Pablo Naval Baudin
@pnavalbaudin.bsky.social
— neuroradiologist @ hBellvitge idi — MultipleSclerosis BrainTumors QuantitativeImaging. Tutor de residentes
October 4, 2025 at 7:00 AM
Proud to share this open-access work with colleagues #CaixaResearch #CaixaImpulse #laCaixaFoundation #MSResearch #Radiology #Neuroimaging
📖 Full text: insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10....
📖 Full text: insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10....

3D T1 turbo spin echo improves detection of gadolinium-enhancing multiple-sclerosis lesions - Insights into Imaging
Objectives To compare the performance of 3D T1 turbo spin echo (3DT1TSE) and 3D T1 turbo field echo (3DT1TFE) MRI in detecting gadolinium-enhancing lesions in multiple sclerosis (MS). Materials and methods We retrospectively analyzed 255 3-T MRIs from MS patients, each including post-contrast 3DT1TSE and 3DT1TFE sequences. Two blinded readers independently assessed enhancing lesions per sequence. A consensus review, incorporating longitudinal imaging and additional sequences, served as the reference standard. Results The consensus identified 70 enhancing lesions in 31 patients. All 70 were visible on 3DT1TSE, while 64 (91%) were detectable on 3DT1TFE. Reader sensitivity was higher for 3DT1TSE (84% and 90%) than 3DT1TFE (45% and 40%) (p < 0.01). Inter-reader agreement was excellent for 3DT1TSE (ICC = 0.90) and moderate for 3DT1TFE (intraclass correlation coefficient = 0.69). Although false positives were more common with 3DT1TSE, they were readily excluded during consensus reading. In six patients, enhancing lesions were detected only on 3DT1TSE, with treatment escalation in two. Conclusion 3DT1TSE outperformed 3DT1TFE in sensitivity and reader agreement for enhancing lesion detection in MS. Incorporating 3DT1TSE into standard MRI protocols may improve disease activity assessment and clinical decision-making. Critical relevance statement Replacing 3D gradient-echo with post-contrast 3D T1 turbo spin-echo brain MRI greatly improves the detection of gadolinium-enhancing multiple-sclerosis lesions, boosting diagnostic sensitivity and reader agreement and directly influencing treatment-escalation decisions in routine practice. Key Points Detecting and enhancing MS lesions is limited by standard 3D T1 turbo field echo (3DT1TFE) MRI. 3D T1 turbo spin echo detects significantly more gadolinium-enhancing MS lesions than conventional 3DT1TFE. Greater lesion detection allows more precise activity assessment and optimal treatment management. Graphical Abstract
insightsimaging.springeropen.com
October 4, 2025 at 6:58 AM
Proud to share this open-access work with colleagues #CaixaResearch #CaixaImpulse #laCaixaFoundation #MSResearch #Radiology #Neuroimaging
📖 Full text: insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10....
📖 Full text: insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10....
‼️ Why it matters: Detecting inflammation earlier → better treatment choices → may improve long-term outcomes.
We’ve already adopted this technique at our hospital.
Real MS patients are benefitting today.
We’ve already adopted this technique at our hospital.
Real MS patients are benefitting today.
October 4, 2025 at 6:58 AM
‼️ Why it matters: Detecting inflammation earlier → better treatment choices → may improve long-term outcomes.
We’ve already adopted this technique at our hospital.
Real MS patients are benefitting today.
We’ve already adopted this technique at our hospital.
Real MS patients are benefitting today.
Robust design:
✔️ Two independent radiologists read the scans blindly
✔️ High agreement between them
✔️ Consensus team validated all findings
✔️ Two independent radiologists read the scans blindly
✔️ High agreement between them
✔️ Consensus team validated all findings

October 4, 2025 at 6:58 AM
Robust design:
✔️ Two independent radiologists read the scans blindly
✔️ High agreement between them
✔️ Consensus team validated all findings
✔️ Two independent radiologists read the scans blindly
✔️ High agreement between them
✔️ Consensus team validated all findings
We analysed 255 MS scans.
🔍 Compared two post-contrast sequences: Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) vs Turbo Field Echo (TFE).
📈 TSE showed almost twice as many enhancing lesions as TFE.
🔍 Compared two post-contrast sequences: Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) vs Turbo Field Echo (TFE).
📈 TSE showed almost twice as many enhancing lesions as TFE.

