@idoamitlab.bsky.social
Single Cell Gescheft @WeizmannScience
http://www.weizmann.ac.il/immunology/AmitLab/front
http://www.weizmann.ac.il/immunology/AmitLab/front
See you in Boston in October!
@idoamitlab.bsky.social , @jonykipnis.bsky.social , @quintanalab.bsky.social, @bethstevenslab.bsky.social
@idoamitlab.bsky.social , @jonykipnis.bsky.social , @quintanalab.bsky.social, @bethstevenslab.bsky.social
April 16, 2025 at 9:19 AM
See you in Boston in October!
@idoamitlab.bsky.social , @jonykipnis.bsky.social , @quintanalab.bsky.social, @bethstevenslab.bsky.social
@idoamitlab.bsky.social , @jonykipnis.bsky.social , @quintanalab.bsky.social, @bethstevenslab.bsky.social
Thank you Carlos! 🙏🏻
April 12, 2025 at 12:22 PM
Thank you Carlos! 🙏🏻
Finally, huge thanks to our collaborators @yuvalshap.bsky.social, @dahanlab.bsky.social, all of our co-authors, and the @cp-cancercell.bsky.social editorial team and reviewers for their constructive feedback! (20/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
Finally, huge thanks to our collaborators @yuvalshap.bsky.social, @dahanlab.bsky.social, all of our co-authors, and the @cp-cancercell.bsky.social editorial team and reviewers for their constructive feedback! (20/20)
