Neuroscience Research 📬
- Population activity separates cooperative from non-cooperative actions.
- Partner’s position is strongly represented, predicting cooperation success.
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

- Population activity separates cooperative from non-cooperative actions.
- Partner’s position is strongly represented, predicting cooperation success.
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
- DNTs carry Ca²⁺ and Aβ; actin disruption blocks transfer.
- DNTs rise early in AD, before plaques, aiding spread.
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

- DNTs carry Ca²⁺ and Aβ; actin disruption blocks transfer.
- DNTs rise early in AD, before plaques, aiding spread.
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
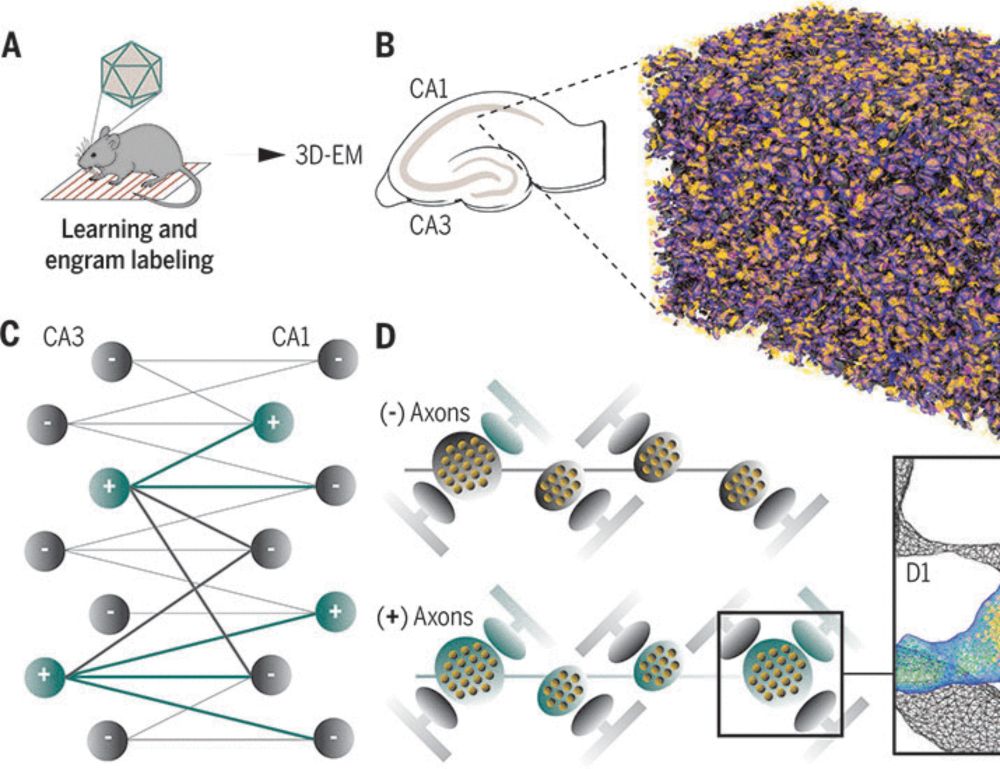
-Only small groups of these neurons reactivate at a time.
-This reactivation helps stabilize and strengthen memories.
-Sleep-linked replay may be key to learning and long-term memory.
doi.org/10.1038/s414...

-Only small groups of these neurons reactivate at a time.
-This reactivation helps stabilize and strengthen memories.
-Sleep-linked replay may be key to learning and long-term memory.
doi.org/10.1038/s414...
-Different cortical layers show unique aging patterns.
-Some layers lose connections, while others remain stable.
-These shifts may explain why hearing and vision decline with age.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...

-Different cortical layers show unique aging patterns.
-Some layers lose connections, while others remain stable.
-These shifts may explain why hearing and vision decline with age.
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
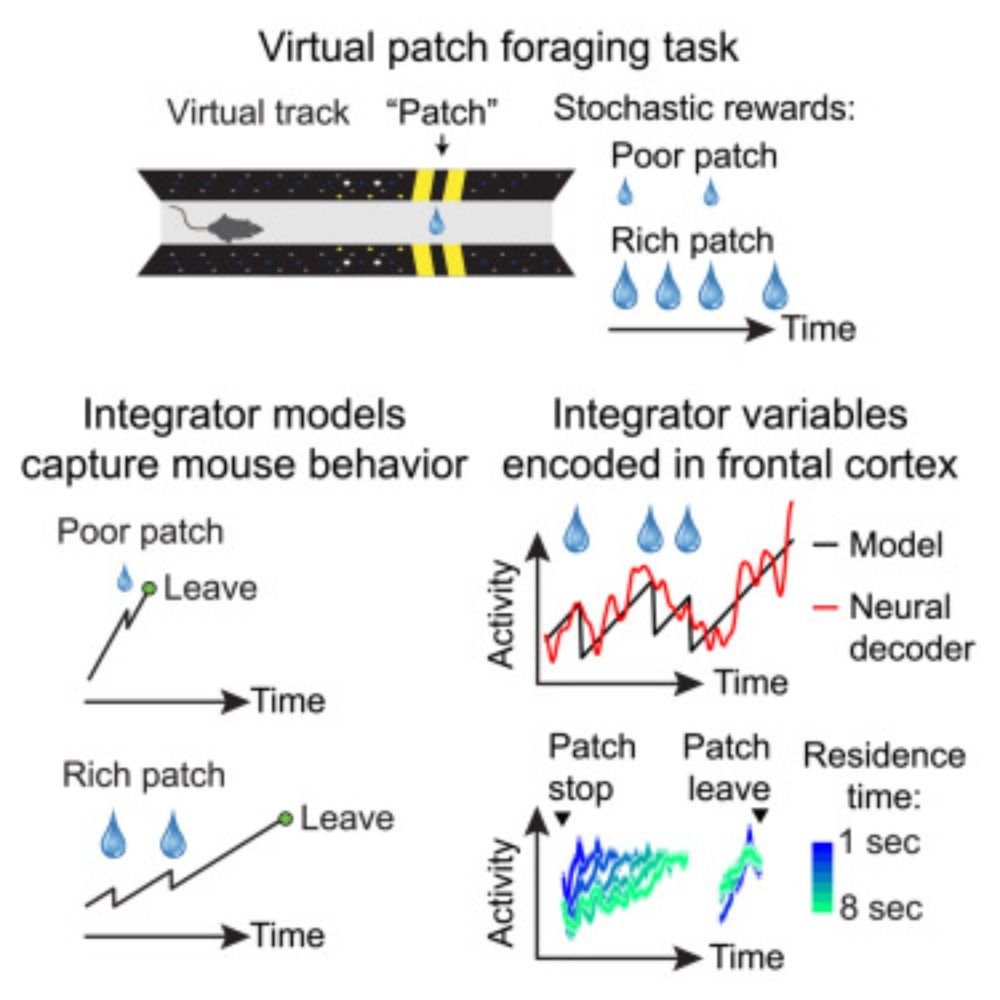
-Their choices shift with a hidden “patience” level.