October 4, 2025 at 6:58 AM
We analysed 255 MS scans.
🔍 Compared two post-contrast sequences: Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) vs Turbo Field Echo (TFE).
📈 TSE showed almost twice as many enhancing lesions as TFE.
🔍 Compared two post-contrast sequences: Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) vs Turbo Field Echo (TFE).
📈 TSE showed almost twice as many enhancing lesions as TFE.
(5/5) 🎉 Huge congratulations to our fantastic team! Full article available open-access here 👉 link.springer.com/article/10.1... 🔗📖 (5/5)
#MultipleSclerosis #Neuroradiology #MRI #SWI #Research #Radiology #Neuroimaging
#MultipleSclerosis #Neuroradiology #MRI #SWI #Research #Radiology #Neuroimaging
https://link.springer.com/article/10.100…🔗📖
March 9, 2025 at 10:53 AM
(5/5) 🎉 Huge congratulations to our fantastic team! Full article available open-access here 👉 link.springer.com/article/10.1... 🔗📖 (5/5)
#MultipleSclerosis #Neuroradiology #MRI #SWI #Research #Radiology #Neuroimaging
#MultipleSclerosis #Neuroradiology #MRI #SWI #Research #Radiology #Neuroimaging
Early detection of active lesions can facilitate timely and effective treatments, potentially improving clinical outcomes for MS patients. 🕒💡(4/5)

March 9, 2025 at 10:53 AM
Early detection of active lesions can facilitate timely and effective treatments, potentially improving clinical outcomes for MS patients. 🕒💡(4/5)
This combination notably boosts agreement among radiologists, especially helpful for less experienced readers, ensuring consistency and reliability in lesion detection. (3/5)

March 9, 2025 at 10:53 AM
This combination notably boosts agreement among radiologists, especially helpful for less experienced readers, ensuring consistency and reliability in lesion detection. (3/5)
With MRI data from over 300 patients, we found that combining SWI+C with conventional contrast-enhanced T1 imaging (T1WI+C) identifies more active MS lesions, improving diagnostic accuracy. link: link.springer.com/article/10.1... 🔗📖 (2/5)
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00062-025-01508-5🔗📖
March 9, 2025 at 10:53 AM
With MRI data from over 300 patients, we found that combining SWI+C with conventional contrast-enhanced T1 imaging (T1WI+C) identifies more active MS lesions, improving diagnostic accuracy. link: link.springer.com/article/10.1... 🔗📖 (2/5)
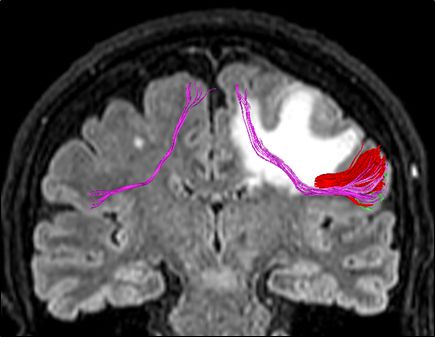
Frontal Aslant Tract. Vertical associative fiber pre-supplementary motor area to IFG. Important role in language production and motor This patient for example had a met with edema englobing the tract and had trouble initiating speech. Resolved after anti-edema drugs and resection
February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Frontal Aslant Tract. Vertical associative fiber pre-supplementary motor area to IFG. Important role in language production and motor This patient for example had a met with edema englobing the tract and had trouble initiating speech. Resolved after anti-edema drugs and resection
Damage to the corticospinal tract can cause permanent motor damage! Especially damage to pre-central fibers.

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Damage to the corticospinal tract can cause permanent motor damage! Especially damage to pre-central fibers.
Corticospinal tract. Most important projection fiber tract. Contains motor and sensory fibers from pre-motor, precentral (primary motor) and post-central cortices via the posterior limb of the internal capsule all the way to the spinal cord. Most fibers decussate in the medulla.

