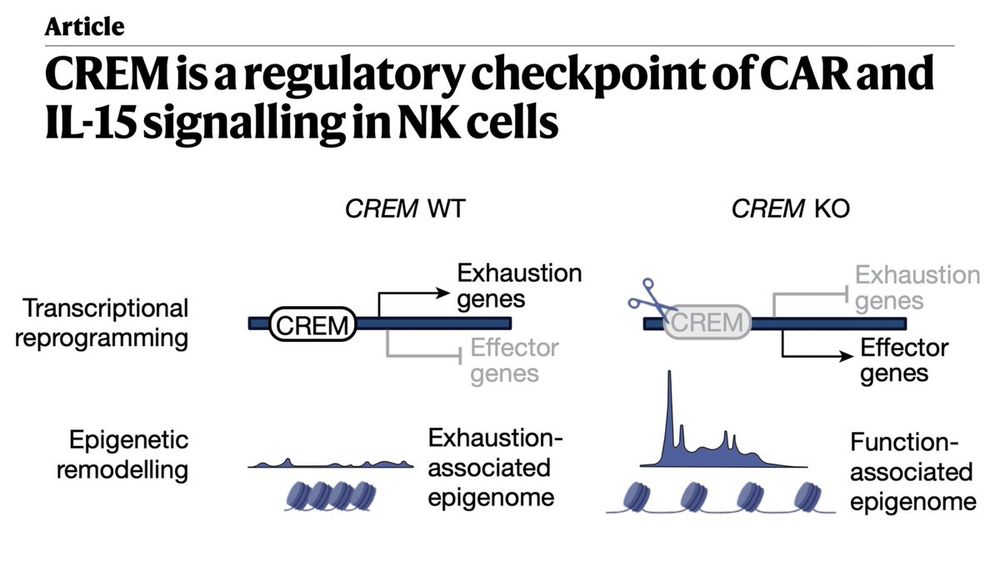
In summary, we identify🔎CREM as a key🔑transcriptional checkpoint that limits CAR-NK cell function and persistence. CREM KO enhances cytotoxicity and in vivo efficacy across tumor models without added toxicity.
These findings highlight CREM as a targetable regulator to improve cell therapies💉.
In summary, we identify🔎CREM as a key🔑transcriptional checkpoint that limits CAR-NK cell function and persistence. CREM KO enhances cytotoxicity and in vivo efficacy across tumor models without added toxicity.
These findings highlight CREM as a targetable regulator to improve cell therapies💉.
How does CREM restrain CAR-NK cell function? We used🔹ChIP-seq🔹RNA-seq🔹ATAC-seq to map CREM’s impact.
CREM rewires the NK cell epigenome, and its ❌ restores a metabolically fit🏃♀️, functionally potent💪🏻phenotype.

How does CREM restrain CAR-NK cell function? We used🔹ChIP-seq🔹RNA-seq🔹ATAC-seq to map CREM’s impact.
CREM rewires the NK cell epigenome, and its ❌ restores a metabolically fit🏃♀️, functionally potent💪🏻phenotype.
In a metastatic CD70⁺ breast cancer PDX model, 🐁 treated with CREM KO CAR70/IL-15 NK cells showed:
✅ Significantly⬇️tumor burden
✅⬆️NK cell proliferation and tissue infiltration
✅🙅🏽♀️toxicity

In a metastatic CD70⁺ breast cancer PDX model, 🐁 treated with CREM KO CAR70/IL-15 NK cells showed:
✅ Significantly⬇️tumor burden
✅⬆️NK cell proliferation and tissue infiltration
✅🙅🏽♀️toxicity
We next tested CREM KO CAR-NK cells in vivo across 3 models of hematologic and solid tumors. In an aggressive Raji lymphoma model, long-term cultured CREM KO cells:
✅Controlled tumor growth more effectively than WT
✅⬆️survival
✅⬆️proliferation & tissue infiltration

We next tested CREM KO CAR-NK cells in vivo across 3 models of hematologic and solid tumors. In an aggressive Raji lymphoma model, long-term cultured CREM KO cells:
✅Controlled tumor growth more effectively than WT
✅⬆️survival
✅⬆️proliferation & tissue infiltration
We further show that:
✅ Effects were strongest💪🏽when both CAR and IL-15 signaling were active.
✅ Mutating⚡️CD3ζ ITAMs abrogated this effect.
Therefore, CREM is a potent intracellular checkpoint that limits CAR-NK efficacy.

