
Jake Scott, MD
@jakescottmd.bsky.social
Infection diseases doctor | Stanford Clinical Associate Professor
Focused on vaccines, data transparency, and antimicrobial stewardship.
Views my own.
Focused on vaccines, data transparency, and antimicrobial stewardship.
Views my own.
Barriers include availability, coverage, and awareness - all addressable through policy and system-level changes.
November 7, 2025 at 11:58 PM
Barriers include availability, coverage, and awareness - all addressable through policy and system-level changes.
In summary: high-dose and adjuvanted flu vaccines provide substantially better protection for older adults. This isn't a small improvement. We're talking about real differences that translate directly to fewer hospitalizations and deaths. Yet many older adults still get standard-dose vaccines.
November 7, 2025 at 10:44 PM
In summary: high-dose and adjuvanted flu vaccines provide substantially better protection for older adults. This isn't a small improvement. We're talking about real differences that translate directly to fewer hospitalizations and deaths. Yet many older adults still get standard-dose vaccines.
When we pooled all studies of older adults, overall effectiveness was just 42%. Why? Most studies used standard-dose vaccines. We could potentially prevent thousands more hospitalizations just by using the enhanced vaccines that already exist.
4/
4/

November 7, 2025 at 10:44 PM
When we pooled all studies of older adults, overall effectiveness was just 42%. Why? Most studies used standard-dose vaccines. We could potentially prevent thousands more hospitalizations just by using the enhanced vaccines that already exist.
4/
4/
This builds on the DANFLU-2 trial which found high-dose vaccine was 43.6% better than standard-dose at preventing flu hospitalizations. The GALFLU trial in Spain found 23.7% better performance.
3/
www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
3/
www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
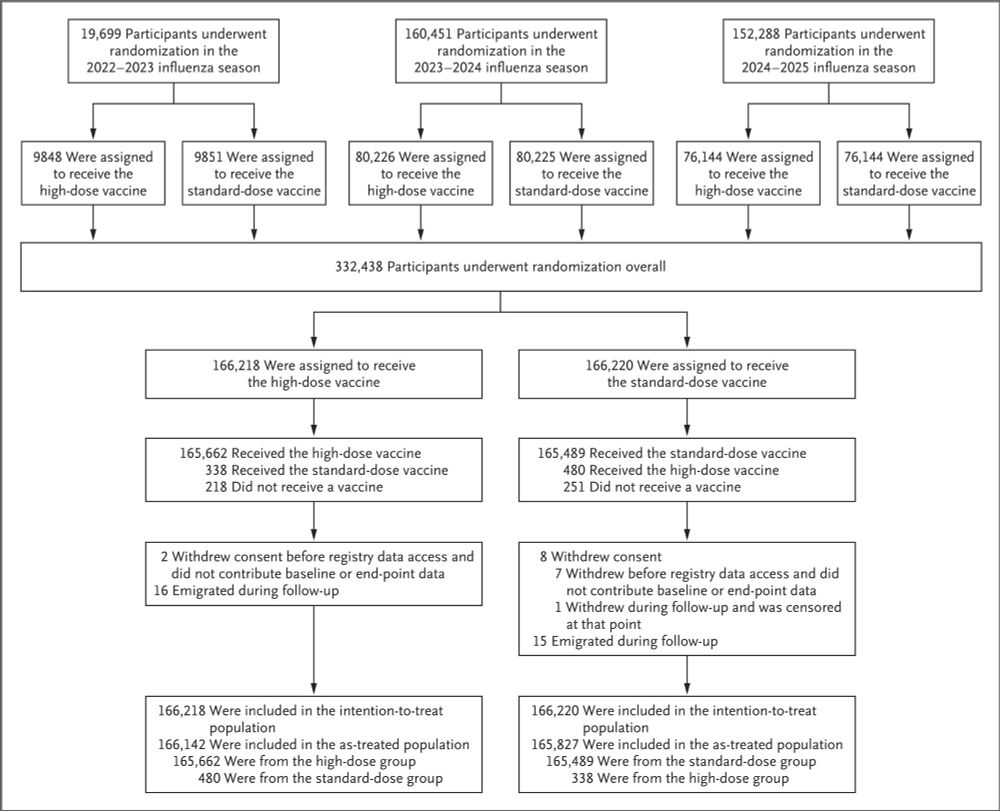
High-Dose Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness against Hospitalization in Older Adults | NEJM
High-dose inactivated influenza vaccine has been shown to provide protection against influenza that is superior to that with the standard dose. However, data from individually randomized trials on ...
www.nejm.org
November 7, 2025 at 10:44 PM
This builds on the DANFLU-2 trial which found high-dose vaccine was 43.6% better than standard-dose at preventing flu hospitalizations. The GALFLU trial in Spain found 23.7% better performance.