-Brain signals in the frontal cortex rise and fall with time and rewards.
-These signals may guide everyday decisions about when to stay or leave
doi.org/10.1016/j.ne...
-Their choices shift with a hidden “patience” level.
-Brain signals in the frontal cortex rise and fall with time and rewards.
-These signals may guide everyday decisions about when to stay or leave
doi.org/10.1016/j.ne...
- Calcium rise alone doesn’t predict Fos expression
- Silencing them doesn’t impair retrieval
- Inhibitory neurons may recruit them
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

- Calcium rise alone doesn’t predict Fos expression
- Silencing them doesn’t impair retrieval
- Inhibitory neurons may recruit them
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
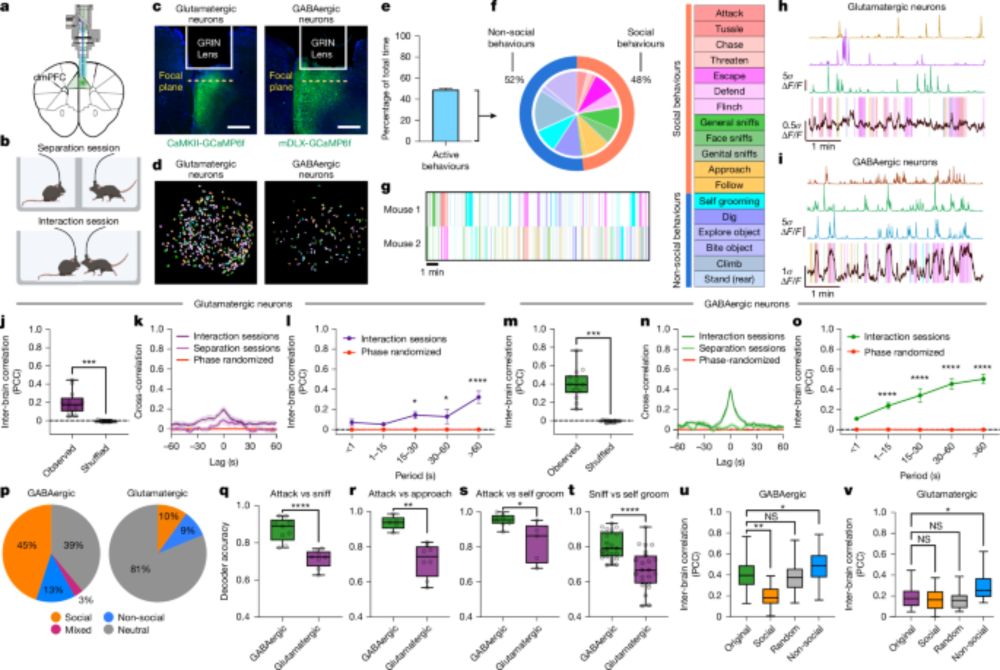
• GABAergic neurons show stronger shared dynamics
• Shared activity reflects self and partner behavior and enables social behavior
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
• GABAergic neurons show stronger shared dynamics
• Shared activity reflects self and partner behavior and enables social behavior
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
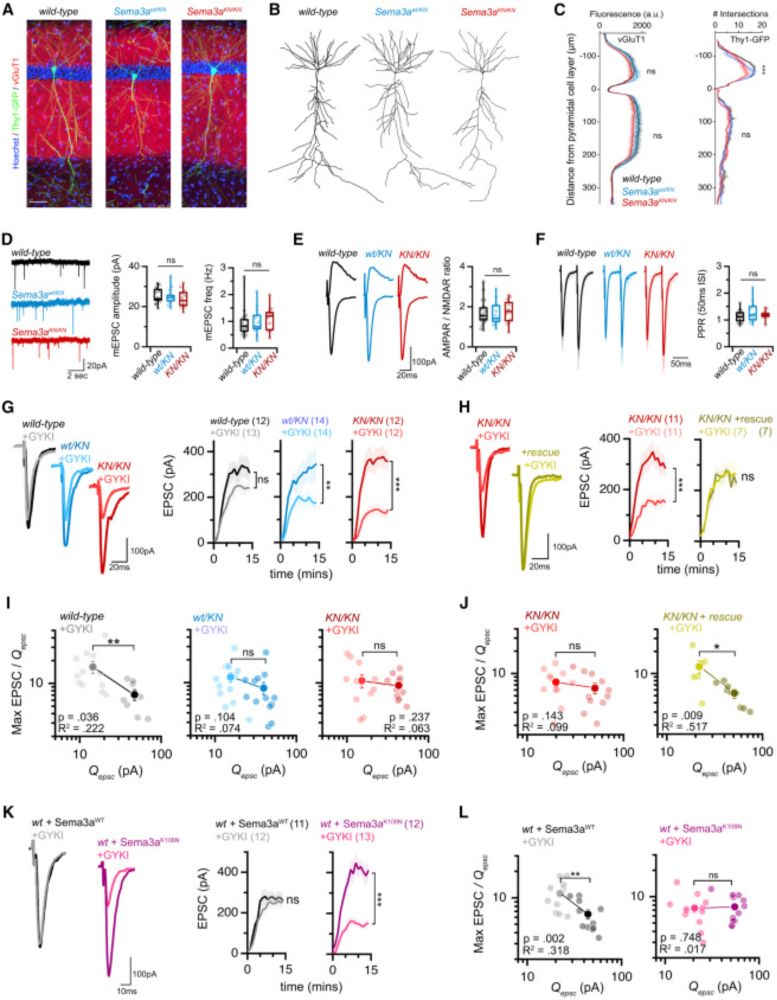
• Sema3a Signals via PlexinA4 and ITGB1 to mediate PHP
• Shifts synaptic vesicles into the release-ready pool for stable output
www.cell.com/neuron/fullt...
