
Yan Boulanger
@trailgeek.bsky.social
Research scientist in Forest Ecology🌲| Working on climate change stuff and wildfires🔥| Like trail running and singing in my car
Same here... eh boboy

April 1, 2025 at 1:48 AM
Same here... eh boboy
With less sea ice in this area over the last few years, many more baby seals are stranded on the shore:
(In French)
ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/214...
(In French)
ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/214...
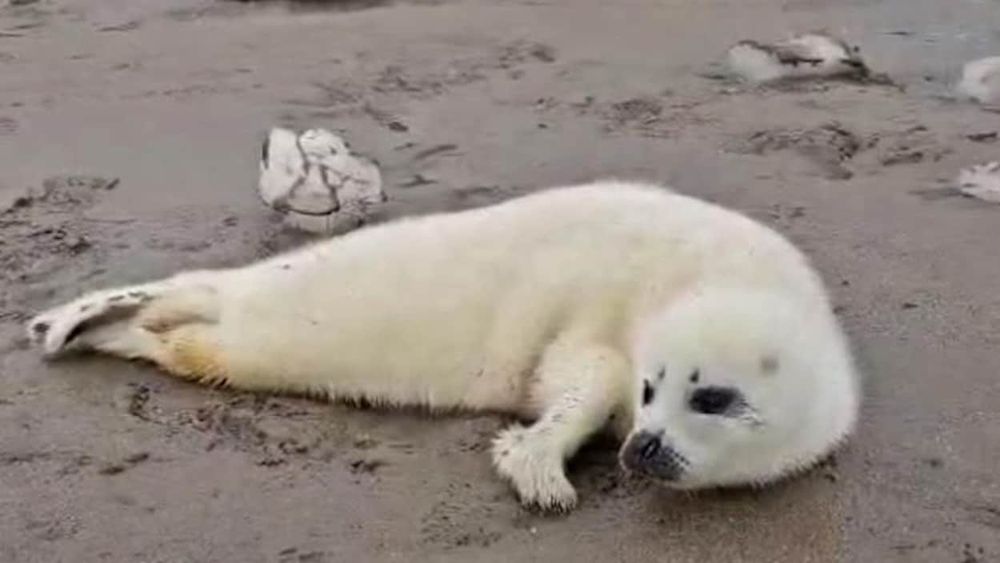

Des gestes illégaux à l’endroit de blanchons
Un nombre anormalement élevé de blanchons est observé depuis une semaine sur les plages de la Gaspésie et des Îles-de-la-Madeleine.
ici.radio-canada.ca
March 22, 2025 at 11:00 PM
With less sea ice in this area over the last few years, many more baby seals are stranded on the shore:
(In French)
ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/214...
(In French)
ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/214...
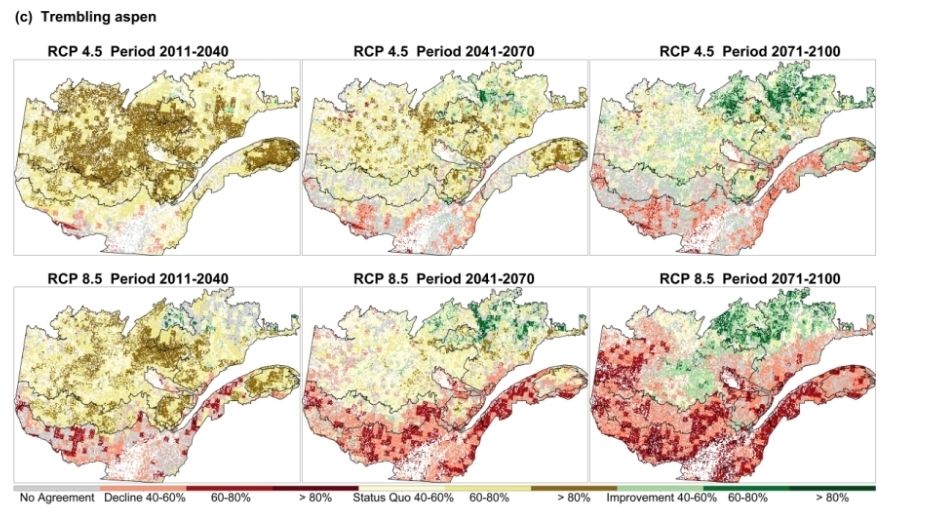
Don't forget that this is considering a species distribution model (SDM) When using a multimodel approach, which includes both SDM and process-based models, iy appears that aspen might take advantage of increased climate-induced disturbances. Up to a certain point...