In summary, our research established the blueprint of tumor macrophages and defined Zeb2 as a master switch controlling the TAM program, with implications for clinical translation and TAM-targeted immunotherapy. (19/20)

April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
In summary, our research established the blueprint of tumor macrophages and defined Zeb2 as a master switch controlling the TAM program, with implications for clinical translation and TAM-targeted immunotherapy. (19/20)
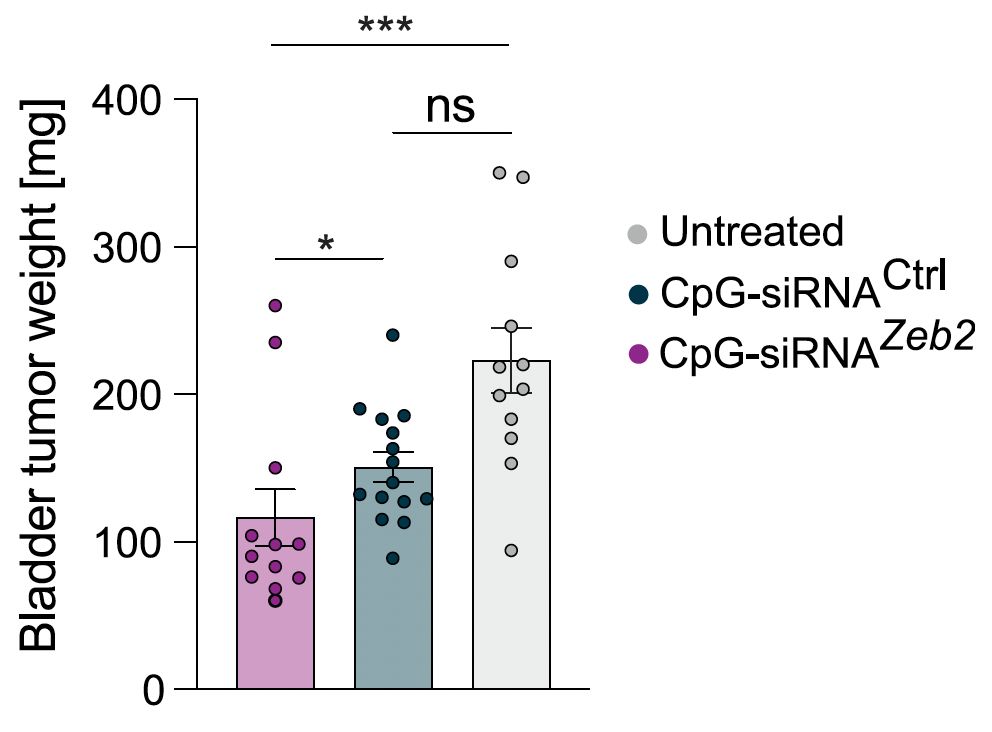
Among the tumor models we tested, we used an orthotopic bladder cancer model and found that intravesical treatment with CpG-conjugated Zeb2 siRNA showed robust tumor control, with the potential to replace conventional BCG therapy. (18/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
Among the tumor models we tested, we used an orthotopic bladder cancer model and found that intravesical treatment with CpG-conjugated Zeb2 siRNA showed robust tumor control, with the potential to replace conventional BCG therapy. (18/20)
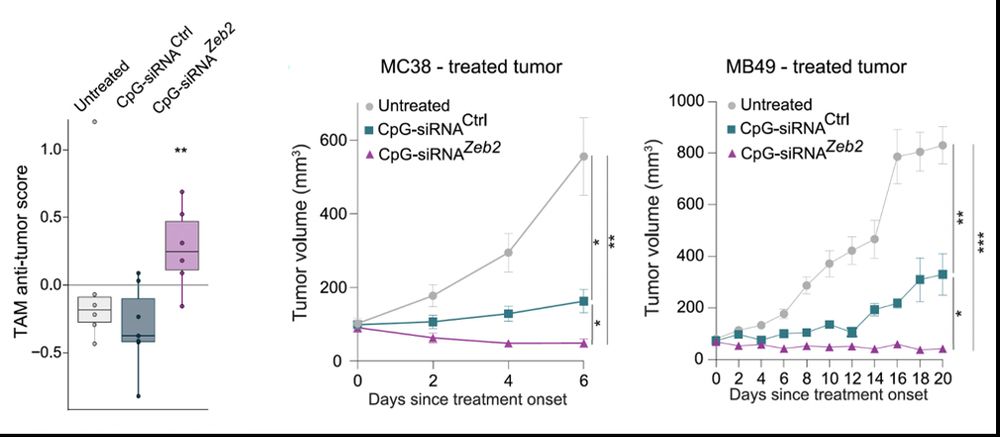
By design, CpG alone activates inflammatory pathways in TAMs - but adding Zeb2 silencing improved significantly TAM reprogramming and tumor control across different tumor models. (17/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