3/
www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
3/
www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
The head-to-head comparison from Denmark 2024/25 season:
High-dose (Efluelda): 53% effective
Adjuvanted (Fluad): 47% effective
Standard-dose: 36% effective
Against hospitalization with lab-confirmed flu A.
2/
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
High-dose (Efluelda): 53% effective
Adjuvanted (Fluad): 47% effective
Standard-dose: 36% effective
Against hospitalization with lab-confirmed flu A.
2/
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...

Enhanced influenza vaccines impact effectiveness in individuals aged 65 years and older, Denmark, 2024/25 influenza season up to 4 March 2025
During the 2024/25 influenza season, enhanced and standard-dose influenza vaccines were available for individuals aged 65 and older. Compared with the standard-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV), the adjuvanted QIV was significantly more ...
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
November 7, 2025 at 10:44 PM
The head-to-head comparison from Denmark 2024/25 season:
High-dose (Efluelda): 53% effective
Adjuvanted (Fluad): 47% effective
Standard-dose: 36% effective
Against hospitalization with lab-confirmed flu A.
2/
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
High-dose (Efluelda): 53% effective
Adjuvanted (Fluad): 47% effective
Standard-dose: 36% effective
Against hospitalization with lab-confirmed flu A.
2/
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC...
As I wrote, "I'm grateful to my co-authors for their dedication to this enormous undertaking, and to the editors at the @nejm.org who recognized the urgency of this work and shepherded it through publication with exceptional efficiency and care."
And huge thanks to @mtosterholm.bsky.social
And huge thanks to @mtosterholm.bsky.social
October 31, 2025 at 7:53 PM
As I wrote, "I'm grateful to my co-authors for their dedication to this enormous undertaking, and to the editors at the @nejm.org who recognized the urgency of this work and shepherded it through publication with exceptional efficiency and care."
And huge thanks to @mtosterholm.bsky.social
And huge thanks to @mtosterholm.bsky.social
Aydillo et al. 2024, which is included in our Supplemental Table S11. The main NEJM text summarizes this as 'increased reactogenicity' without the specific percentages due to space constraints. www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....

Updated Evidence for Covid-19, RSV, and Influenza Vaccines for 2025–2026 | NEJM
Changes in the vaccine advisory process in the United States have disrupted immunization
guidance, which reinforces the need for independent evidence review to inform decisions
regarding immunizati...
www.nejm.org
October 30, 2025 at 7:48 PM
Aydillo et al. 2024, which is included in our Supplemental Table S11. The main NEJM text summarizes this as 'increased reactogenicity' without the specific percentages due to space constraints. www.nejm.org/doi/full/10....
15/ These immunizations show consistent effectiveness and safety, reducing risk of hospitalization across populations. Our synthesis underscores the enduring value of vaccination as preventive care and demonstrates that rigorous, evidence-based guidance can continue during institutional disruption.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
15/ These immunizations show consistent effectiveness and safety, reducing risk of hospitalization across populations. Our synthesis underscores the enduring value of vaccination as preventive care and demonstrates that rigorous, evidence-based guidance can continue during institutional disruption.
14/ Coadministration:
All combinations showed non-inferior immune responses. COVID+flu: more side effects (42-46% vs 18%) but mild. Triple vaccination (COVID+RSV+flu) met immunogenicity goals. No serious safety signals - no myocarditis, pericarditis, or stroke in any coadmin RCTs."
All combinations showed non-inferior immune responses. COVID+flu: more side effects (42-46% vs 18%) but mild. Triple vaccination (COVID+RSV+flu) met immunogenicity goals. No serious safety signals - no myocarditis, pericarditis, or stroke in any coadmin RCTs."
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
14/ Coadministration:
All combinations showed non-inferior immune responses. COVID+flu: more side effects (42-46% vs 18%) but mild. Triple vaccination (COVID+RSV+flu) met immunogenicity goals. No serious safety signals - no myocarditis, pericarditis, or stroke in any coadmin RCTs."
All combinations showed non-inferior immune responses. COVID+flu: more side effects (42-46% vs 18%) but mild. Triple vaccination (COVID+RSV+flu) met immunogenicity goals. No serious safety signals - no myocarditis, pericarditis, or stroke in any coadmin RCTs."
