www.maraddatz.com
Stand with UC to protect our vital mission: www.universityofcalifornia.edu/get-involved...
Stand with UC to protect our vital mission: www.universityofcalifornia.edu/get-involved...
In summary, IL-6 may play a beneficial role in cardiovascular adaptation, and this may impact cardiovascular adaptation to exercise in patients taking an IL-6 inhibitor for RA. Read the full paper in this month’s issue of #JACCBTS! doi.org/10.1016/j.ja...
In summary, IL-6 may play a beneficial role in cardiovascular adaptation, and this may impact cardiovascular adaptation to exercise in patients taking an IL-6 inhibitor for RA. Read the full paper in this month’s issue of #JACCBTS! doi.org/10.1016/j.ja...
Given the reported beneficial effects of IL-6i in coronary disease (doi.org/10.1016/j.ja...) & ongoing related trials in cardiovascular patients (e.g., clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT061...), this work reminds us that IL-6 biology is complex. There may be a right time, place, & amount for IL-6. 🤔

Given the reported beneficial effects of IL-6i in coronary disease (doi.org/10.1016/j.ja...) & ongoing related trials in cardiovascular patients (e.g., clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT061...), this work reminds us that IL-6 biology is complex. There may be a right time, place, & amount for IL-6. 🤔
While the LV mass and stroke volume increases were only significant in the TNFi group, only the IL-6i group had a significant ⬆️ in relative VO2 peak. This is counterintuitive given the role of cardiac output in VO2, but may be explained by positive effects of IL-6i outside of cardiac remodeling.
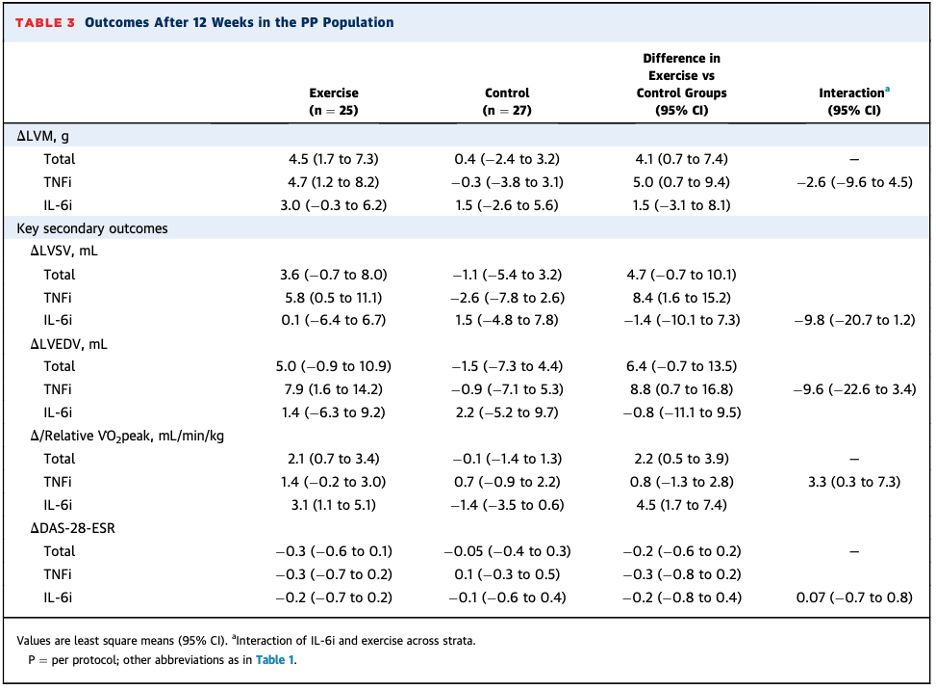
While the LV mass and stroke volume increases were only significant in the TNFi group, only the IL-6i group had a significant ⬆️ in relative VO2 peak. This is counterintuitive given the role of cardiac output in VO2, but may be explained by positive effects of IL-6i outside of cardiac remodeling.
After 12 weeks of exercise, they underwent repeat testing. There was a physiologic ⬆️ in LV mass in the exercise group among those using a TNFi, but not among those using an IL-6i. This supports the authors’ hypothesis that IL-6 signaling is important for exercise adaptation in RA patients. 💭
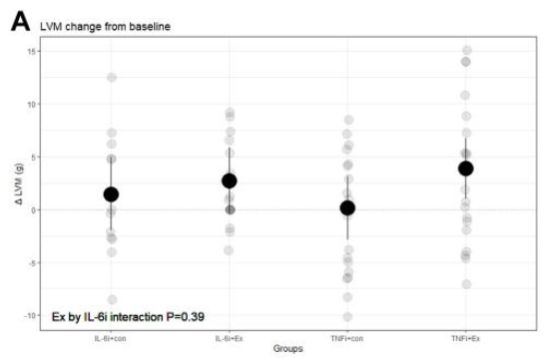
After 12 weeks of exercise, they underwent repeat testing. There was a physiologic ⬆️ in LV mass in the exercise group among those using a TNFi, but not among those using an IL-6i. This supports the authors’ hypothesis that IL-6 signaling is important for exercise adaptation in RA patients. 💭
Prior to the exercise regimen, patients underwent cardiac MRI and metabolic testing. As seen here and further summarized in the full manuscript, patients had normal cardiac MRI metrics, low rates of cardiac comorbidities, and below average fitness as measured by VO2 peak. 😮💨
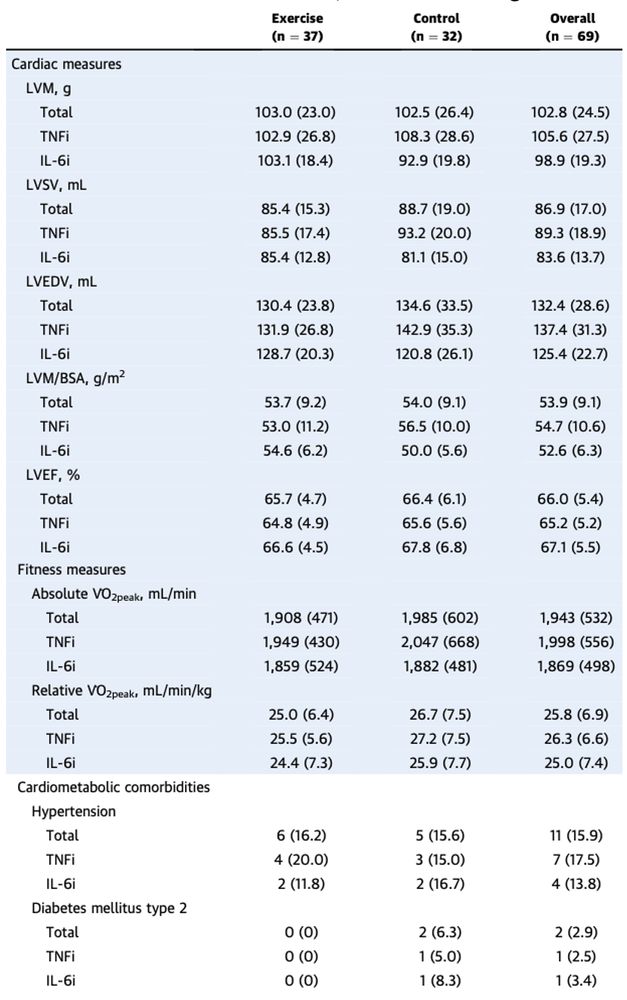
Prior to the exercise regimen, patients underwent cardiac MRI and metabolic testing. As seen here and further summarized in the full manuscript, patients had normal cardiac MRI metrics, low rates of cardiac comorbidities, and below average fitness as measured by VO2 peak. 😮💨
Patients were then randomized, with half of the patients undergoing supervised 45-minute exercise sessions on an ergometer bicycle three times a week in addition to their usual activity. 🚴📆
Patients were then randomized, with half of the patients undergoing supervised 45-minute exercise sessions on an ergometer bicycle three times a week in addition to their usual activity. 🚴📆
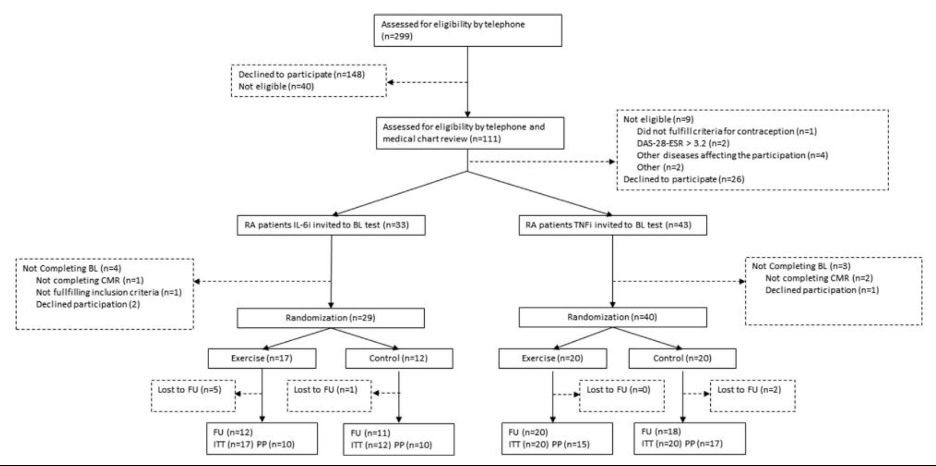
They enrolled pts 18-69 yrs old with RA stably treated with a TNFi or IL-6i for >4 months. Their RA had to be well-controlled ✅ measured by DAS28-ESR score & minimal corticosteroid use. Importantly, pts receiving IL-6i had more often & more frequently tried other prior biologics for RA control.
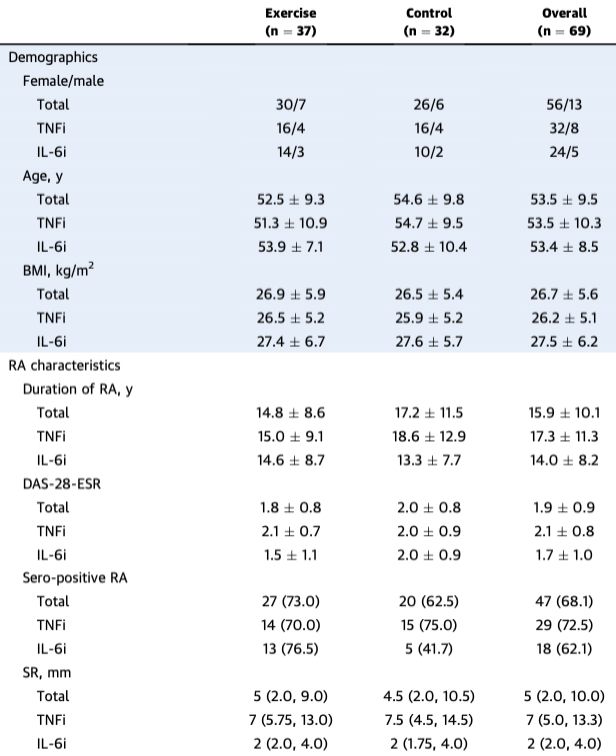
They enrolled pts 18-69 yrs old with RA stably treated with a TNFi or IL-6i for >4 months. Their RA had to be well-controlled ✅ measured by DAS28-ESR score & minimal corticosteroid use. Importantly, pts receiving IL-6i had more often & more frequently tried other prior biologics for RA control.
Given previously described beneficial effects of IL-6 during exercise (onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...), the authors hypothesized that patients receiving TNF inhibitors would see more beneficial cardiovascular adaptation from guided exercise than those receiving IL-6 inhibitors. 🫀💪

Given previously described beneficial effects of IL-6 during exercise (onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...), the authors hypothesized that patients receiving TNF inhibitors would see more beneficial cardiovascular adaptation from guided exercise than those receiving IL-6 inhibitors. 🫀💪
In summary, diseased AVICs have mitochondrial dysfunction, and spermidine supplementation or DNMT1 inhibition might hold promise as therapeutics to reverse this process and treat valve calcification. Read the full paper in this month’s issue of #JACCBTS! www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

In summary, diseased AVICs have mitochondrial dysfunction, and spermidine supplementation or DNMT1 inhibition might hold promise as therapeutics to reverse this process and treat valve calcification. Read the full paper in this month’s issue of #JACCBTS! www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
The authors finally attempted to treat this same pathway through DNMT1 inhibition. They show that DNMT1 is ⬆️ with disease in human valves, as anticipated. Use of a DNMT1 inhibitor (5-Azacytidine) in diseased human AVICs increases SIRT1, PPARG, and markers of mitochondrial biogenesis. 📈
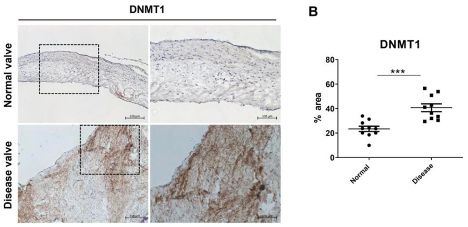
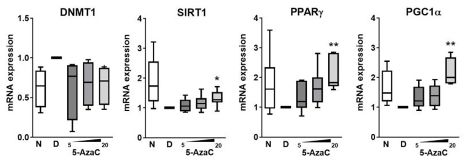
The authors finally attempted to treat this same pathway through DNMT1 inhibition. They show that DNMT1 is ⬆️ with disease in human valves, as anticipated. Use of a DNMT1 inhibitor (5-Azacytidine) in diseased human AVICs increases SIRT1, PPARG, and markers of mitochondrial biogenesis. 📈
Returning to the initial mitochondrial phenotype, they show that spermidine improves mitochondrial function, even beyond healthy AVIC function. 🪃
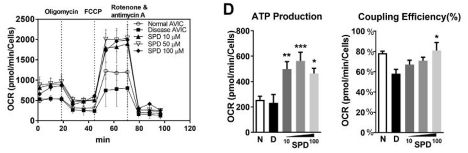
Returning to the initial mitochondrial phenotype, they show that spermidine improves mitochondrial function, even beyond healthy AVIC function. 🪃
Back in the dish, they showed that spermidine induces the same molecular changes in AVICs. 🧫
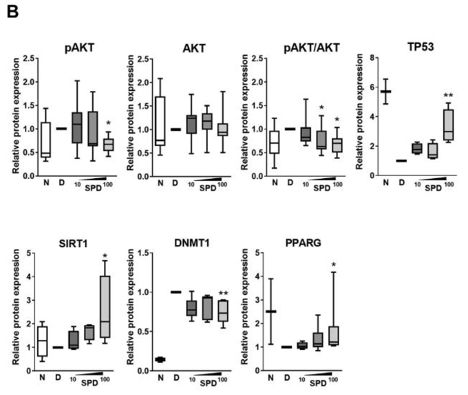
Back in the dish, they showed that spermidine induces the same molecular changes in AVICs. 🧫
They confirmed the expression patterns of TP53 ⬆️, SIRT1 ⬆️, DNMT1 ⬇️, and PPARG ⬆️ directly in the AVs from mice treated with spermidine or water.
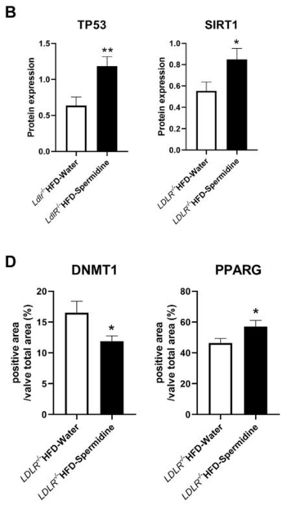
They confirmed the expression patterns of TP53 ⬆️, SIRT1 ⬆️, DNMT1 ⬇️, and PPARG ⬆️ directly in the AVs from mice treated with spermidine or water.
They next performed LC-MS proteomics on AVs from 🐭 with and without spermidine supplementation. They identified activation of the oxidative phosphorylation protein pathway. Further network analysis identified DNMT1 as a ⬇️ node, and PPARG, SIRT1 and TP53 as ⬆️ with spermidine.
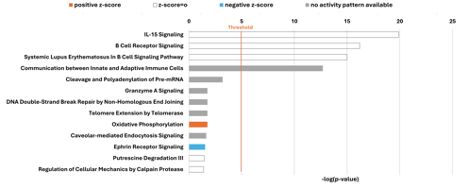
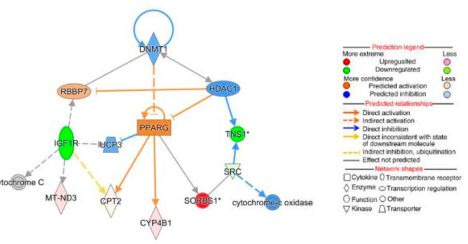
They next performed LC-MS proteomics on AVs from 🐭 with and without spermidine supplementation. They identified activation of the oxidative phosphorylation protein pathway. Further network analysis identified DNMT1 as a ⬇️ node, and PPARG, SIRT1 and TP53 as ⬆️ with spermidine.
They translated this in vitro finding to an Ldlr-/- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed 🐭 model of CAVD and found improved echocardiographic metrics of aortic stenosis (AV peak gradient) and ⬇️ valve calcification and fibrosis with spermidine treatment.
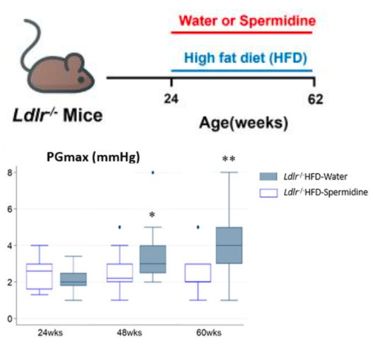
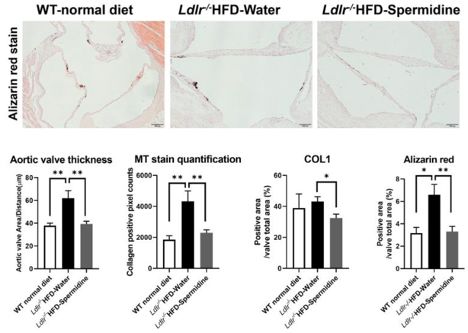
They translated this in vitro finding to an Ldlr-/- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed 🐭 model of CAVD and found improved echocardiographic metrics of aortic stenosis (AV peak gradient) and ⬇️ valve calcification and fibrosis with spermidine treatment.
The authors hypothesized that spermidine could be used to augment mitochondrial function (💪 read more: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29371440/). They first showed that spermidine ⬇️ expression of calcification-related genes, both in diseased AVICs and in osteogenic media. 🧫
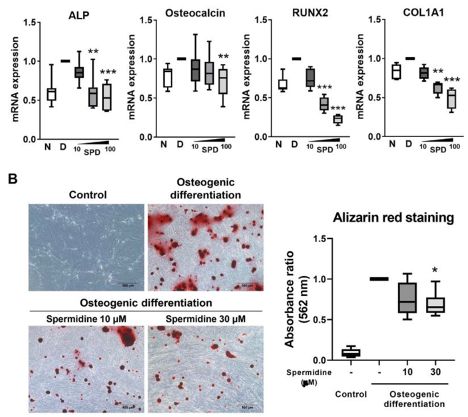
The authors hypothesized that spermidine could be used to augment mitochondrial function (💪 read more: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29371440/). They first showed that spermidine ⬇️ expression of calcification-related genes, both in diseased AVICs and in osteogenic media. 🧫