• Sema3a Signals via PlexinA4 and ITGB1 to mediate PHP
• Shifts synaptic vesicles into the release-ready pool for stable output
www.cell.com/neuron/fullt...
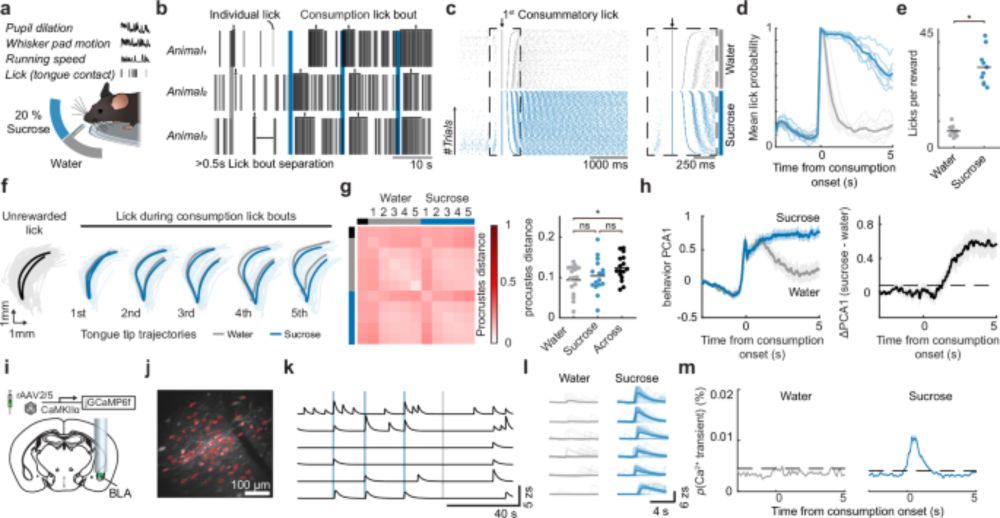
- BLA neurons adaptively update value based on learning.
- Positive and negative value representations are distinct.
- Neurons remap value when contingencies change.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- BLA neurons adaptively update value based on learning.
- Positive and negative value representations are distinct.
- Neurons remap value when contingencies change.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- SST+ interneurons are key regulators of this inhibition.
- Termination occurs locally at the dendritic site of the plateau.
- Blocking SST+ cells prolongs plateau duration.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

- SST+ interneurons are key regulators of this inhibition.
- Termination occurs locally at the dendritic site of the plateau.
- Blocking SST+ cells prolongs plateau duration.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
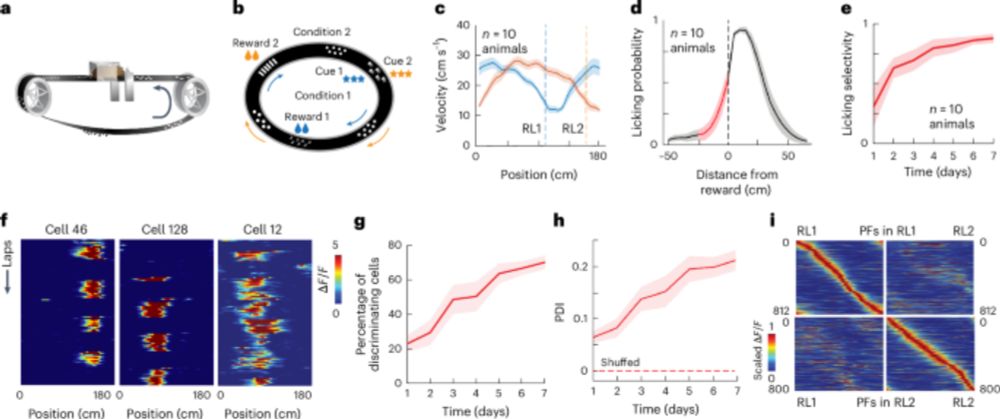
- New neurons join the memory trace while initial ones remain active.
- Ensemble expansion predicts memory strength.
- Inhibition of expanding cells impairs memory recall.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- New neurons join the memory trace while initial ones remain active.
- Ensemble expansion predicts memory strength.
- Inhibition of expanding cells impairs memory recall.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
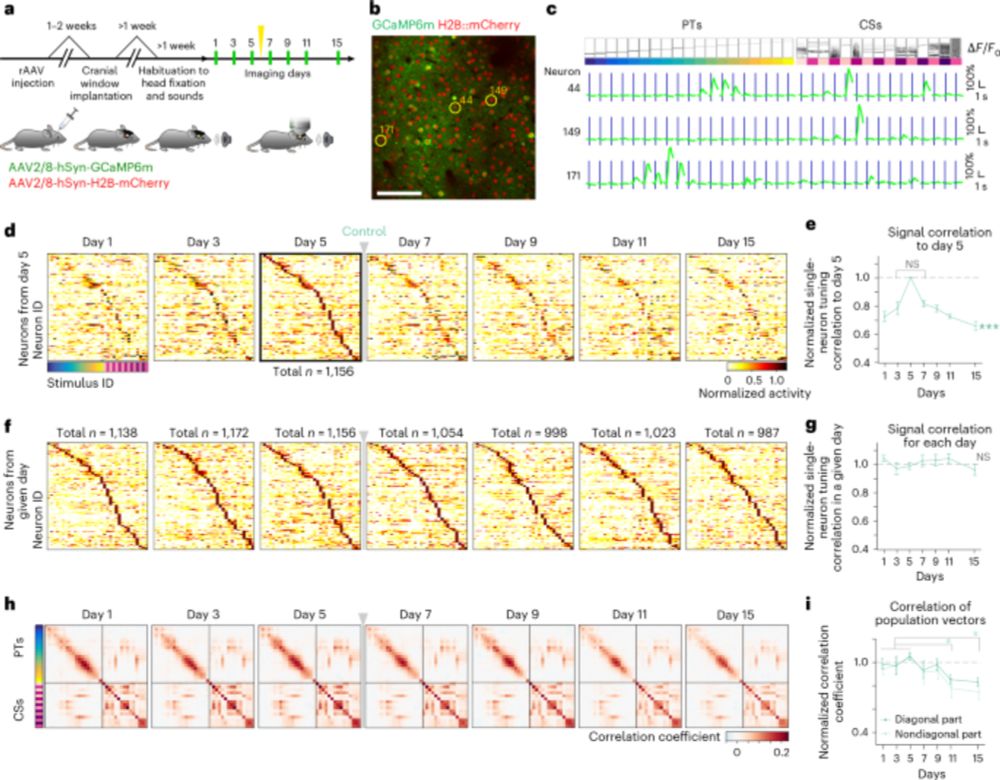
-Sensory perturbation leads to temporary changes but map structure recovers.