By design, CpG alone activates inflammatory pathways in TAMs - but adding Zeb2 silencing improved significantly TAM reprogramming and tumor control across different tumor models. (17/20)
To evaluate the in vivo impact of targeting Zeb2, and since TFs are not easily targeted - we teamed up with the Kortylewski lab to design a CpG-conjugated Zeb2 siRNA that delivers Zeb2 siRNA preferably to TAMs through their expression of the CpG receptor TLR9. (16/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
To evaluate the in vivo impact of targeting Zeb2, and since TFs are not easily targeted - we teamed up with the Kortylewski lab to design a CpG-conjugated Zeb2 siRNA that delivers Zeb2 siRNA preferably to TAMs through their expression of the CpG receptor TLR9. (16/20)
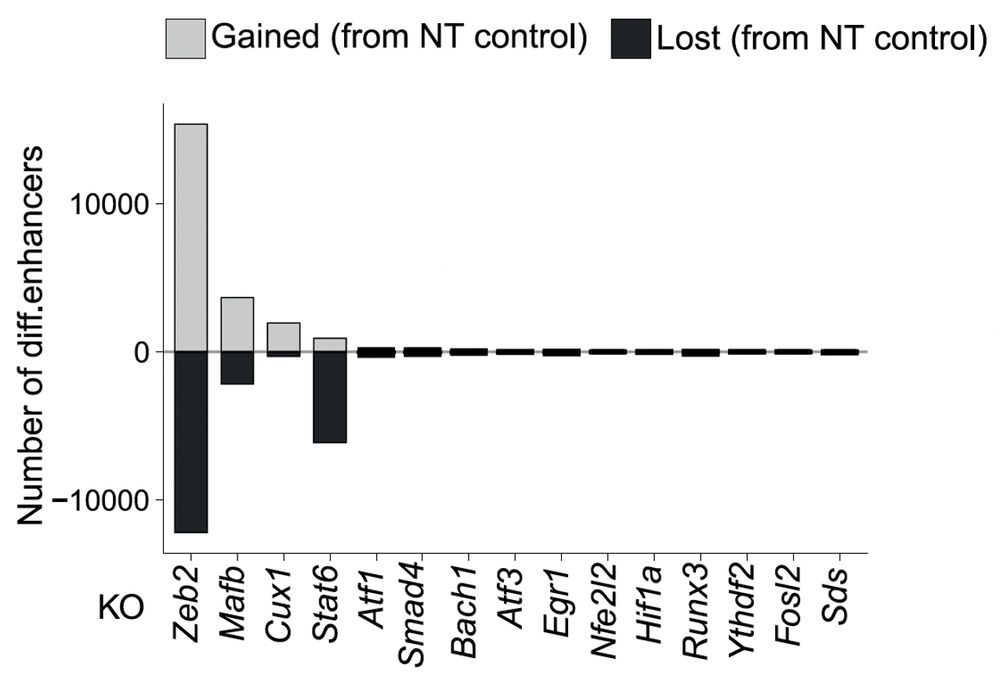
Next, since Zeb2 is a transcription factor, we asked if it also controls these programs at the chromatin level. ATAC-seq revealed that Zeb2 KO causes massive enhancer remodeling—opening sites near anti-tumor genes while closing pro-tumor ones. (15/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