February 25, 2025 at 1:50 AM
Don't forget that this is considering a species distribution model (SDM) When using a multimodel approach, which includes both SDM and process-based models, iy appears that aspen might take advantage of increased climate-induced disturbances. Up to a certain point...
5/ 🔗 Want to dive deeper? Read our full study here:
📖 journals.plos.org/climate/arti...
📖 journals.plos.org/climate/arti...

Recent climate change strongly impacted the population dynamic of a North American insect pest species
Climate change is redefining the dynamics of forest ecosystems globally, particularly through its impact on forest pest populations such as the spruce budworm (SBW, Choristoneura fumiferana [Clem.]), ...
journals.plos.org
February 15, 2025 at 2:36 PM
5/ 🔗 Want to dive deeper? Read our full study here:
📖 journals.plos.org/climate/arti...
📖 journals.plos.org/climate/arti...
4/ 🛠️ Why does this matter?
➡️ Changing pest distributions impact forest health & management
➡️ Increased defoliation risks in new areas
➡️ Need for proactive strategies to reduce vulnerability
➡️ Changing pest distributions impact forest health & management
➡️ Increased defoliation risks in new areas
➡️ Need for proactive strategies to reduce vulnerability
February 15, 2025 at 2:36 PM
4/ 🛠️ Why does this matter?
➡️ Changing pest distributions impact forest health & management
➡️ Increased defoliation risks in new areas
➡️ Need for proactive strategies to reduce vulnerability
➡️ Changing pest distributions impact forest health & management
➡️ Increased defoliation risks in new areas
➡️ Need for proactive strategies to reduce vulnerability
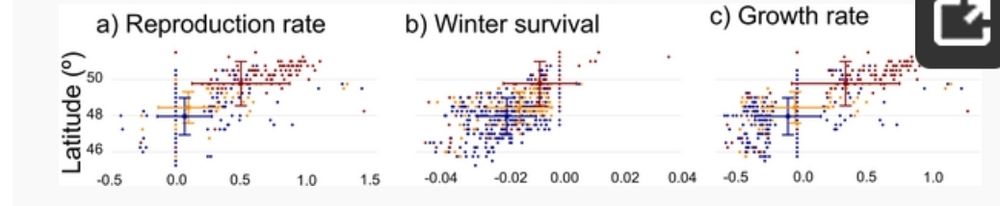
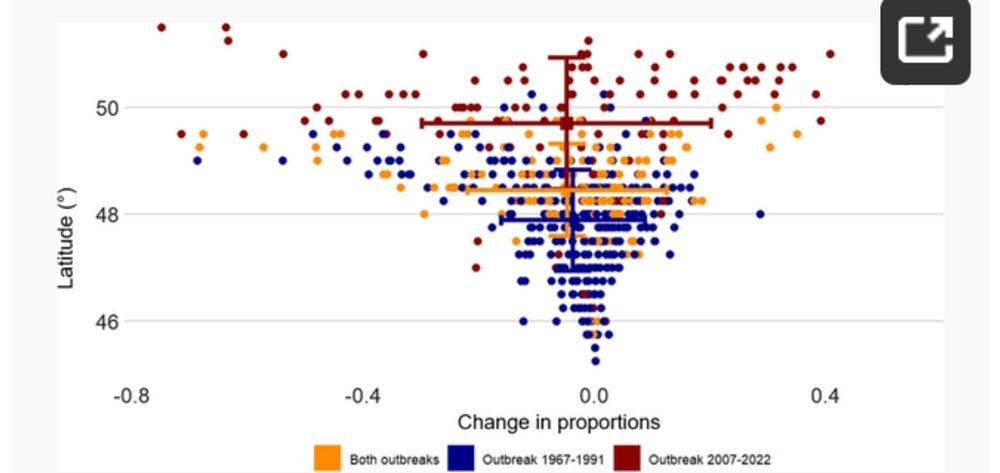
3/ 🌎 Most importantly, climate change is a bigger driver of SBW dynamics than landscape changes!
This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
February 15, 2025 at 2:36 PM
3/ 🌎 Most importantly, climate change is a bigger driver of SBW dynamics than landscape changes!