-It involves balanced excitation-inhibition across layers.
-Recurrent activity stabilizes identity.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-Sensory perturbation leads to temporary changes but map structure recovers.
-It involves balanced excitation-inhibition across layers.
-Recurrent activity stabilizes identity.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
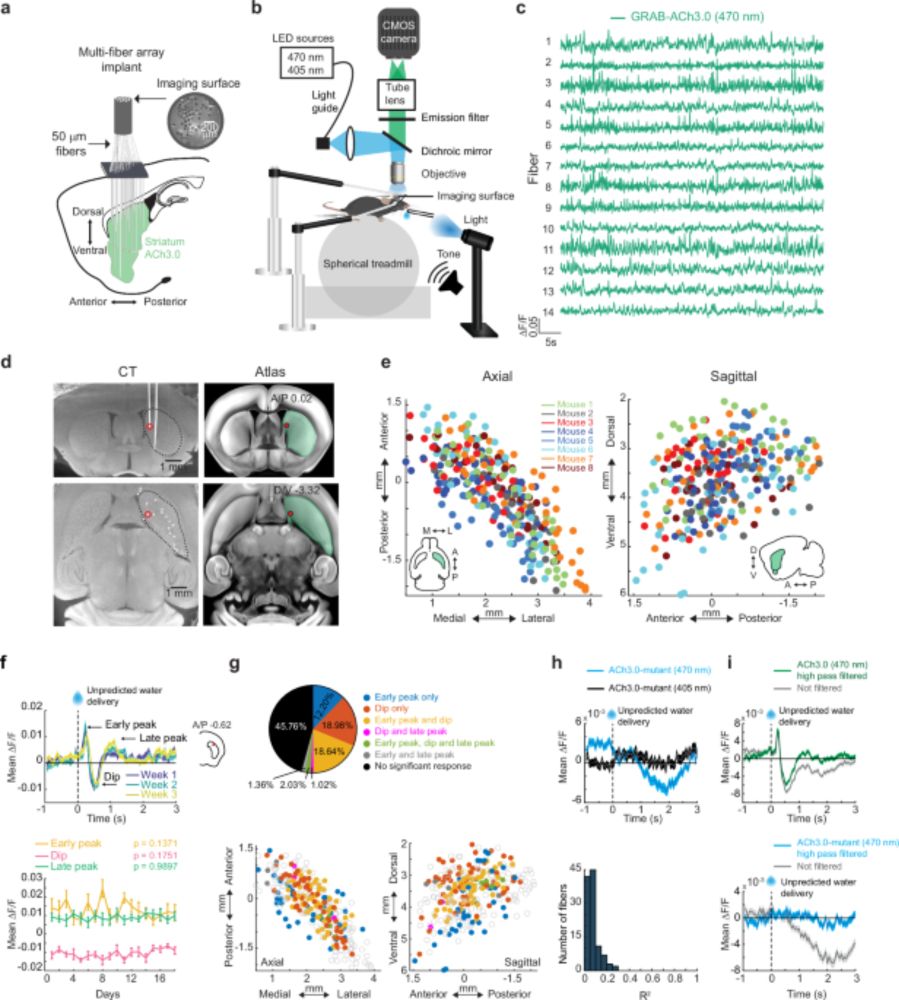
- aDS ACh dips and late peaks encode opposing reward prediction errors.
- Silencing ACh in aDS impairs extinction but not learning.
- ACh and DA show opposite cue responses in aDS.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- aDS ACh dips and late peaks encode opposing reward prediction errors.
- Silencing ACh in aDS impairs extinction but not learning.