Next, since Zeb2 is a transcription factor, we asked if it also controls these programs at the chromatin level. ATAC-seq revealed that Zeb2 KO causes massive enhancer remodeling—opening sites near anti-tumor genes while closing pro-tumor ones. (15/20)
Functionally, Zeb2 KO macrophages were less immunosuppressive and robustly upregulated immune activities such as antigen presentation—especially to CD4+ T cells, activating more IFN-γ–producing T cells in multiple functional in-vitro models. (14/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
Functionally, Zeb2 KO macrophages were less immunosuppressive and robustly upregulated immune activities such as antigen presentation—especially to CD4+ T cells, activating more IFN-γ–producing T cells in multiple functional in-vitro models. (14/20)
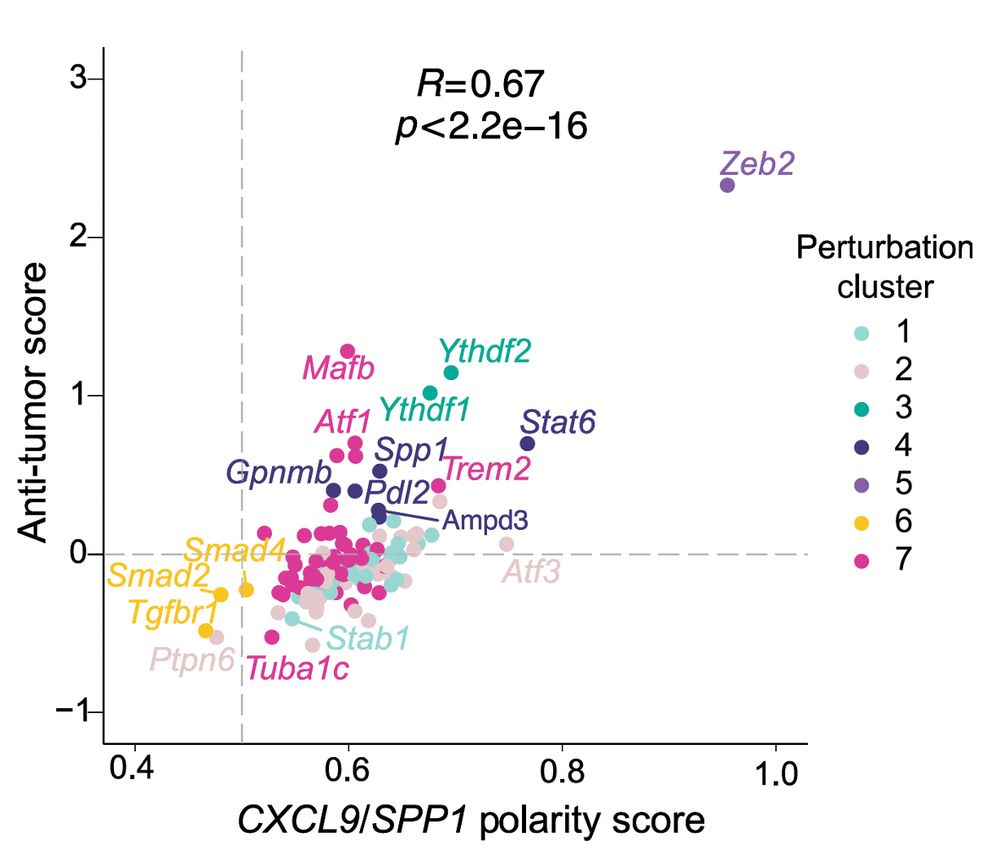
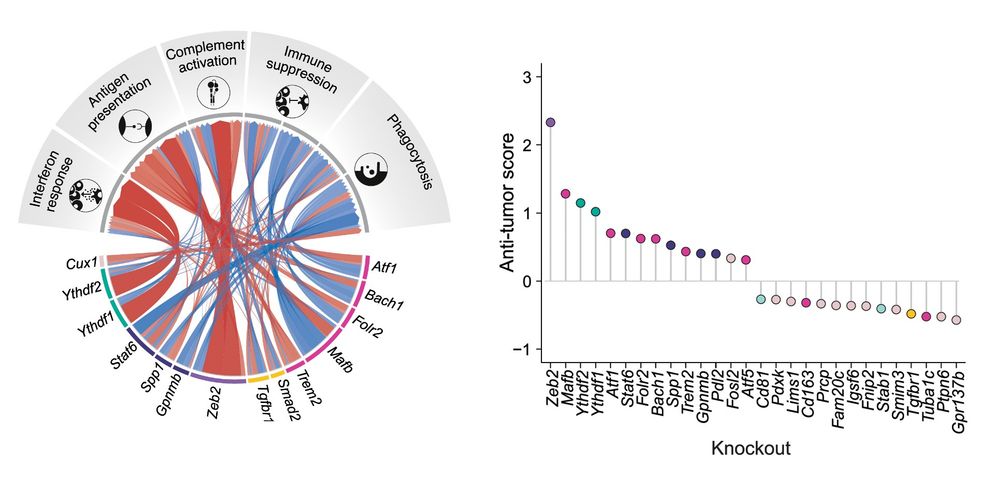
To validate our proposed anti-tumor score in a human context, we compared it to the CXCL9:SPP1 TAM polarity score linked to patient survival (beautiful work by Bill et al.). The effect of each regulator on the activity scores correlated well, with Zeb2 topping the list. (13/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
