
NetScience
@netscience.bsky.social
Reader in Applied Mathematics at Queen Mary University working on Network Science, Data Science, and digital Epidemiology. Website: www.nicolaperra.com
Inferring tree structure with hidden traps from first-passage times link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...

Inferring tree structure with hidden traps from first-passage times
Inferring tree structure is a problem of practical relevance across diverse domains, from biological transport networks to engineered systems. The results presented here lend themselves to potential a...
link.aps.org
November 10, 2025 at 5:41 PM
Inferring tree structure with hidden traps from first-passage times link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Symmetry breaking in a metapopulation model with fitness-dependent dispersal link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Symmetry breaking in a metapopulation model with fitness-dependent dispersal
This study investigates the emergence of symmetry-breaking dynamics and the associated bifurcation behavior in an identically coupled Rosenzweig-MacArthur model with fitness-dependent dispersal betwee...
link.aps.org
November 10, 2025 at 5:40 PM
Symmetry breaking in a metapopulation model with fitness-dependent dispersal link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
‘Google Maps’ for Roman roads reveals vast extent of ancient network www.nature.com/articles/d41...

‘Google Maps’ for Roman roads reveals vast extent of ancient network
A high-resolution digital map nearly doubles the known length of the ancient road network.
www.nature.com
November 10, 2025 at 8:47 AM
‘Google Maps’ for Roman roads reveals vast extent of ancient network www.nature.com/articles/d41...
One pathogen does not an epidemic make: A review of interacting contagions, diseases, beliefs, and stories arxiv.org/abs/2504.15053

One pathogen does not an epidemic make: A review of interacting contagions, diseases, beliefs, and stories
From pathogens and computer viruses to genes and memes, contagion models have found widespread utility across the natural and social sciences. Despite their success and breadth of adoption, the approa...
arxiv.org
November 10, 2025 at 8:43 AM
One pathogen does not an epidemic make: A review of interacting contagions, diseases, beliefs, and stories arxiv.org/abs/2504.15053
Mesoscale community organization governs epidemic onset and spread in metapopulations arxiv.org/abs/2504.05653

Mesoscale community organization governs epidemic onset and spread in metapopulations
Understanding how internal community structure shapes the course of epidemics remains a fundamental challenge in modeling real-world populations. Standard metapopulation models often assume uniform mi...
arxiv.org
November 10, 2025 at 8:41 AM
Mesoscale community organization governs epidemic onset and spread in metapopulations arxiv.org/abs/2504.05653
Predicting steady-state behavior in complex networks with graph neural networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Predicting steady-state behavior in complex networks with graph neural networks
In complex systems, information propagation can be defined as diffused or delocalized, weakly localized, and strongly localized. This study investigates the application of graph neural network models ...
link.aps.org
November 10, 2025 at 8:29 AM
Predicting steady-state behavior in complex networks with graph neural networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Emerging activity temporal hypergraph: A model for generating realistic time-varying hypergraphs link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Emerging activity temporal hypergraph: A model for generating realistic time-varying hypergraphs
Time-varying group interactions constitute the building blocks of many complex systems. The framework of temporal hypergraphs makes it possible to represent them by taking into account the higher-orde...
link.aps.org
November 10, 2025 at 8:25 AM
Emerging activity temporal hypergraph: A model for generating realistic time-varying hypergraphs link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Null models for comparing information decomposition across complex systems journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol...

