
🌾 Focused on understanding the role of biodiversity in rice production
🌐 https://nperezmendez.weebly.com/
📸Wildlife photography in https://www.instagram.com/raw_natura
Views my own





#SIBECOLAEET2025 #Ecology

#SIBECOLAEET2025 #Ecology



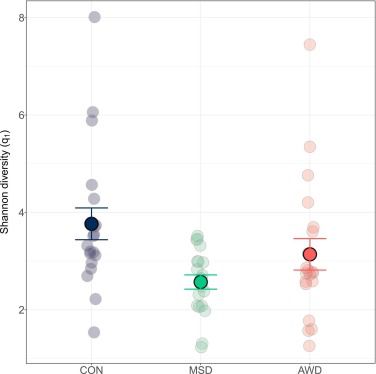
– AWD reduced methane by 92.5%
– MSD by 67.3%
when compared to continuous flooding. This confirms strong mitigation potential associated to the drainage periods, which inhibits methanogenesis.

– AWD reduced methane by 92.5%
– MSD by 67.3%
when compared to continuous flooding. This confirms strong mitigation potential associated to the drainage periods, which inhibits methanogenesis.
* Traditional continuous flooding (CONV) – no drying periods during the growing season
* Mid-Season Drainage (MSD) – 1 drying period
* Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) – Multiple drying periods

* Traditional continuous flooding (CONV) – no drying periods during the growing season
* Mid-Season Drainage (MSD) – 1 drying period
* Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) – Multiple drying periods
















m.youtube.com/watch?v=D-rB...

m.youtube.com/watch?v=D-rB...