To validate our proposed anti-tumor score in a human context, we compared it to the CXCL9:SPP1 TAM polarity score linked to patient survival (beautiful work by Bill et al.). The effect of each regulator on the activity scores correlated well, with Zeb2 topping the list. (13/20)
With this, we established a TAM functional network and proposed a quantitative reprogramming metric—an 'anti-tumor score': how much a perturbation upregulates anti-tumor and downregulates pro-tumor functions. Among known hits like Trem2, Zeb2 emerged as a key switch. (12/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
With this, we established a TAM functional network and proposed a quantitative reprogramming metric—an 'anti-tumor score': how much a perturbation upregulates anti-tumor and downregulates pro-tumor functions. Among known hits like Trem2, Zeb2 emerged as a key switch. (12/20)
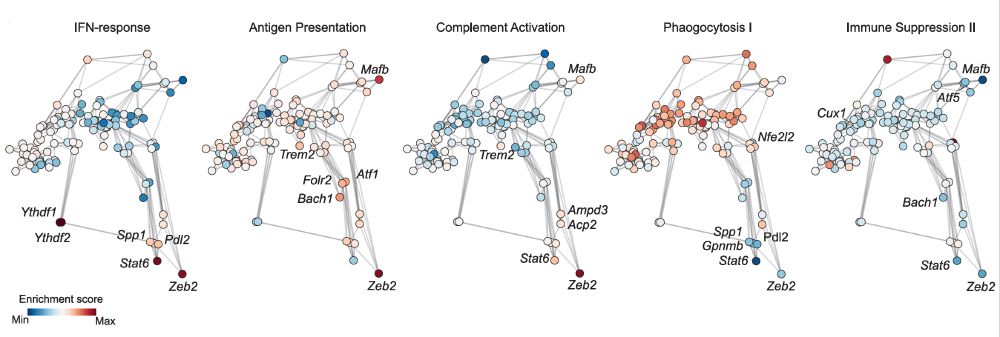
Next, we went back to our network and asked how the different perturbations affect these TAM programs. This is useful. Why? Because a major reprogramming target would upregulate anti-tumor (e.g. IFN-response) and downregulate pro-tumor (e.g. immunosuppression) programs. (11/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
Next, we went back to our network and asked how the different perturbations affect these TAM programs. This is useful. Why? Because a major reprogramming target would upregulate anti-tumor (e.g. IFN-response) and downregulate pro-tumor (e.g. immunosuppression) programs. (11/20)