13/ Influenza safety reassuring:
No GBS signal in older adults. Mixed stroke findings - one Medicare study found small risk, but Canadian cohort (3.7 million doses) showed 34% reduction.
Pregnancy: protective associations with some outcomes, no safety concerns.
No GBS signal in older adults. Mixed stroke findings - one Medicare study found small risk, but Canadian cohort (3.7 million doses) showed 34% reduction.
Pregnancy: protective associations with some outcomes, no safety concerns.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
13/ Influenza safety reassuring:
No GBS signal in older adults. Mixed stroke findings - one Medicare study found small risk, but Canadian cohort (3.7 million doses) showed 34% reduction.
Pregnancy: protective associations with some outcomes, no safety concerns.
No GBS signal in older adults. Mixed stroke findings - one Medicare study found small risk, but Canadian cohort (3.7 million doses) showed 34% reduction.
Pregnancy: protective associations with some outcomes, no safety concerns.
12/ Influenza VE consistent with 15-year patterns:
Pooled VE against hospitalization: children 67%, adults 18-64: 48%, ≥65: 42% (standard) vs 53% (high-dose). 2023-24 confirmed stability: overall 44% outpatient, 40% hospitalization. Highest against B/Victoria (74%).
Pooled VE against hospitalization: children 67%, adults 18-64: 48%, ≥65: 42% (standard) vs 53% (high-dose). 2023-24 confirmed stability: overall 44% outpatient, 40% hospitalization. Highest against B/Victoria (74%).

October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
12/ Influenza VE consistent with 15-year patterns:
Pooled VE against hospitalization: children 67%, adults 18-64: 48%, ≥65: 42% (standard) vs 53% (high-dose). 2023-24 confirmed stability: overall 44% outpatient, 40% hospitalization. Highest against B/Victoria (74%).
Pooled VE against hospitalization: children 67%, adults 18-64: 48%, ≥65: 42% (standard) vs 53% (high-dose). 2023-24 confirmed stability: overall 44% outpatient, 40% hospitalization. Highest against B/Victoria (74%).
11/ Nirsevimab well-tolerated:
HARMONIE trial reported treatment-related events in just 2.1% of recipients. No safety concerns in observational studies across multiple countries. Maternal RSVpreF showed no association with stillbirth, congenital anomalies, or hypertensive disorders.
HARMONIE trial reported treatment-related events in just 2.1% of recipients. No safety concerns in observational studies across multiple countries. Maternal RSVpreF showed no association with stillbirth, congenital anomalies, or hypertensive disorders.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
11/ Nirsevimab well-tolerated:
HARMONIE trial reported treatment-related events in just 2.1% of recipients. No safety concerns in observational studies across multiple countries. Maternal RSVpreF showed no association with stillbirth, congenital anomalies, or hypertensive disorders.
HARMONIE trial reported treatment-related events in just 2.1% of recipients. No safety concerns in observational studies across multiple countries. Maternal RSVpreF showed no association with stillbirth, congenital anomalies, or hypertensive disorders.
10/ Maternal RSVpreF and preterm birth:
MATISSE trial showed 5.7% vs 4.7% (not powered for comparison). But subsequent studies found NO association when given at 32-36 weeks - Jin Hsieh (aRR 1.01) and Blauvelt (aOR 1.03). Current 32-36 week recommendation appears safe.
MATISSE trial showed 5.7% vs 4.7% (not powered for comparison). But subsequent studies found NO association when given at 32-36 weeks - Jin Hsieh (aRR 1.01) and Blauvelt (aOR 1.03). Current 32-36 week recommendation appears safe.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
10/ Maternal RSVpreF and preterm birth:
MATISSE trial showed 5.7% vs 4.7% (not powered for comparison). But subsequent studies found NO association when given at 32-36 weeks - Jin Hsieh (aRR 1.01) and Blauvelt (aOR 1.03). Current 32-36 week recommendation appears safe.
MATISSE trial showed 5.7% vs 4.7% (not powered for comparison). But subsequent studies found NO association when given at 32-36 weeks - Jin Hsieh (aRR 1.01) and Blauvelt (aOR 1.03). Current 32-36 week recommendation appears safe.
9/ Adult RSV vaccines and GBS:
Fry et al. found 18.2 excess cases/million (RSVpreF) vs 5.2 (RSVPreF3-AS01, not significant). FDA's 2024 analysis: ~9/million for RSVpreF. Prior ACIP considered risk equivalent. Both vaccines now carry FDA GBS warnings.