- ACh and DA show opposite cue responses in aDS.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
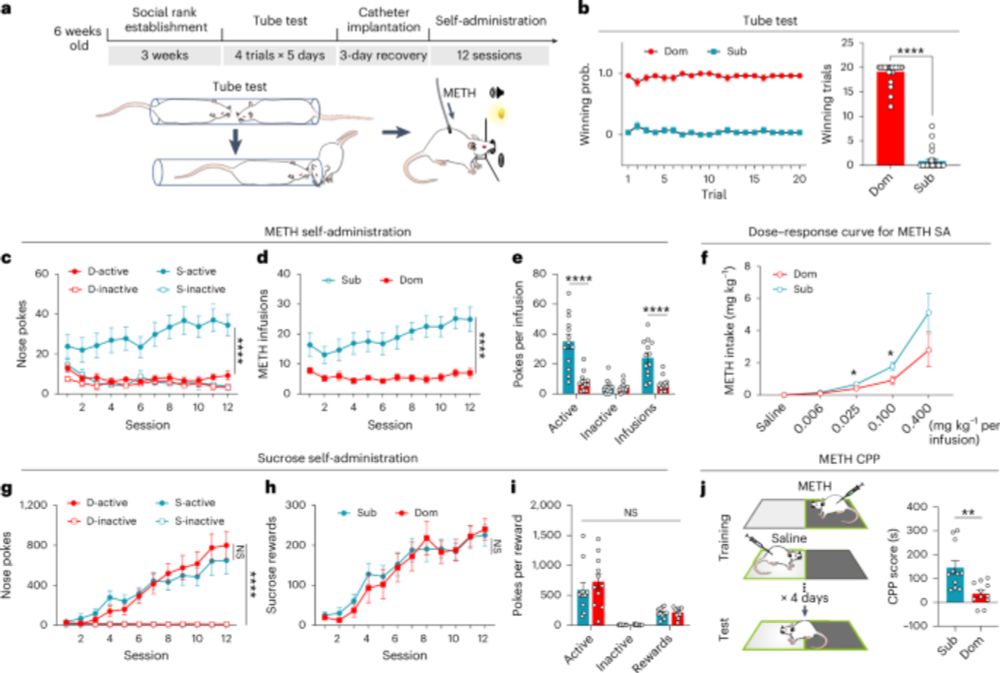
- Subordinates show more METH seeking via mesolimbic DA
- Activating mesocortical DA reduces drug seeking, boosts dominance
- Females, regardless of rank, remain METH-vulnerable.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- Subordinates show more METH seeking via mesolimbic DA
- Activating mesocortical DA reduces drug seeking, boosts dominance
- Females, regardless of rank, remain METH-vulnerable.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-Reward-driven whisker input boosts contralateral S1 responses
-No enhancement in naïve or disengaged mice
- Corpus callosum is essential for interhemispheric coordination
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
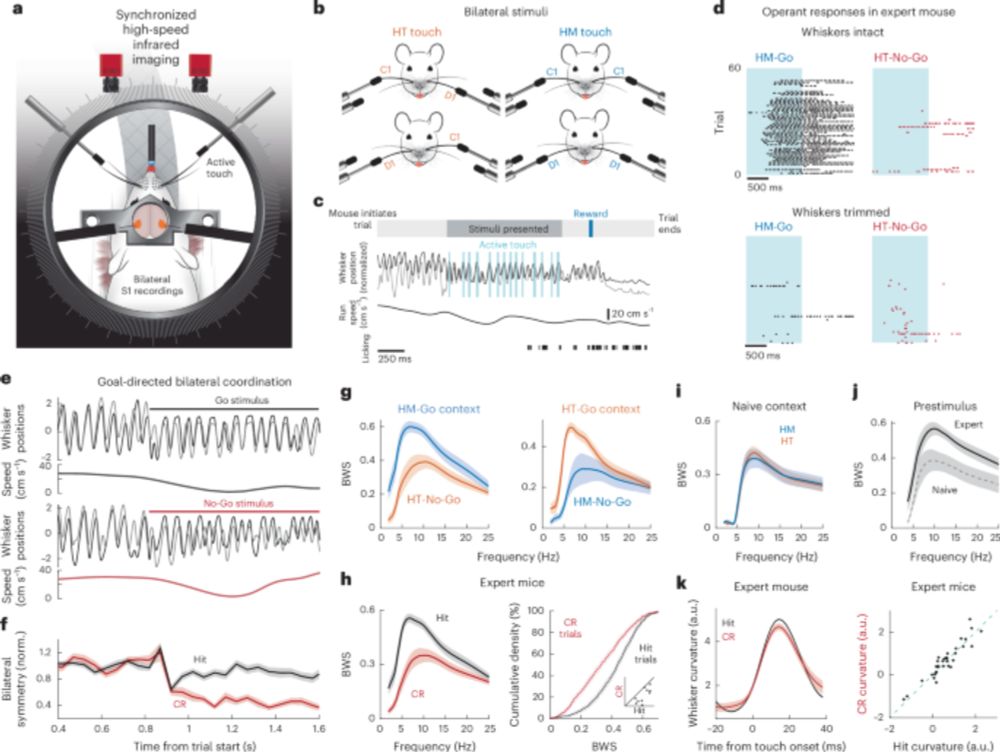
-Reward-driven whisker input boosts contralateral S1 responses
-No enhancement in naïve or disengaged mice
- Corpus callosum is essential for interhemispheric coordination
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-This predicts more drug use and escape.
-Shared dopamine dip drives escape and promotes drug-seeking behavior.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
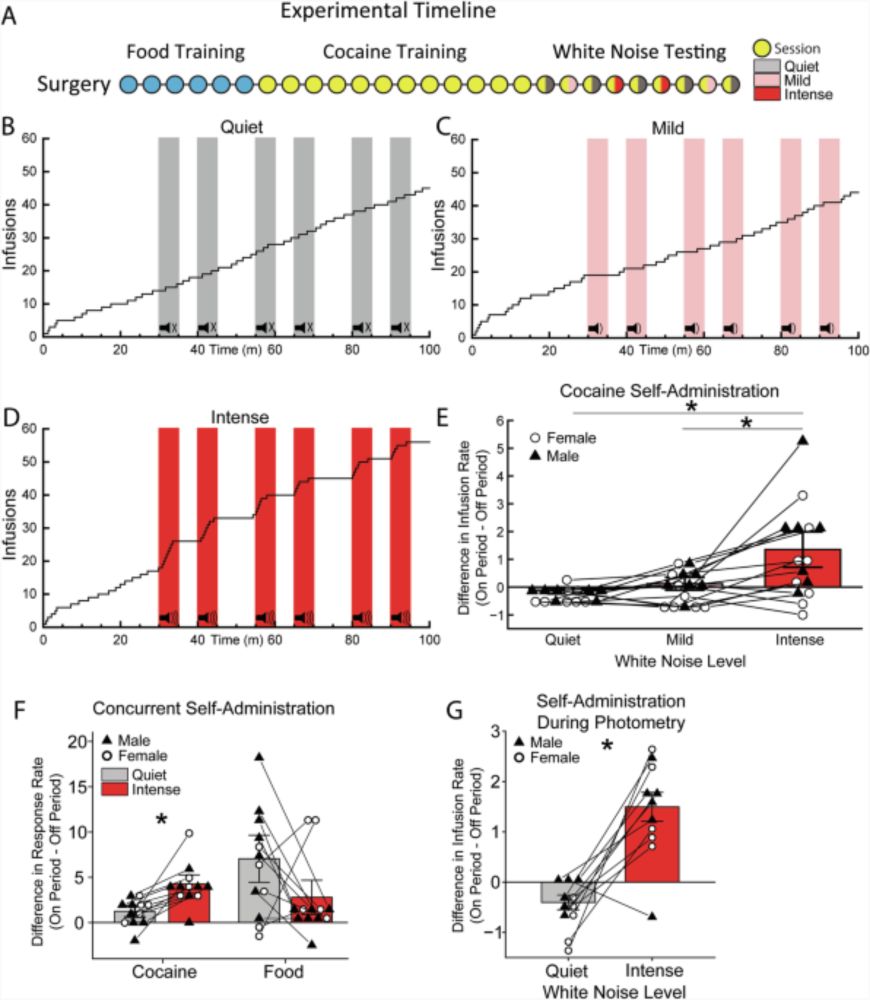
-This predicts more drug use and escape.