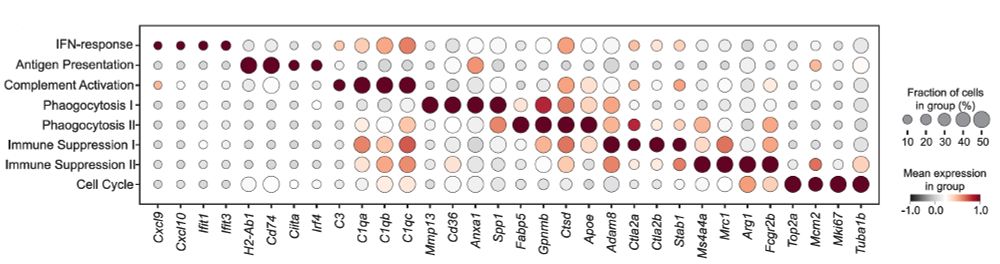
To understand how the different perturbations reprogrammed TAMs, we grouped autocorrelated genes using MrVI’s perturbation-aware latent space. This yielded distinct gene modules with known roles in TAM biology, linked to either positive or negative tumor immunity. (10/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
To understand how the different perturbations reprogrammed TAMs, we grouped autocorrelated genes using MrVI’s perturbation-aware latent space. This yielded distinct gene modules with known roles in TAM biology, linked to either positive or negative tumor immunity. (10/20)
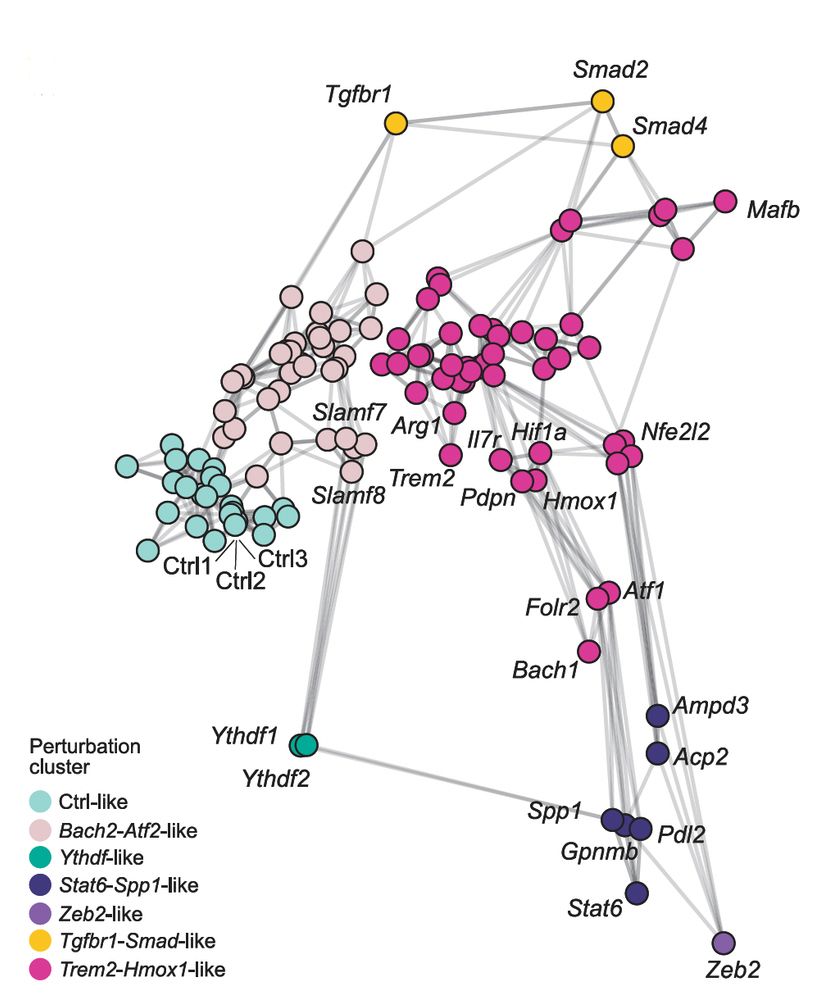
This AI-driven analysis enabled us to construct a perturbation network, where perturbations that evoke similar effects on the single-cell states are located in close proximity—and vice versa. (9/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
This AI-driven analysis enabled us to construct a perturbation network, where perturbations that evoke similar effects on the single-cell states are located in close proximity—and vice versa. (9/20)
