
shawnferguson.bsky.social
@shawnferguson.bsky.social
Cell Biologist and Neuroscientist at Yale University. Outdoor explorer.
We are also interested in links to Parkinson’s disease based on recent studies that place JIP4 downstream of LRRK2 gain-of-function mutations, a major genetic cause of autosomal-dominant inherited Parkinson's disease. JIP4-mediated cystine release may therefore be relevant for Parkinson's disease.
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
We are also interested in links to Parkinson’s disease based on recent studies that place JIP4 downstream of LRRK2 gain-of-function mutations, a major genetic cause of autosomal-dominant inherited Parkinson's disease. JIP4-mediated cystine release may therefore be relevant for Parkinson's disease.
With this new knowledge, we wonder if cysteamine, a therapy for cystinosis, would also help people with recently discovered loss of function mutations in JIP4?
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
With this new knowledge, we wonder if cysteamine, a therapy for cystinosis, would also help people with recently discovered loss of function mutations in JIP4?
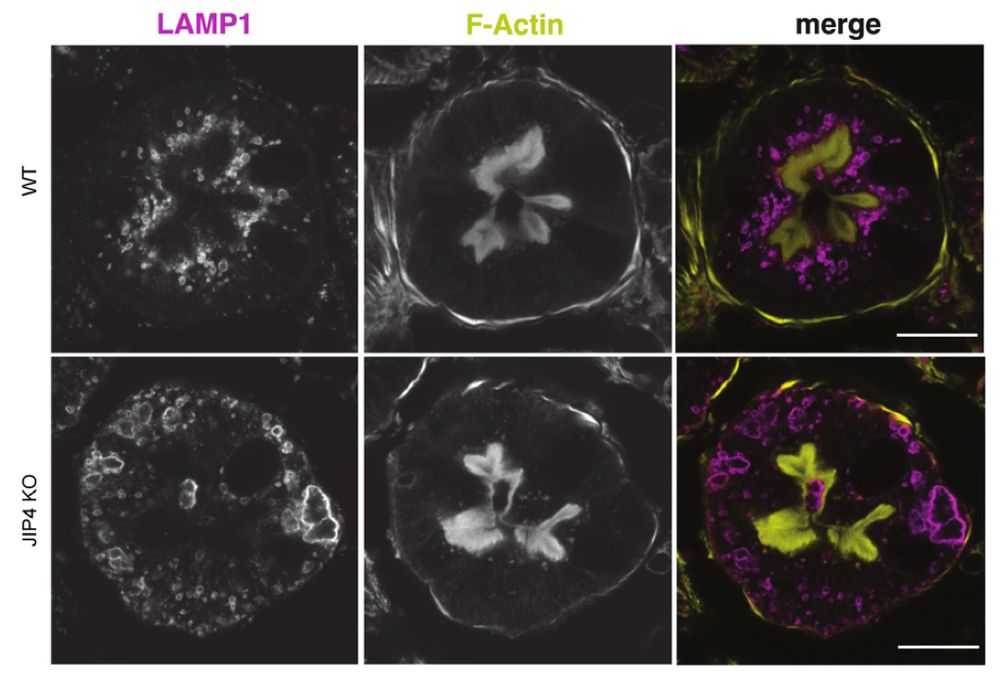
Just like in cystinosis, proximal tubule lysosomes are particularly sensitive to loss of JIP4! They lose their apical enrichment and exhibit a major storage defect!
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
Just like in cystinosis, proximal tubule lysosomes are particularly sensitive to loss of JIP4! They lose their apical enrichment and exhibit a major storage defect!
We demonstrate, in both cultured human cells and a new JIP4 knockout mouse model, that loss of JIP4 phenocopies key features of cystinosis, the well-characterized lysosome storage disease caused by CTNS loss-of-function mutations.
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
We demonstrate, in both cultured human cells and a new JIP4 knockout mouse model, that loss of JIP4 phenocopies key features of cystinosis, the well-characterized lysosome storage disease caused by CTNS loss-of-function mutations.
Layla also we define the basis for a new lysosome storage disease arising from JIP4 loss-of-function mutations as well as a new category of lysosome storage disease arising from disruption of the machinery that regulates degradation of a nutrient transporter.
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
Layla also we define the basis for a new lysosome storage disease arising from JIP4 loss-of-function mutations as well as a new category of lysosome storage disease arising from disruption of the machinery that regulates degradation of a nutrient transporter.
Our work from cultured human cells and a newly developed knockout mouse model demonstrates that the JIP4 scaffold protein suppresses ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cystinosin (CTNS), the transporter responsible for cystine efflux from lysosomes.
June 9, 2025 at 1:35 PM
Our work from cultured human cells and a newly developed knockout mouse model demonstrates that the JIP4 scaffold protein suppresses ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cystinosin (CTNS), the transporter responsible for cystine efflux from lysosomes.
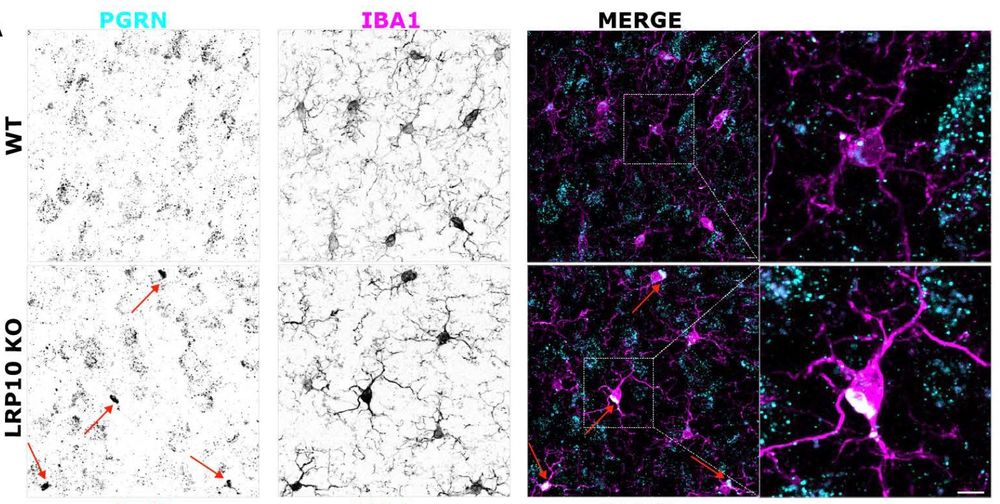
Progranulin accumulates in the Golgi of microglia in the motor cortex of LRP10 KO mice
May 3, 2025 at 6:23 PM
Progranulin accumulates in the Golgi of microglia in the motor cortex of LRP10 KO mice
This research was supported by @pfresearchteam.bsky.social , @asapresearch.parkinsonsroadmap.org and The Bluefield Project to Cure FTD.
May 3, 2025 at 5:08 PM
This research was supported by @pfresearchteam.bsky.social , @asapresearch.parkinsonsroadmap.org and The Bluefield Project to Cure FTD.
These discoveries are a foundation for future investigations of how this newly defined relationship between progranulin (GRN) and LRP10 affects the neurodegenerative diseases linked to these genes that include frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
May 3, 2025 at 5:02 PM
These discoveries are a foundation for future investigations of how this newly defined relationship between progranulin (GRN) and LRP10 affects the neurodegenerative diseases linked to these genes that include frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.

