https://www.rosettainstitute.org/
med.stanford.edu/news/all-new...

med.stanford.edu/news/all-new...
tinyurl.com/yx5wp3x8
tinyurl.com/mvfs75du

tinyurl.com/yx5wp3x8
tinyurl.com/mvfs75du
www.scientificamerican.com/article/myst...

www.scientificamerican.com/article/myst...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/content/arti...

www.science.org/content/arti...
www.rosettainstitute.org/biomedical-s...

www.rosettainstitute.org/biomedical-s...
www.hhmi.org/beautifulbio...

www.hhmi.org/beautifulbio...
www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemi...

www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemi...
www.rosettainstitute.org/biomedical-s...

www.rosettainstitute.org/biomedical-s...
open.spotify.com/show/5L7kmKP...

open.spotify.com/show/5L7kmKP...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
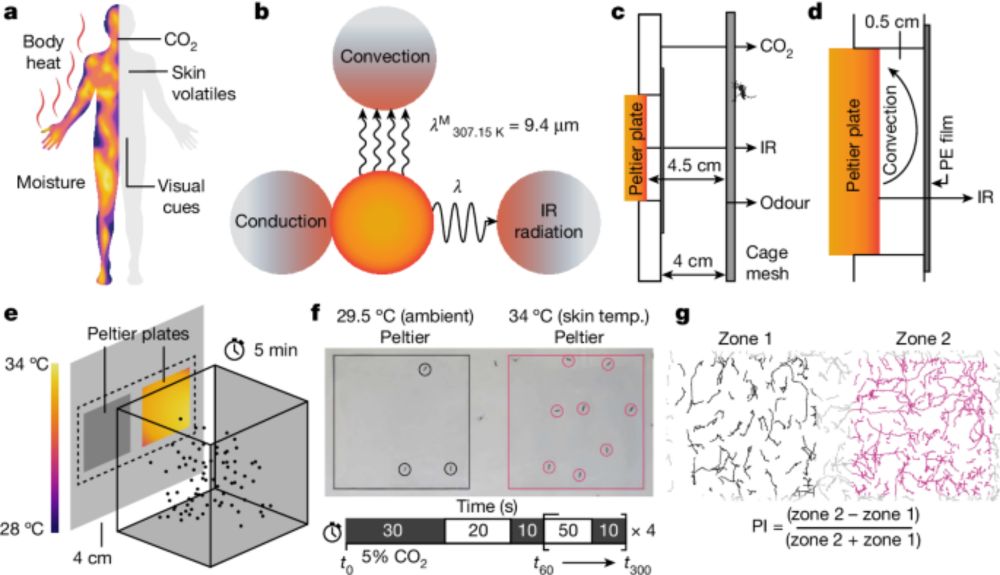
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
news.yale.edu/2024/01/22/r...
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

news.yale.edu/2024/01/22/r...
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.washingtonpost.com/health/2023/...
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

www.washingtonpost.com/health/2023/...
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
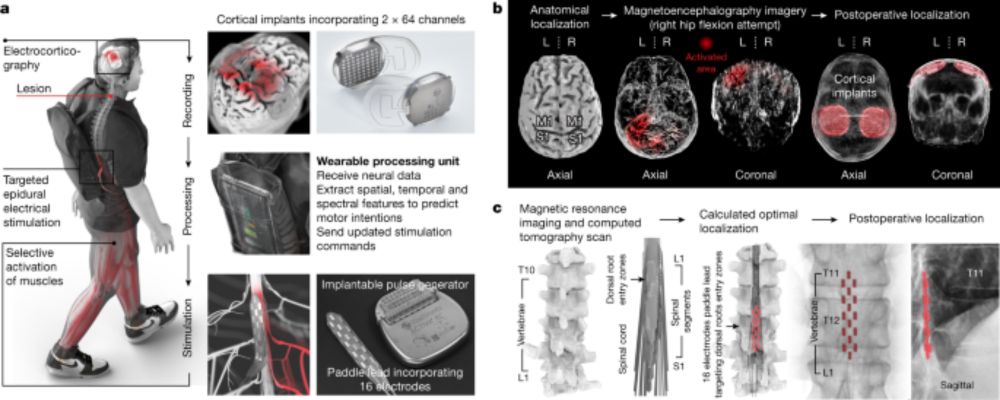
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
nature.com/articles/d41...

nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...