-Shared dopamine dip drives escape and promotes drug-seeking behavior.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-VIS and SM networks reach adult-like patterns at birth; DM and FP mature by ages 4–6.
-Regional connectivity peaks around age 31.4, aligned with sensorimotor–association axis.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
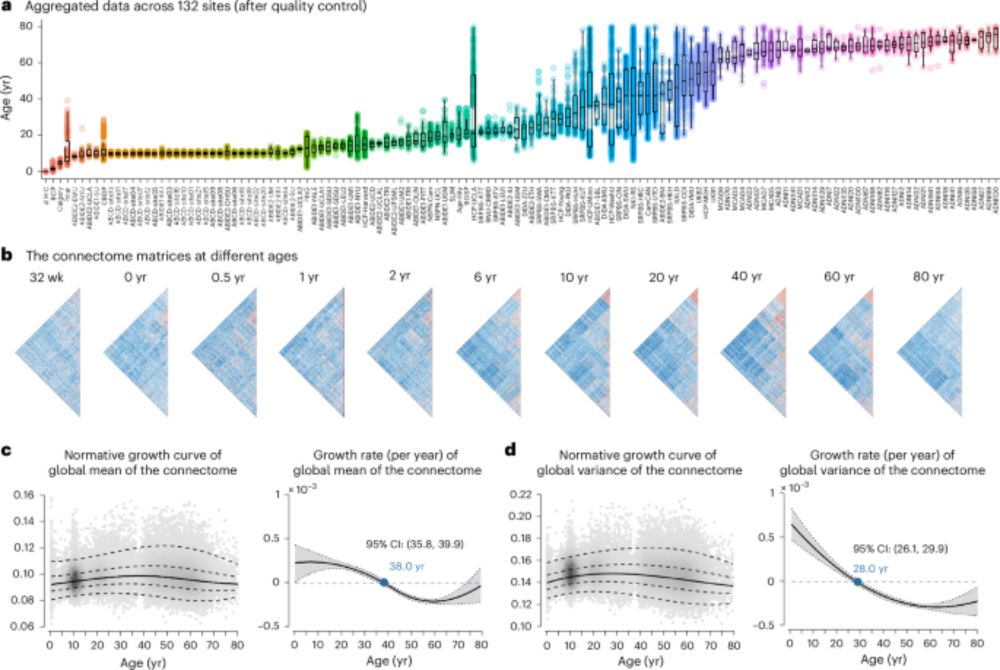
-VIS and SM networks reach adult-like patterns at birth; DM and FP mature by ages 4–6.
-Regional connectivity peaks around age 31.4, aligned with sensorimotor–association axis.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- Dysregulation in these circuits can lead to excessive food intake and obesity.
www.cell.com/neuron/fullt...
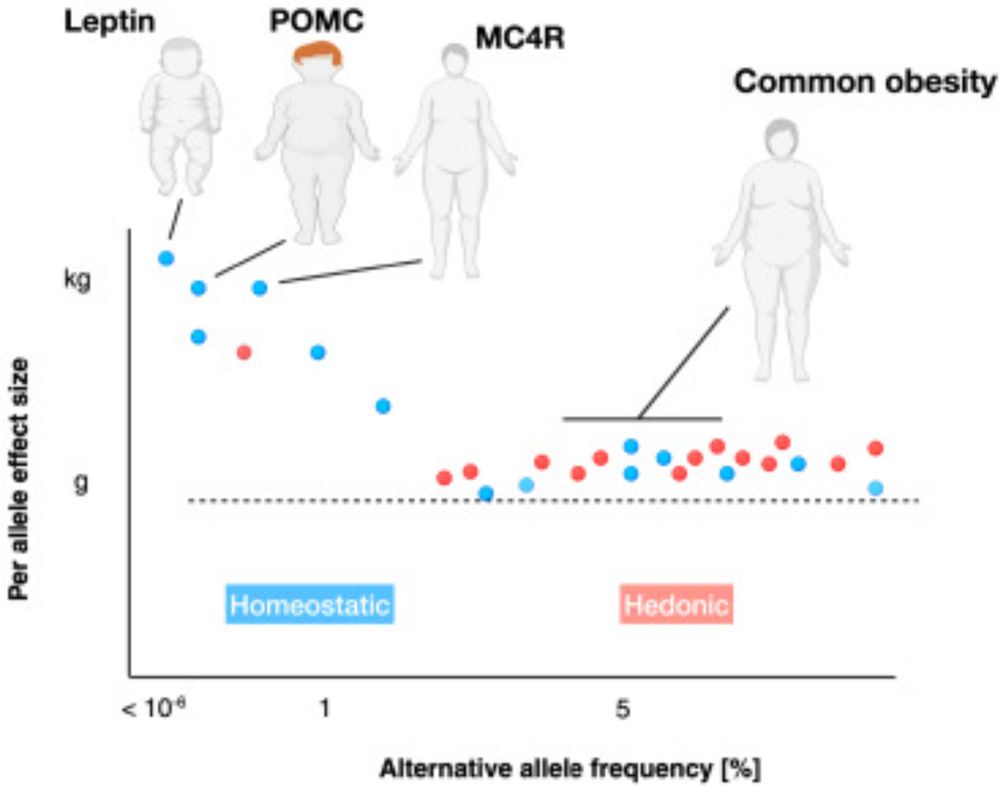
- Dysregulation in these circuits can lead to excessive food intake and obesity.
www.cell.com/neuron/fullt...
