
Morgan Wack
@morganwack.bsky.social
PostDoc at UZH. Formerly Clemson & UW. Technology & democracy, political misinformation, African politics, and LFC.
Here is the link to the full (open source) paper! 🔗
academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar... We welcome feedback & potential collaboration focused on how to counter emerging AI-driven disinformation campaigns!
academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar... We welcome feedback & potential collaboration focused on how to counter emerging AI-driven disinformation campaigns!
Generative propaganda: Evidence of AI’s impact from a state-backed disinformation campaign
Abstract. Can AI bolster state-backed propaganda campaigns, in practice? Growing use of AI and large language models has drawn attention to the potential f
academic.oup.com
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
Here is the link to the full (open source) paper! 🔗
academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar... We welcome feedback & potential collaboration focused on how to counter emerging AI-driven disinformation campaigns!
academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar... We welcome feedback & potential collaboration focused on how to counter emerging AI-driven disinformation campaigns!
Finding Three 📝: Even with the shift to AI, the persuasive potential and credibility of the articles persisted. This finding suggests that even in rapid scaling article production the website did not need to sacrifice its perceived authenticity or potential impact. 6/
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
Finding Three 📝: Even with the shift to AI, the persuasive potential and credibility of the articles persisted. This finding suggests that even in rapid scaling article production the website did not need to sacrifice its perceived authenticity or potential impact. 6/
Finding Two 📊: AI-use corresponded with greater topic breadth. By rewriting stories, the website covered more diverse subjects (from gun crime to the Ukraine invasion). Prompt leaks also suggest use of AI to rate potential materials by their alignment with campaign goals. 5/
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
Finding Two 📊: AI-use corresponded with greater topic breadth. By rewriting stories, the website covered more diverse subjects (from gun crime to the Ukraine invasion). Prompt leaks also suggest use of AI to rate potential materials by their alignment with campaign goals. 5/
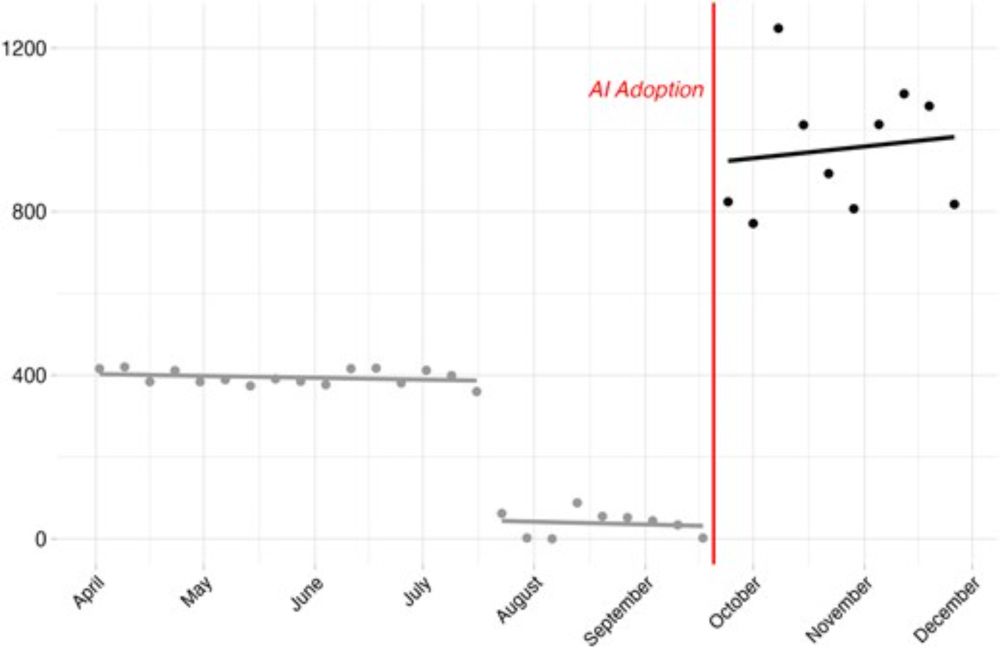
Finding One 📈: AI use significantly increased the quantity of disinformation. This aligns with the idea that generative models reduce the cost/time of writing, editing, and curating. Once the site adopted LLM tools, weekly post counts soared. 4/
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
Finding One 📈: AI use significantly increased the quantity of disinformation. This aligns with the idea that generative models reduce the cost/time of writing, editing, and curating. Once the site adopted LLM tools, weekly post counts soared. 4/
We focus on a site identified by the Clemson Forensics Hub that presented itself as a genuine U.S. news outlet but which was actually part of a Russian-affiliated influence operation. By pinpointing a transition away from human-editing to LLM-edited content, we show: 3/
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
We focus on a site identified by the Clemson Forensics Hub that presented itself as a genuine U.S. news outlet but which was actually part of a Russian-affiliated influence operation. By pinpointing a transition away from human-editing to LLM-edited content, we show: 3/
There have been growing concerns about the use of large language models (LLMs) in the production of disinformation, but real-world evidence has been difficult to track. Our paper provides a direct look at a Russian-linked campaign which used AI tools to target Americans. 2/
April 1, 2025 at 8:06 PM
There have been growing concerns about the use of large language models (LLMs) in the production of disinformation, but real-world evidence has been difficult to track. Our paper provides a direct look at a Russian-linked campaign which used AI tools to target Americans. 2/

