
Alex Chase 🧬🌋🌊
@microbomics.bsky.social
Assist Prof of Earth Sciences at SMU
Microbial ecologist 🔬🦠
English bulldog enthusiast 🐶🐾
Microbial ecologist 🔬🦠
English bulldog enthusiast 🐶🐾
I do a hybrid approach with interactive lectures using the white board and slides. Then I’ll assign primary lit reading and have them breakout into small groups for discussion questions on the other day of the week. Walk around and engage with each group. I love it 📚
November 5, 2025 at 2:08 PM
I do a hybrid approach with interactive lectures using the white board and slides. Then I’ll assign primary lit reading and have them breakout into small groups for discussion questions on the other day of the week. Walk around and engage with each group. I love it 📚
Details and application info:
🔗 smu.edu/dedman/academics/departments/earth-sciences/graduate
Funding + microbes = happiness.
DM or email if you’re ready to dive in.
🔗 smu.edu/dedman/academics/departments/earth-sciences/graduate
Funding + microbes = happiness.
DM or email if you’re ready to dive in.

Graduate Programs
smu.edu
October 30, 2025 at 6:13 PM
Details and application info:
🔗 smu.edu/dedman/academics/departments/earth-sciences/graduate
Funding + microbes = happiness.
DM or email if you’re ready to dive in.
🔗 smu.edu/dedman/academics/departments/earth-sciences/graduate
Funding + microbes = happiness.
DM or email if you’re ready to dive in.
We study how microbial lineages evolve and assemble linking genomes, metabolites, and ecological roles. Fieldwork, mass specs, metagenomes, and a bit of chaos.
🧬 PhDs are fully funded (tuition, stipend, the works). Additional competitive fellowships are available through SMU’s grad school.
🧬 PhDs are fully funded (tuition, stipend, the works). Additional competitive fellowships are available through SMU’s grad school.
October 30, 2025 at 6:13 PM
We study how microbial lineages evolve and assemble linking genomes, metabolites, and ecological roles. Fieldwork, mass specs, metagenomes, and a bit of chaos.
🧬 PhDs are fully funded (tuition, stipend, the works). Additional competitive fellowships are available through SMU’s grad school.
🧬 PhDs are fully funded (tuition, stipend, the works). Additional competitive fellowships are available through SMU’s grad school.
I somewhat agree with what you’re saying. But our point was that these terms are used interchangeably all. The. Time. And no one defines them (or at least consistently), especially when considering evolution in microbiomes. Personally, I like using biology to define, but this is a frame of ref 🤷🏻♂️
August 20, 2025 at 12:04 AM
I somewhat agree with what you’re saying. But our point was that these terms are used interchangeably all. The. Time. And no one defines them (or at least consistently), especially when considering evolution in microbiomes. Personally, I like using biology to define, but this is a frame of ref 🤷🏻♂️
If you want something very simple but does a great job visualizing. Just need input genbank files:
github.com/gamcil/clinker
github.com/gamcil/clinker
GitHub - gamcil/clinker: Gene cluster comparison figure generator
Gene cluster comparison figure generator. Contribute to gamcil/clinker development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
July 13, 2025 at 12:11 AM
If you want something very simple but does a great job visualizing. Just need input genbank files:
github.com/gamcil/clinker
github.com/gamcil/clinker
and another recent one giving some ecological context to RiPPs in the human gut: five AIPs effectively inhibit the biofilm formation of disease-associated pathogens
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
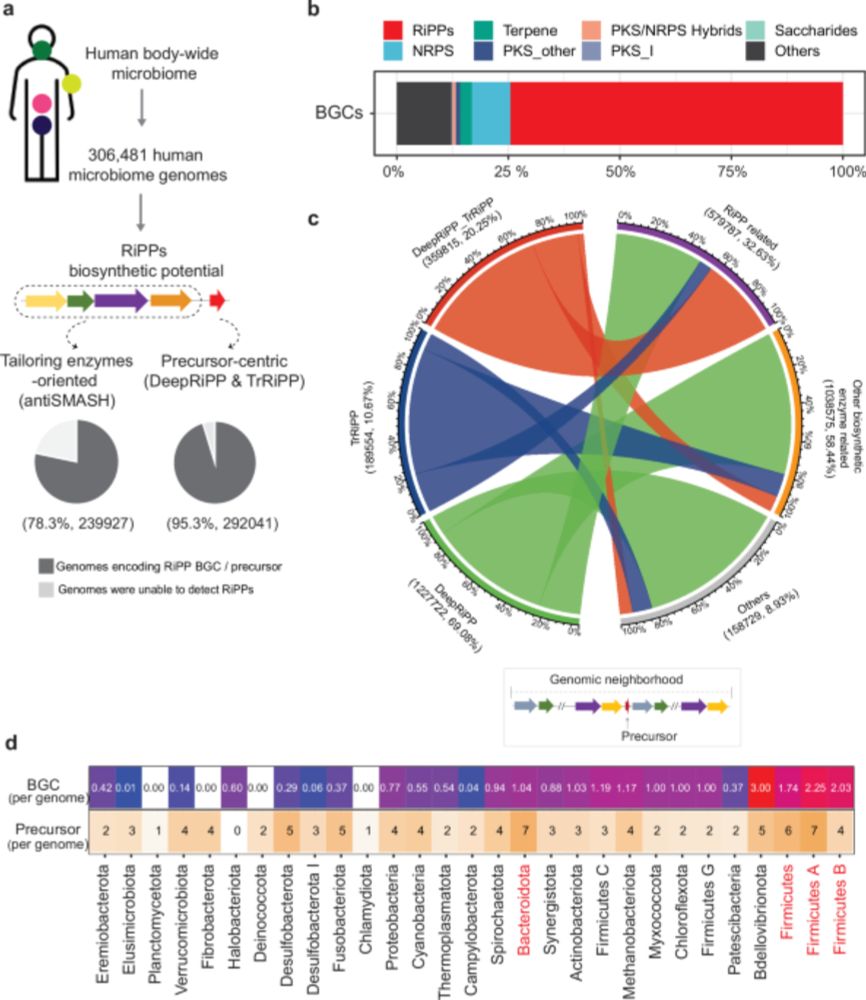
Large-scale biosynthetic analysis of human microbiomes reveals diverse protective ribosomal peptides - Nature Communications
Here, by analyzing 306481 microbial genomes from human-associated microbiomes, the authors reveal a largely unexplored biosynthetic landscape of ribosomal peptides (RiPPs), identifying protective pept...
www.nature.com
April 7, 2025 at 2:13 PM
and another recent one giving some ecological context to RiPPs in the human gut: five AIPs effectively inhibit the biofilm formation of disease-associated pathogens
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