Fry et al. found 18.2 excess cases/million (RSVpreF) vs 5.2 (RSVPreF3-AS01, not significant). FDA's 2024 analysis: ~9/million for RSVpreF. Prior ACIP considered risk equivalent. Both vaccines now carry FDA GBS warnings.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
9/ Adult RSV vaccines and GBS:
Fry et al. found 18.2 excess cases/million (RSVpreF) vs 5.2 (RSVPreF3-AS01, not significant). FDA's 2024 analysis: ~9/million for RSVpreF. Prior ACIP considered risk equivalent. Both vaccines now carry FDA GBS warnings.
Fry et al. found 18.2 excess cases/million (RSVpreF) vs 5.2 (RSVPreF3-AS01, not significant). FDA's 2024 analysis: ~9/million for RSVpreF. Prior ACIP considered risk equivalent. Both vaccines now carry FDA GBS warnings.
8/ RSV prevention first became available in 2023. Three approaches:
Maternal vaccination 68% effective protecting infants from hospitalization.
Nirsevimab (monoclonal antibody) 83% in infants.
Adult vaccines 79% effective ≥60 years.
Maternal vaccination 68% effective protecting infants from hospitalization.
Nirsevimab (monoclonal antibody) 83% in infants.
Adult vaccines 79% effective ≥60 years.

October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
8/ RSV prevention first became available in 2023. Three approaches:
Maternal vaccination 68% effective protecting infants from hospitalization.
Nirsevimab (monoclonal antibody) 83% in infants.
Adult vaccines 79% effective ≥60 years.
Maternal vaccination 68% effective protecting infants from hospitalization.
Nirsevimab (monoclonal antibody) 83% in infants.
Adult vaccines 79% effective ≥60 years.
7/ Guillain-Barré syndrome:
Most mRNA vaccine studies found no association. Some conflicting data exists (e.g., one study showed elevated risk with mRNA-1273 in younger adults), but weight of evidence from large multinational studies shows no consistent mRNA signal.
Most mRNA vaccine studies found no association. Some conflicting data exists (e.g., one study showed elevated risk with mRNA-1273 in younger adults), but weight of evidence from large multinational studies shows no consistent mRNA signal.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
7/ Guillain-Barré syndrome:
Most mRNA vaccine studies found no association. Some conflicting data exists (e.g., one study showed elevated risk with mRNA-1273 in younger adults), but weight of evidence from large multinational studies shows no consistent mRNA signal.
Most mRNA vaccine studies found no association. Some conflicting data exists (e.g., one study showed elevated risk with mRNA-1273 in younger adults), but weight of evidence from large multinational studies shows no consistent mRNA signal.
6/ Stroke findings:
Most studies found no association or protective effects. Initial signal with bivalent boosters in 65+ (especially with flu coadmin) attenuated as data accumulated. Context crucial: SARS-CoV-2 infection itself increases stroke risk 3.5-fold - far exceeding any vaccine signal.
Most studies found no association or protective effects. Initial signal with bivalent boosters in 65+ (especially with flu coadmin) attenuated as data accumulated. Context crucial: SARS-CoV-2 infection itself increases stroke risk 3.5-fold - far exceeding any vaccine signal.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
6/ Stroke findings:
Most studies found no association or protective effects. Initial signal with bivalent boosters in 65+ (especially with flu coadmin) attenuated as data accumulated. Context crucial: SARS-CoV-2 infection itself increases stroke risk 3.5-fold - far exceeding any vaccine signal.
Most studies found no association or protective effects. Initial signal with bivalent boosters in 65+ (especially with flu coadmin) attenuated as data accumulated. Context crucial: SARS-CoV-2 infection itself increases stroke risk 3.5-fold - far exceeding any vaccine signal.
5/ Pregnancy data across 7 observational studies tracking millions:
No increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital anomalies. Evidence of protective associations: lower preterm birth (OR 0.72-0.93), reduced low birthweight (aOR 0.86). These are large, population-level analyses.
No increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital anomalies. Evidence of protective associations: lower preterm birth (OR 0.72-0.93), reduced low birthweight (aOR 0.86). These are large, population-level analyses.
October 30, 2025 at 4:12 PM
5/ Pregnancy data across 7 observational studies tracking millions:
No increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital anomalies. Evidence of protective associations: lower preterm birth (OR 0.72-0.93), reduced low birthweight (aOR 0.86). These are large, population-level analyses.
No increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital anomalies. Evidence of protective associations: lower preterm birth (OR 0.72-0.93), reduced low birthweight (aOR 0.86). These are large, population-level analyses.