Null models for comparing information decomposition across complex systems
Author summary How do complex systems process information? Perhaps more interestingly, when can we say two systems process information in the same way? Information-theoretic methods have been shown to...
journals.plos.org
November 6, 2025 at 10:38 AM
Null models for comparing information decomposition across complex systems journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol...
Intersectional inequalities in social ties | Science Advances www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
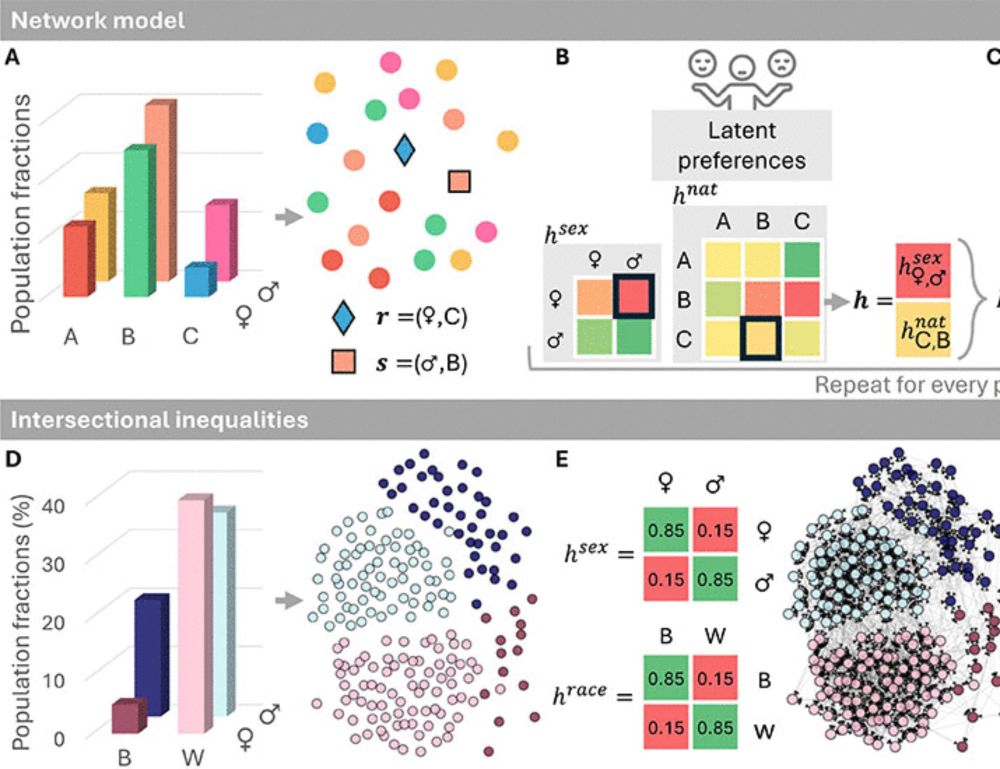
Intersectional inequalities in social ties
At identity intersections, inequality transforms, revealing network patterns that single-dimensional models fail to explain.
www.science.org
November 6, 2025 at 10:23 AM
Intersectional inequalities in social ties | Science Advances www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Scaling laws of human mobility persist during extreme floods arxiv.org/abs/2511.02783

Scaling laws of human mobility persist during extreme floods
Although a number of studies have investigated human mobility patterns during natural hazards, mechanistic models that capture mobility dynamics under large-scale perturbations, such as extreme floods...
arxiv.org
November 6, 2025 at 10:22 AM
Scaling laws of human mobility persist during extreme floods arxiv.org/abs/2511.02783
Higher-order shortest paths in hypergraphs link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Higher-order shortest paths in hypergraphs
One of the defining features of complex networks is the connectivity properties that we observe emerging from local interactions. Recently, hypergraphs have emerged as a versatile tool to model networ...
link.aps.org
November 6, 2025 at 10:21 AM
Higher-order shortest paths in hypergraphs link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Calibration of transmission-dynamic infectious disease models: A scoping review and reporting framework journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol...

Calibration of transmission-dynamic infectious disease models: A scoping review and reporting framework
Author summary Calibration, the identification of parameter values so that model outcomes are consistent with observed data or other evidence, is often employed in the process of obtaining model resul...
journals.plos.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:24 AM
Calibration of transmission-dynamic infectious disease models: A scoping review and reporting framework journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol...
Human Mobility in Epidemic Modeling arxiv.org/abs/2507.22799

Human Mobility in Epidemic Modeling
Human mobility forms the backbone of contact patterns through which infectious diseases propagate, fundamentally shaping the spatio-temporal dynamics of epidemics and pandemics. While traditional mode...
arxiv.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:20 AM
Human Mobility in Epidemic Modeling arxiv.org/abs/2507.22799
The Three Books of Science arxiv.org/abs/2511.00368

The Three Books of Science
We venture that the long evolution of science may be viewed as unfolding over three blurred epochs. The first epoch spans the slow, haphazard, error-ridden realization of scientific truths along with ...
arxiv.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:16 AM
The Three Books of Science arxiv.org/abs/2511.00368
Detectability threshold in weighted modular networks arxiv.org/abs/2511.00214

Detectability threshold in weighted modular networks
We study the necessary condition to detect, by means of spectral modularity optimization, the ground-truth partition in networks generated according to the weighted planted-partition model with two eq...
arxiv.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:15 AM
Detectability threshold in weighted modular networks arxiv.org/abs/2511.00214
Connectivity Structure and Dynamics of Nonlinear Recurrent Neural Networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...

