Philipp Frank
@philippfrank.bsky.social
Senior Research Fellow at UCL Division of Psychiatry
✅ The main enriched pathway involved the upregulation of the pro-inflammatory regulator NF-κB2. Chronic stress—whether biological or social—can trigger activation of this pathway. Persistent activation accelerates tissue damage and increases susceptibility to age-related conditions.
March 14, 2025 at 11:16 AM
✅ The main enriched pathway involved the upregulation of the pro-inflammatory regulator NF-κB2. Chronic stress—whether biological or social—can trigger activation of this pathway. Persistent activation accelerates tissue damage and increases susceptibility to age-related conditions.
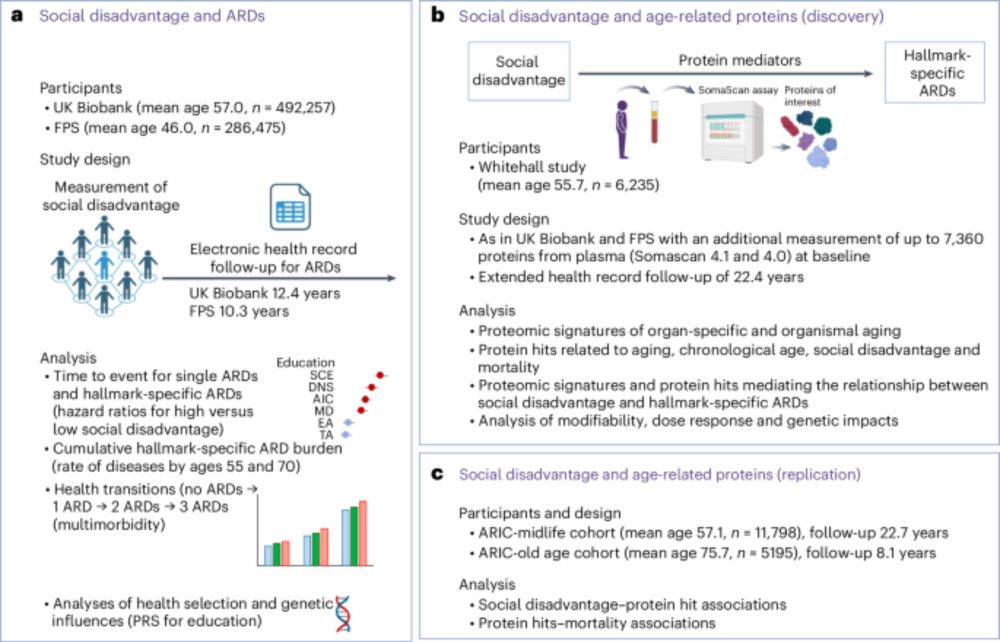
✅ Social disadvantage is associated with proteomic signatures of accelerated immune aging
✅ 14 age-related #proteins mediate up to 39% of the link between social disadvantage and age-related diseases
✅ Individuals facing social disadvantage had an increased risk for 66 age-related diseases
✅ 14 age-related #proteins mediate up to 39% of the link between social disadvantage and age-related diseases
✅ Individuals facing social disadvantage had an increased risk for 66 age-related diseases
March 14, 2025 at 11:16 AM
✅ Social disadvantage is associated with proteomic signatures of accelerated immune aging
✅ 14 age-related #proteins mediate up to 39% of the link between social disadvantage and age-related diseases
✅ Individuals facing social disadvantage had an increased risk for 66 age-related diseases
✅ 14 age-related #proteins mediate up to 39% of the link between social disadvantage and age-related diseases
✅ Individuals facing social disadvantage had an increased risk for 66 age-related diseases
Our research has also been featured in the @financialtimes.com www.ft.com/content/9510...
‘Quick and easy’ blood tests for ageing organs detect disease risks
Advanced early warning systems boost ability to flag higher likelihood of health threats
www.ft.com
February 26, 2025 at 10:33 AM
Our research has also been featured in the @financialtimes.com www.ft.com/content/9510...
📌 In most cases, ageing of one organ increased susceptibility to diseases in multiple organs.
📌 Plasma-based organ age signatures could provide a quick, non-invasive way to improve disease prediction and prevention.
@uclpsychiatry.bsky.social @helsinki.fi www.ft.com/content/9510...
📌 Plasma-based organ age signatures could provide a quick, non-invasive way to improve disease prediction and prevention.
@uclpsychiatry.bsky.social @helsinki.fi www.ft.com/content/9510...

‘Quick and easy’ blood tests for ageing organs detect disease risks
Advanced early warning systems boost ability to flag higher likelihood of health threats
www.ft.com
February 26, 2025 at 10:33 AM
📌 In most cases, ageing of one organ increased susceptibility to diseases in multiple organs.
📌 Plasma-based organ age signatures could provide a quick, non-invasive way to improve disease prediction and prevention.
@uclpsychiatry.bsky.social @helsinki.fi www.ft.com/content/9510...
📌 Plasma-based organ age signatures could provide a quick, non-invasive way to improve disease prediction and prevention.
@uclpsychiatry.bsky.social @helsinki.fi www.ft.com/content/9510...
📌 Faster organ ageing was associated with an increased risk of 30 age-related diseases.
📌 The development of some diseases—such as liver failure, chronic heart failure, and lung cancer—was exclusively associated with accelerated ageing of their respective organ.
📌 The development of some diseases—such as liver failure, chronic heart failure, and lung cancer—was exclusively associated with accelerated ageing of their respective organ.
February 26, 2025 at 10:33 AM
📌 Faster organ ageing was associated with an increased risk of 30 age-related diseases.
📌 The development of some diseases—such as liver failure, chronic heart failure, and lung cancer—was exclusively associated with accelerated ageing of their respective organ.
📌 The development of some diseases—such as liver failure, chronic heart failure, and lung cancer—was exclusively associated with accelerated ageing of their respective organ.
Using proteomic data from 6,235 participants of the Whitehall II study , we determined how much an organ's biological age deviates from what’s typically expected for someone of the same age. We then tracked participants for 20 years to examine their risk of developing 45 age-related diseases.
February 26, 2025 at 10:33 AM
Using proteomic data from 6,235 participants of the Whitehall II study , we determined how much an organ's biological age deviates from what’s typically expected for someone of the same age. We then tracked participants for 20 years to examine their risk of developing 45 age-related diseases.