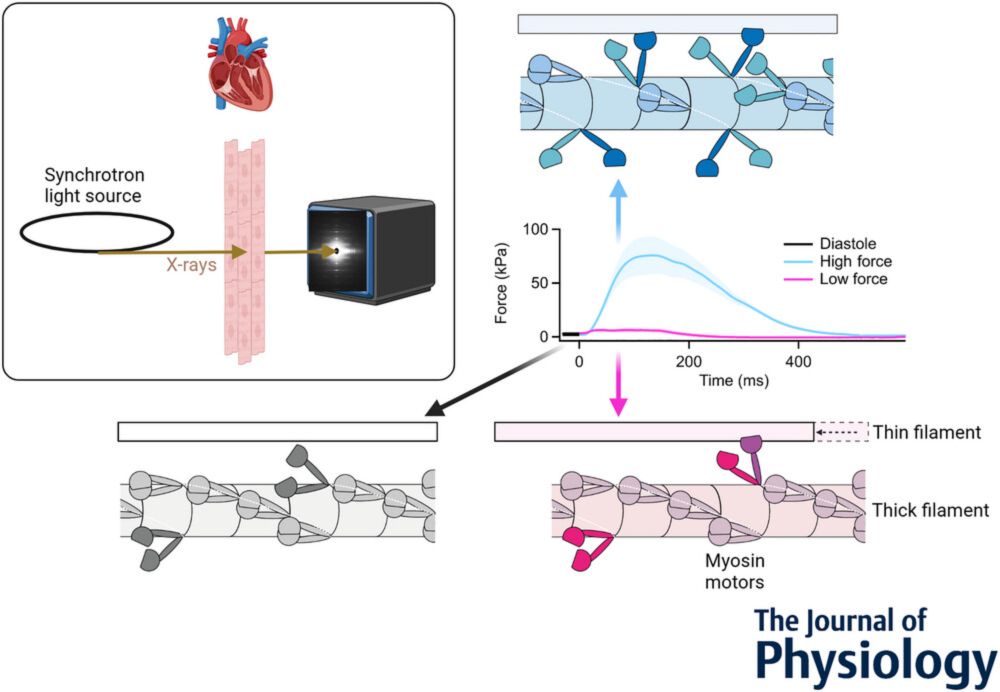
@pnas.org where we use time-resolved X-ray diffraction to elucidate the regulatory roles of the thick and thin filaments during muscle relaxation #myoblue
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

www.emc2025amsterdam.com
The ECA have a number of travel awards available for ECR's attending. We will be hosting an online meeting on 14/05/25 at 1600 CET to provide further information about the travel awards, so come along for more info

www.emc2025amsterdam.com
The ECA have a number of travel awards available for ECR's attending. We will be hosting an online meeting on 14/05/25 at 1600 CET to provide further information about the travel awards, so come along for more info

www.emc2025amsterdam.com
The ECA have a number of travel awards available for ECR's attending. We will be hosting an online meeting on 14/05/25 at 1600 CET to provide further information about the travel awards, so come along for more info
We looked at the trajectory of age-related serial sarcomere loss across young (8 mo), middle-aged (20 mo), old (32 mo), and very old rats (36 mo) in 5 different muscles. A simple study but it provided a lot of cool insight!
SSN loss contributed to the loss of muscle mass. Increasing SSN is a target for improving muscle performance in old age. @hinksave.bsky.social
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We looked at the trajectory of age-related serial sarcomere loss across young (8 mo), middle-aged (20 mo), old (32 mo), and very old rats (36 mo) in 5 different muscles. A simple study but it provided a lot of cool insight!
www.esrf.fr/home/news/ge...
#myoblue
www.esrf.fr/home/news/ge...
#myoblue
@pnas.org where we use time-resolved X-ray diffraction to elucidate the regulatory roles of the thick and thin filaments during muscle relaxation #myoblue
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

@pnas.org where we use time-resolved X-ray diffraction to elucidate the regulatory roles of the thick and thin filaments during muscle relaxation #myoblue
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
duke.zoom.us/j/91574693682 (Meeting ID: 915 7469 3682)
duke.zoom.us/j/91574693682 (Meeting ID: 915 7469 3682)

www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...