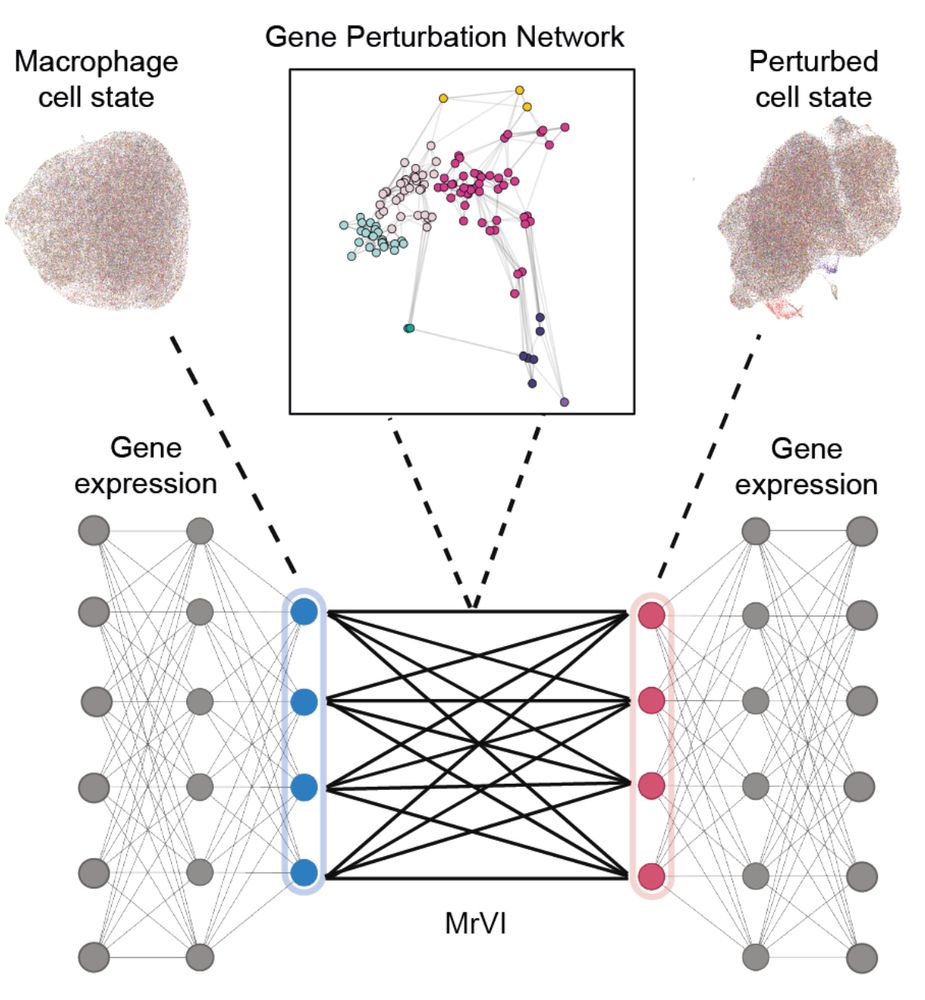
To systematically resolve how candidate regulators impact macrophage functions we collaborated with the Yosef lab who recently developed MrVI, a deep generative model designed to dissect how sample-level covariates like gene perturbation affect gene expression in single cells. (8/20)
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
To systematically resolve how candidate regulators impact macrophage functions we collaborated with the Yosef lab who recently developed MrVI, a deep generative model designed to dissect how sample-level covariates like gene perturbation affect gene expression in single cells. (8/20)
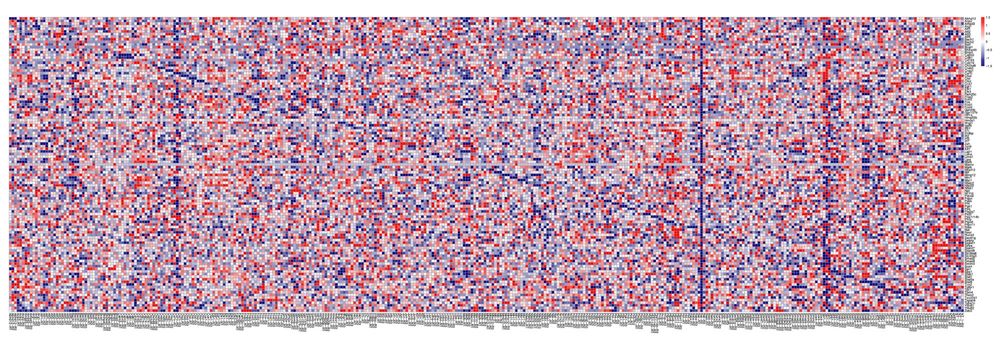
The first look at the data confirmed that the putative regulators were effectively targeted—the blue diagonal indicates reduced gene expression of the perturbed genes. But the data, as you can see, is complex, high-dimensional, and not easily interpretable. (7/20).
April 10, 2025 at 7:05 PM
The first look at the data confirmed that the putative regulators were effectively targeted—the blue diagonal indicates reduced gene expression of the perturbed genes. But the data, as you can see, is complex, high-dimensional, and not easily interpretable. (7/20).