Connectivity Structure and Dynamics of Nonlinear Recurrent Neural Networks
The structure of brain connectivity predicts collective neural activity, with a small number of connectivity features determining activity dimensionality, linking circuit architecture to network-level...
link.aps.org
November 5, 2025 at 8:14 AM
Connectivity Structure and Dynamics of Nonlinear Recurrent Neural Networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Reducibility of higher-order networks via information flow arxiv.org/abs/2404.08547

Reducibility of higher-order networks via information flow
Empirical complex systems can be characterized not only by pairwise interactions, but also by higher-order (group) interactions influencing collective phenomena, from metabolic reactions to epidemics....
arxiv.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:29 AM
Reducibility of higher-order networks via information flow arxiv.org/abs/2404.08547
Beyond Demographics: Behavioural Segmentation and Spatial Analytics to Enhance Visitor Experience at The British Museum arxiv.org/abs/2510.27542

Beyond Demographics: Behavioural Segmentation and Spatial Analytics to Enhance Visitor Experience at The British Museum
This study explores visitor behaviour at The British Museum using data science methods applied to novel sources, including audio guide usage logs and TripAdvisor reviews. Analysing 42,000 visitor jour...
arxiv.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:11 AM
Beyond Demographics: Behavioural Segmentation and Spatial Analytics to Enhance Visitor Experience at The British Museum arxiv.org/abs/2510.27542
Mapping Regional Disparities in Discounted Grocery Products arxiv.org/abs/2510.27493

Mapping Regional Disparities in Discounted Grocery Products
Food waste represents a major challenge to global climate resilience, accounting for almost 10\% of annual greenhouse gas emissions. The retail sector is a critical player, mediating product flows bet...
arxiv.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:09 AM
Mapping Regional Disparities in Discounted Grocery Products arxiv.org/abs/2510.27493
Polarization and echo chambers in Reddit's political discourse arxiv.org/abs/2510.27467

Polarization and echo chambers in Reddit's political discourse
Political debate nowadays takes place mainly on online social media, with election periods amplifying ideological engagement. Reddit is generally considered more resistant to polarization and echo cha...
arxiv.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:08 AM
Polarization and echo chambers in Reddit's political discourse arxiv.org/abs/2510.27467
Information theory for hypergraph similarity arxiv.org/abs/2510.27411

Information theory for hypergraph similarity
Comparing networks is essential for a number of downstream tasks, from clustering to anomaly detection. Despite higher-order interactions being critical for understanding the dynamics of complex syste...
arxiv.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:07 AM
Information theory for hypergraph similarity arxiv.org/abs/2510.27411
Mean-field game approach to epidemic propagation on networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Mean-field game approach to epidemic propagation on networks
We investigate an SIR model of epidemic propagation on networks in the context of mean-field games. In a real epidemic, individuals adjust their behavior depending on the epidemic level and the impact...
link.aps.org
November 4, 2025 at 8:04 AM
Mean-field game approach to epidemic propagation on networks link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Exploring the relationship between cancer incidence and the sustainable development goals through complex networks and machine learning epjdatascience.springeropen.com/articles/10....

Exploring the relationship between cancer incidence and the sustainable development goals through complex networks and machine learning - EPJ Data Science
The awareness that socioeconomic factors play a significant role in the potential onset of cancer is increasingly widespread; however, a clear understanding of the most influential factors is still la...
epjdatascience.springeropen.com
October 30, 2025 at 8:24 AM
Exploring the relationship between cancer incidence and the sustainable development goals through complex networks and machine learning epjdatascience.springeropen.com/articles/10....
Scale invariance and statistical significance in complex weighted networks arxiv.org/abs/2510.23964

Scale invariance and statistical significance in complex weighted networks
Most networks encountered in nature, society, and technology have weighted edges, representing the strength of the interaction/association between their vertices. Randomizing the structure of a networ...
arxiv.org
October 30, 2025 at 8:21 AM
Scale invariance and statistical significance in complex weighted networks arxiv.org/abs/2510.23964
Decomposing multivariate information rates in networks of random processes link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...
Decomposing multivariate information rates in networks of random processes
The partial information decomposition (PID) framework has emerged as a powerful tool for analyzing high-order interdependencies in complex network systems. However, its application to dynamic processe...
link.aps.org
October 30, 2025 at 8:19 AM
Decomposing multivariate information rates in networks of random processes link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/...