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Corticospinal tract. Most important projection fiber tract. Contains motor and sensory fibers from pre-motor, precentral (primary motor) and post-central cortices via the posterior limb of the internal capsule all the way to the spinal cord. Most fibers decussate in the medulla.
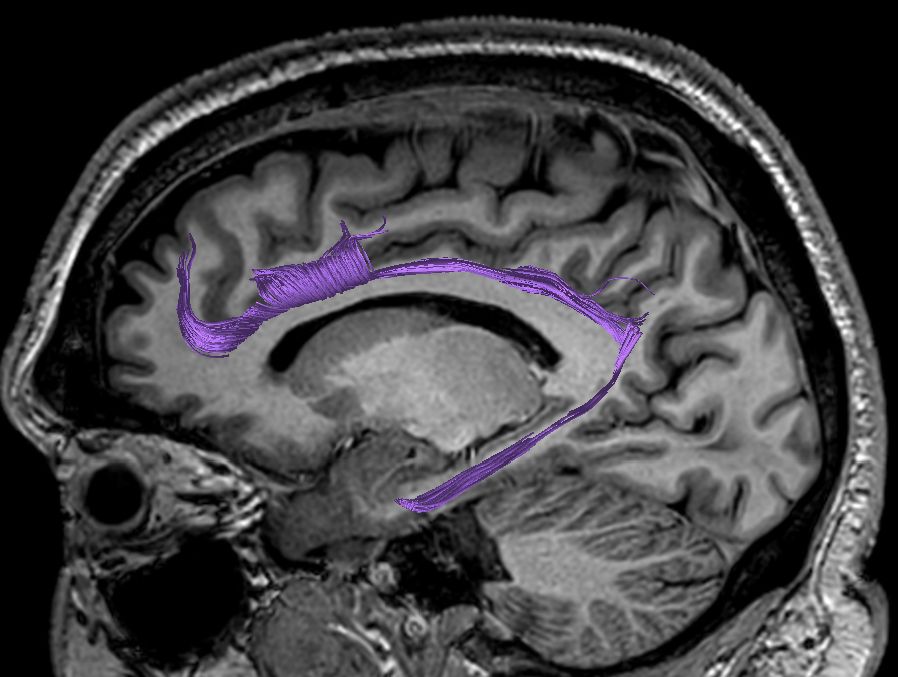
Cingulum. Part of the limbic system, surrounds the corpus callosum medial to other associative and projection fibers. At the level of the splenium an narrow extension of white-matter tract through the parahippocampal gyrus extends to the amygdala.
February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Cingulum. Part of the limbic system, surrounds the corpus callosum medial to other associative and projection fibers. At the level of the splenium an narrow extension of white-matter tract through the parahippocampal gyrus extends to the amygdala.
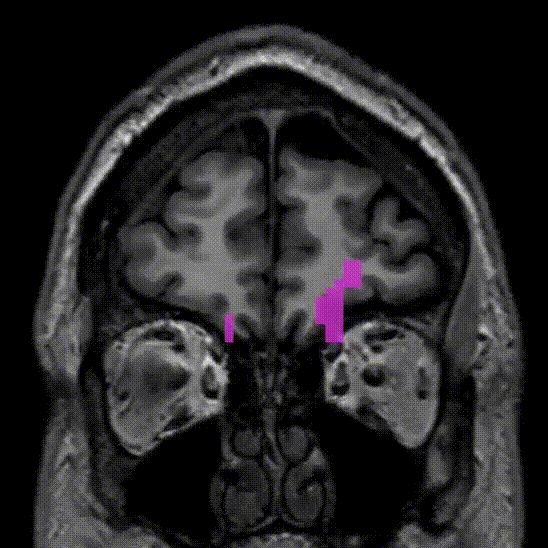
Uncinate fasciculus. Part of the indirect ventral stream and also part of the limbic system. Connects prefrontal regions to temporal pole via the temporal stem.
February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Uncinate fasciculus. Part of the indirect ventral stream and also part of the limbic system. Connects prefrontal regions to temporal pole via the temporal stem.
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus. Along with Uncinate fasciculus, it is part of the indirect ventral associative stream. Connects anterior temporal pole to occipital pole. Courses immediately infero-lateral to IFOF.

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus. Along with Uncinate fasciculus, it is part of the indirect ventral associative stream. Connects anterior temporal pole to occipital pole. Courses immediately infero-lateral to IFOF.
IFOF superficial (yellow) and deep (orange segments). Longest associative tract connects prefrontal areas to parietal (superficial segment) and occipital (deep segment) lobes via the infeiror external capsule and posterior temporal white-matter.

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
IFOF superficial (yellow) and deep (orange segments). Longest associative tract connects prefrontal areas to parietal (superficial segment) and occipital (deep segment) lobes via the infeiror external capsule and posterior temporal white-matter.
Ventral associative stream. WHAT pathway. Language role. Words -> meaning.
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)



February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Ventral associative stream. WHAT pathway. Language role. Words -> meaning.
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)
RED: Long segment of arcuate: Inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) to posterior lateral temporal region
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
RED: Long segment of arcuate: Inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) to posterior lateral temporal region
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.
Dorsal associative stream. WHERE pathway. Language role: Speech articulation and phonological processing.
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)

February 9, 2025 at 7:51 PM
Dorsal associative stream. WHERE pathway. Language role: Speech articulation and phonological processing.
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)
THE PAPER:
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

The T1-dark-rim: A novel imaging sign for detecting smoldering inflammation in multiple sclerosis
Paramagnetic rim lesions (PRLs), usually identified in susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI), are a promising prognostic biomarker of disability progr…
www.sciencedirect.com
February 9, 2025 at 7:26 PM
THE PAPER:
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
Way to go yet: the findings are still hypothetical. Work must demonstrate generalizability, inter-reader correlation, diagnostic and prognostic relevance, and pathological correlation. However, our findings are transparent and very encouraging! 6/6
February 9, 2025 at 7:26 PM
Way to go yet: the findings are still hypothetical. Work must demonstrate generalizability, inter-reader correlation, diagnostic and prognostic relevance, and pathological correlation. However, our findings are transparent and very encouraging! 6/6