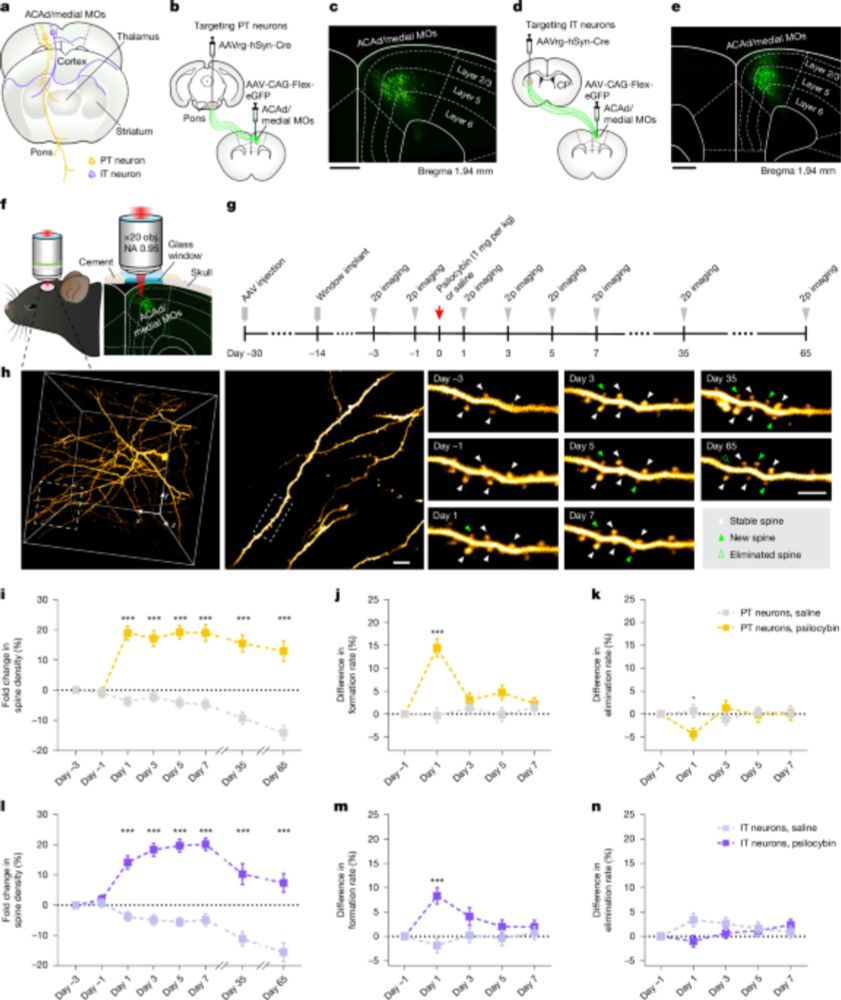
-Silencing PT neurons negates psilocybin’s stress-related behavioral benefits. 
-5-HT₂A receptor mediates psilocybin’s effects.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-Silencing PT neurons negates psilocybin’s stress-related behavioral benefits. 
-5-HT₂A receptor mediates psilocybin’s effects.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
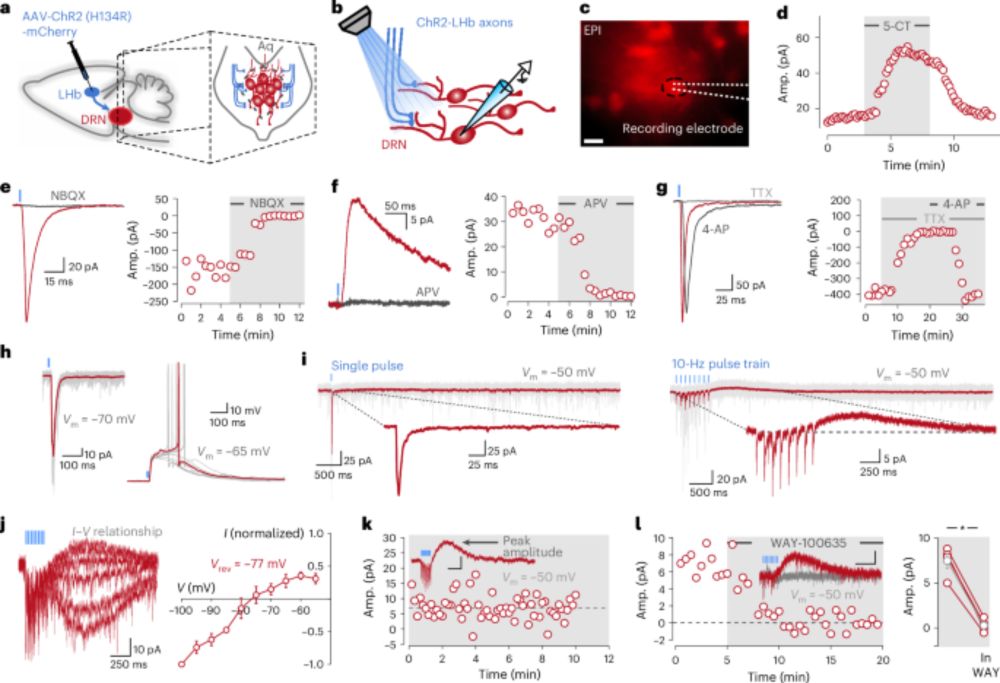
-Serotonin release is facilitated by prior activity, strengthening inhibition with continued use.
-This mechanism allows flexible control of output.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-Serotonin release is facilitated by prior activity, strengthening inhibition with continued use.