This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
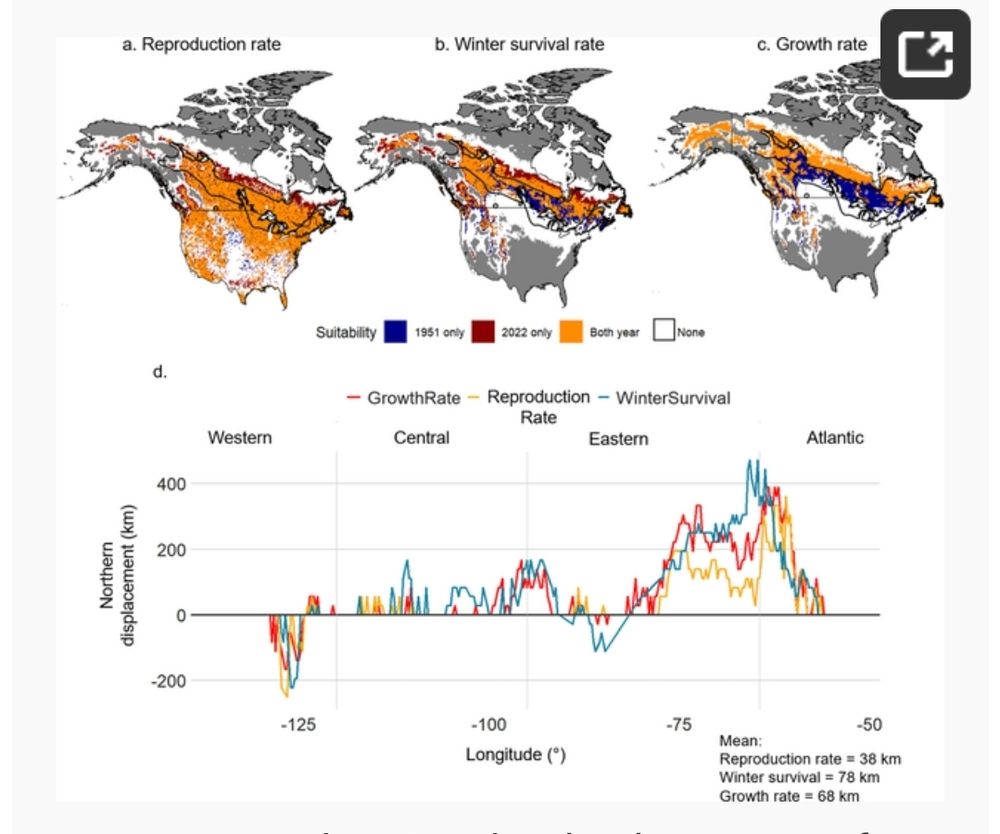
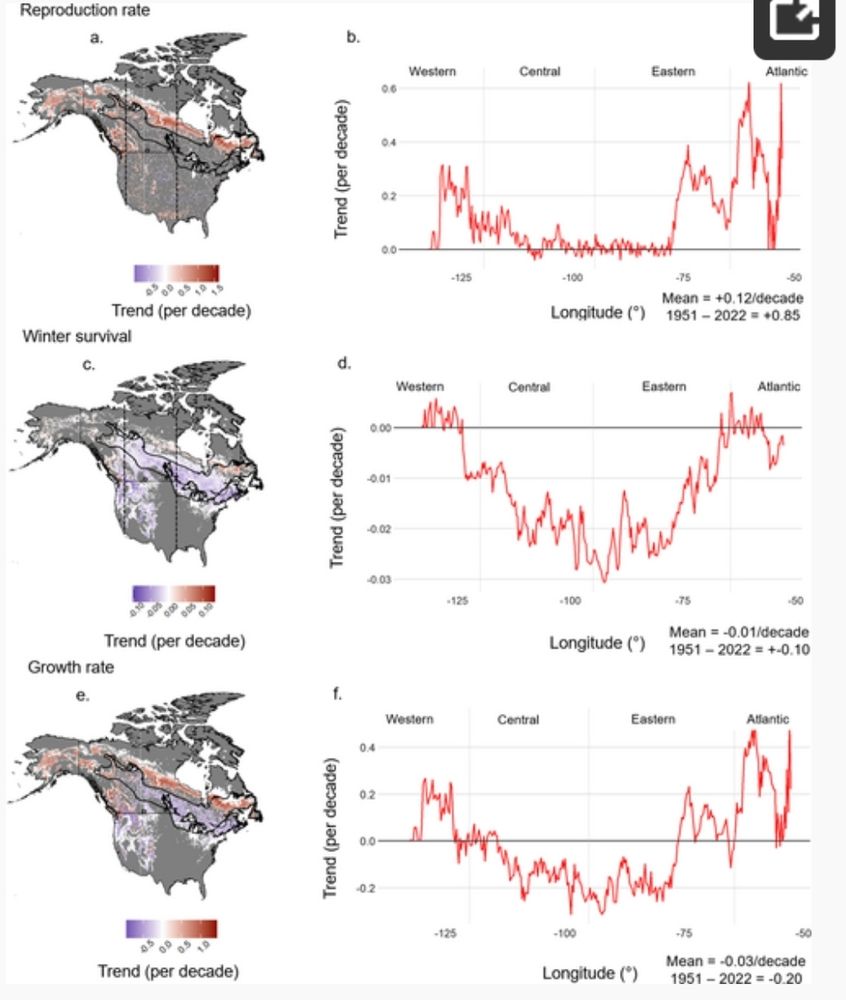
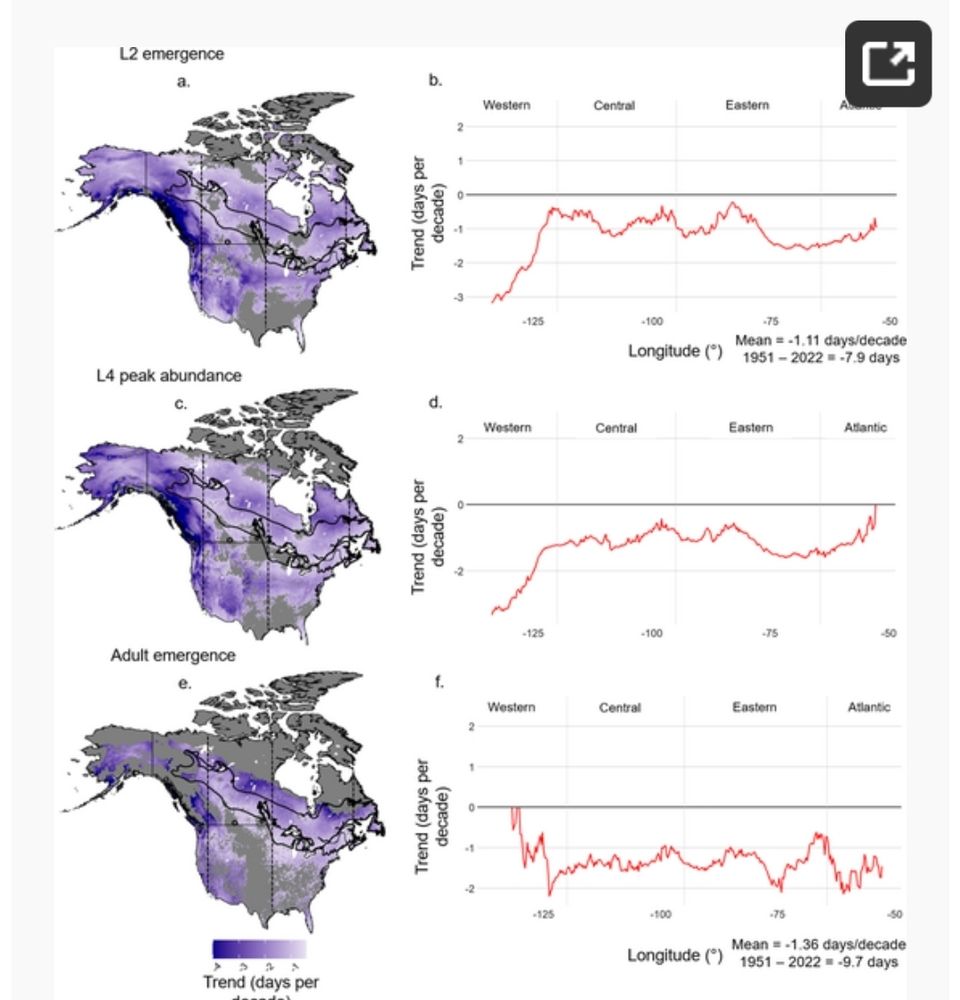
2/ 📈 Key findings (1950–2022):
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures
February 15, 2025 at 2:35 PM
2/ 📈 Key findings (1950–2022):
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures


