
Josh Fowler
@joshuacfowler.bsky.social
population demography, range limits, mutualism, plants and fungi | postdoc at the University of Miami | He/Him
https://joshuacfowler.github.io/
https://joshuacfowler.github.io/
Newly published in @globalchangebio.bsky.social, we look within seeds of historic herbarium specimens for changes in the prevalence of beneficial fungal symbionts in response to climate change drivers. onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...

October 30, 2025 at 5:04 PM
Newly published in @globalchangebio.bsky.social, we look within seeds of historic herbarium specimens for changes in the prevalence of beneficial fungal symbionts in response to climate change drivers. onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
Reposted by Josh Fowler
Check out our new Tansley review on climate, plants, and microbes! I enjoyed working with a team of friendly and knowledgeable scientists.
@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....
@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....

Unraveling complexity in climate change effects on beneficial plant–microbe interactions: mechanisms, resilience, and future directions
Plant microbiomes have the potential to mitigate the impacts of climate change, yet both the complexity of climate change and the complexity of plant–microbe interactions make applications and future....
doi.org
October 14, 2025 at 3:05 PM
Check out our new Tansley review on climate, plants, and microbes! I enjoyed working with a team of friendly and knowledgeable scientists.
@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....
@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....
Reposted by Josh Fowler
My 2nd dissertation chapter is out in Plant, Cell, & Environment!
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
June 2, 2025 at 1:12 PM
My 2nd dissertation chapter is out in Plant, Cell, & Environment!
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
Reposted by Josh Fowler
Excited to share our paper in @pnas.org with Aldo Compagnoni and Tom Miller !
Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

Forecasting range shifts of dioecious plants under climate change | PNAS
Global climate change has triggered an urgent need for predicting the reorganization
of Earth’s biodiversity. For dioecious species (those with sep...
www.pnas.org
May 20, 2025 at 6:22 PM
Excited to share our paper in @pnas.org with Aldo Compagnoni and Tom Miller !
Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
Hot off the digital presses of the Highlands News-Sun: www.midfloridanewspapers.com/highlands_ne...

Florida citrus lands offer hope for habitat recovery
Florida citrus production has been in decline due to widespread citrus greening disease introduced as early as 2004, also known as Huanglongbing (HLB). But is there some lemonade to be
www.midfloridanewspapers.com
April 22, 2025 at 5:19 PM
Hot off the digital presses of the Highlands News-Sun: www.midfloridanewspapers.com/highlands_ne...
Reposted by Josh Fowler
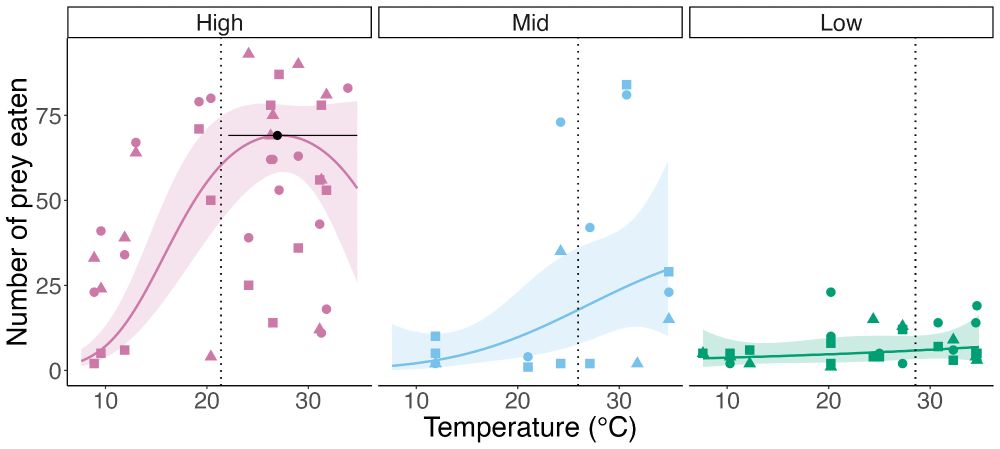
To understand how climate change affects natural ecosystems we need to know how warming influences species interactions. In our newest paper we show that predator-prey interactions fundamentally change across latitude leading to context dependent effects of warming. 🧪
doi.org/10.1111/oik....
doi.org/10.1111/oik....
January 8, 2025 at 6:07 PM
To understand how climate change affects natural ecosystems we need to know how warming influences species interactions. In our newest paper we show that predator-prey interactions fundamentally change across latitude leading to context dependent effects of warming. 🧪
doi.org/10.1111/oik....
doi.org/10.1111/oik....
Reposted by Josh Fowler
My dissertation chapter is in Ecology Letters!
We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....
We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....

Central Taxa Are Keystone Microbes During Early Succession
For decades, microbiome network theory has predicted that highly connected ‘hub’ taxa act as keystone species that disproportionately affect their communities. However, this has never been empiricall...
doi.org
December 31, 2024 at 8:36 PM
My dissertation chapter is in Ecology Letters!
We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....
We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....