-This mechanism allows flexible control of output.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
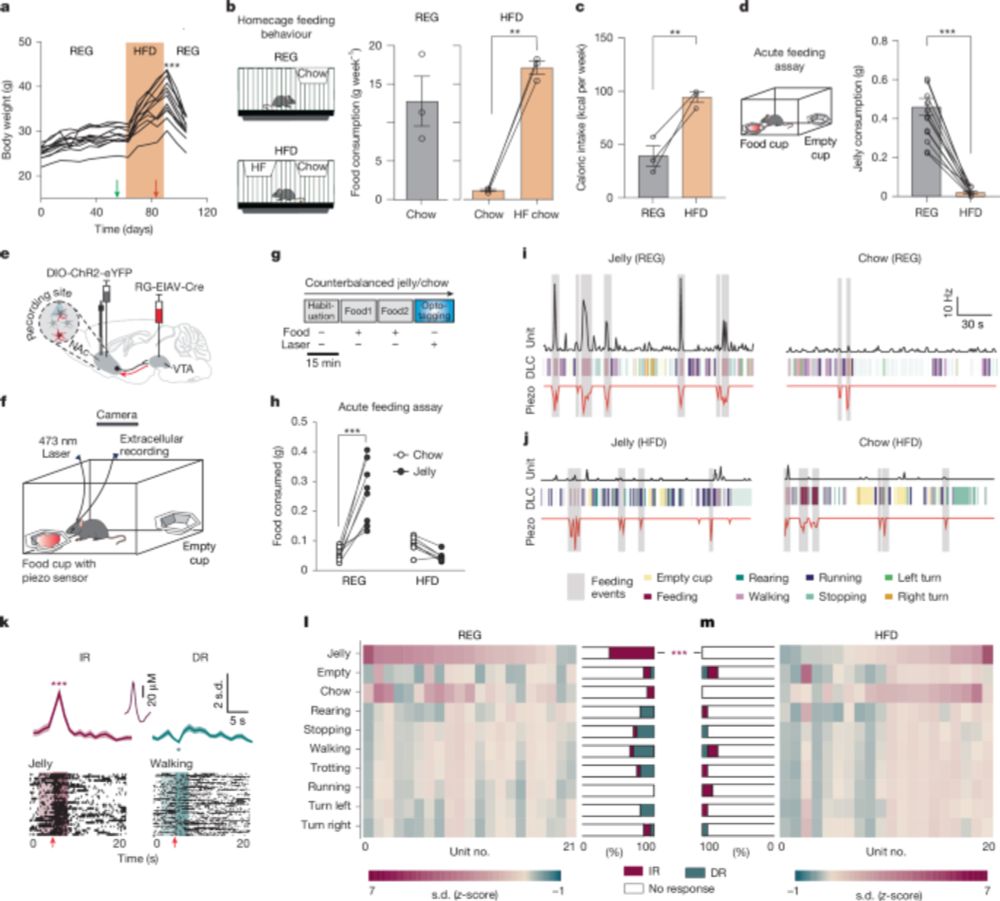
-NAcLat→VTA activity was impaired.
-Neurotensin expression and release decreased in high-fat diet mice.
-Boosting neurotensin restored feeding behavior and weight balance.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
-NAcLat→VTA activity was impaired.
-Neurotensin expression and release decreased in high-fat diet mice.
-Boosting neurotensin restored feeding behavior and weight balance.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
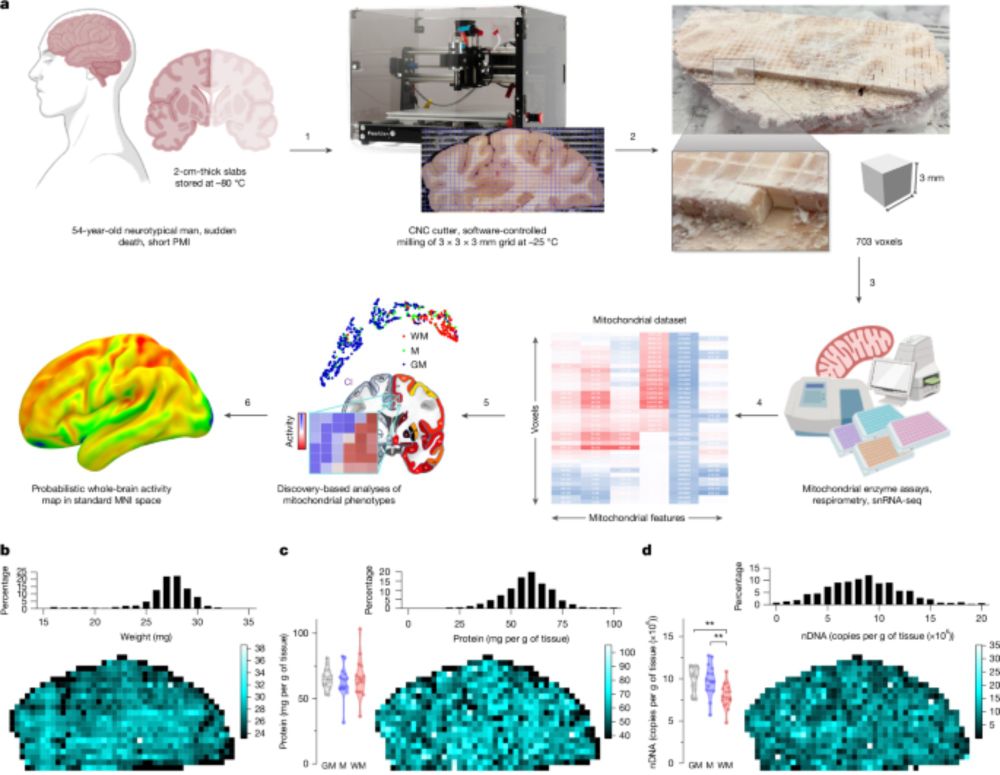
- The brain was divided into 703 voxels to analyze mitochondrial phenotypes.
- Grey matter has 50% more mitochondria than white matter, optimized for energy use.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
- The brain was divided into 703 voxels to analyze mitochondrial phenotypes.
- Grey matter has 50% more mitochondria than white matter, optimized for energy use.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

