
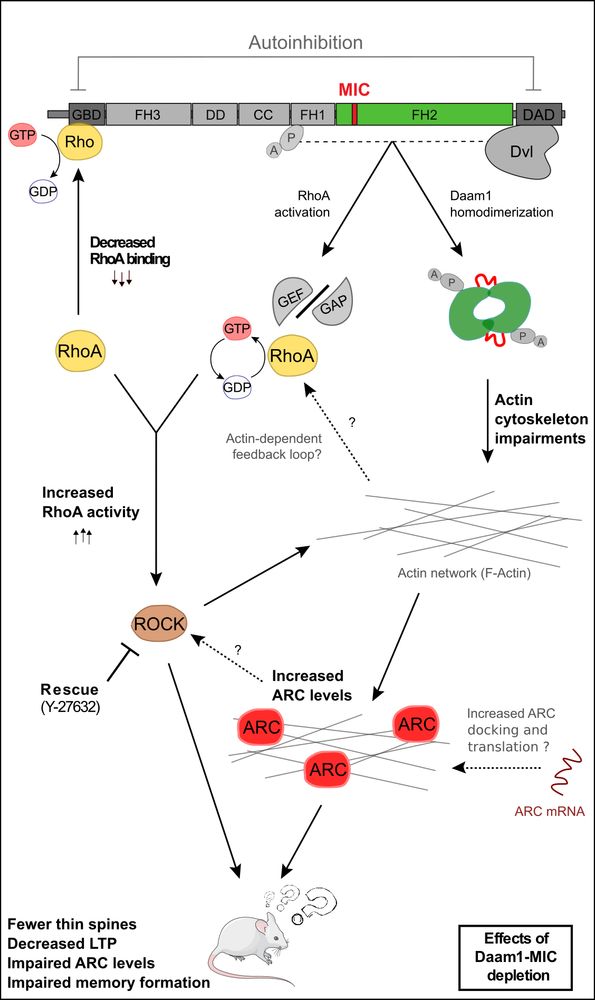
Excitingly, treatment with a ROCK inhibitor partially rescued observed phenotypes, including learning deficits!

Excitingly, treatment with a ROCK inhibitor partially rescued observed phenotypes, including learning deficits!
One of the leads guided us to increased RHOA/ROCK signaling in KO neurons! RhoA is a direct interactor of Daam1, whose activity is commonly associated with the number of “learning spines”.

One of the leads guided us to increased RHOA/ROCK signaling in KO neurons! RhoA is a direct interactor of Daam1, whose activity is commonly associated with the number of “learning spines”.
Moreover, dendritic spine analysis by @eloisaherrera.bsky.social revealed defects mainly in postsynaptic regions and a significant decrease in thin "learning spines."

Moreover, dendritic spine analysis by @eloisaherrera.bsky.social revealed defects mainly in postsynaptic regions and a significant decrease in thin "learning spines."
We performed multiple assays to evaluate animal behavior. Strikingly, they showed clear learning impairments after microexon removal. What are the cellular and molecular bases for this?

We performed multiple assays to evaluate animal behavior. Strikingly, they showed clear learning impairments after microexon removal. What are the cellular and molecular bases for this?
We KO the microexon in mESCs using CRISPR/Cas9, differentiated them into neurons in vitro, and examined changes in synaptic functioning. Microexon removal increased Ca2+ flux, suggesting enhanced neuronal firing.
@gercrcat.bsky.social
@vhir.bsky.social

We KO the microexon in mESCs using CRISPR/Cas9, differentiated them into neurons in vitro, and examined changes in synaptic functioning. Microexon removal increased Ca2+ flux, suggesting enhanced neuronal firing.
@gercrcat.bsky.social
@vhir.bsky.social

Bioinformatic analysis identified a neural-specific and evolutionarily conserved microexon in DAAM1 (DAAM1-MIC) that modifies its core enzymatic unit without major structural changes.

Bioinformatic analysis identified a neural-specific and evolutionarily conserved microexon in DAAM1 (DAAM1-MIC) that modifies its core enzymatic unit without major structural changes.