We further show that:
✅ Effects were strongest💪🏽when both CAR and IL-15 signaling were active.
✅ Mutating⚡️CD3ζ ITAMs abrogated this effect.
Therefore, CREM is a potent intracellular checkpoint that limits CAR-NK efficacy.
Functionally, CREM knockout (KO) in 2 different CAR models significantly enhanced cytotoxicity in 2D, 3D, and rechallenge assays. See👀for yourself:
Functionally, CREM knockout (KO) in 2 different CAR models significantly enhanced cytotoxicity in 2D, 3D, and rechallenge assays. See👀for yourself:
Mechanistically⚙️, we found that CREM is induced via the cAMP–PKA–CREB signaling cascade and is a direct transcriptional target of CREB, integrating↪️↩️signals from both CAR and cytokine activation.

Mechanistically⚙️, we found that CREM is induced via the cAMP–PKA–CREB signaling cascade and is a direct transcriptional target of CREB, integrating↪️↩️signals from both CAR and cytokine activation.
Is CREM relevant in the tumor microenvironment?
Across multiple scRNA-seq datasets, CREM was broadly enriched in tumor-infiltrating immune cells especially NK cells, T cells, and monocytes/macrophages.
It also correlated with poor prognosis in certain cancers from TCGA.

Is CREM relevant in the tumor microenvironment?
Across multiple scRNA-seq datasets, CREM was broadly enriched in tumor-infiltrating immune cells especially NK cells, T cells, and monocytes/macrophages.
It also correlated with poor prognosis in certain cancers from TCGA.
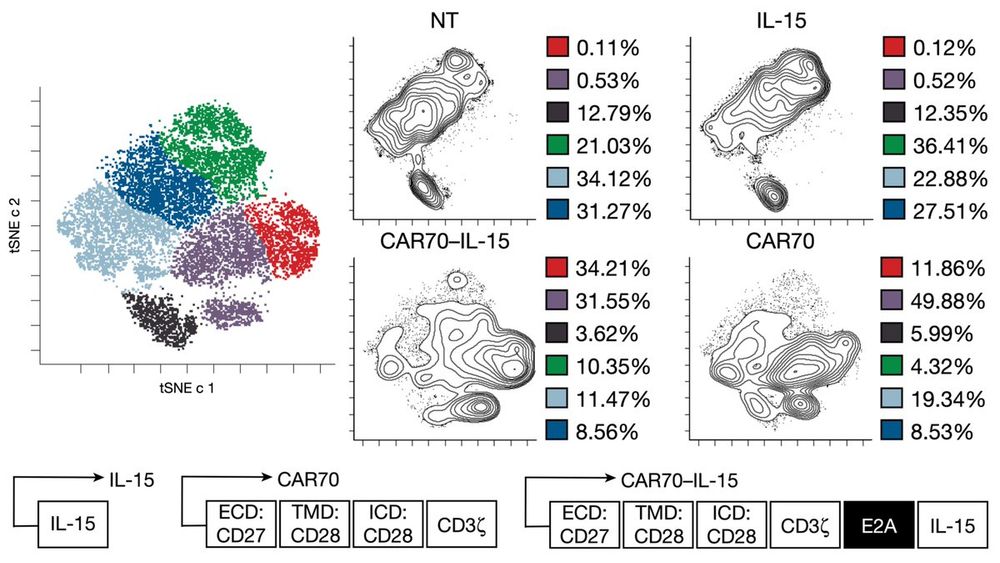
Using CyTOF, when co-cultured with tumor, CREM-high NK cells were enriched in a cluster (red🔴) expressing both:
⬆️Activation markers (CD25, GZMB, NKp30, NKG2D)
⬆️Exhaustion/inhibitory receptors (TIGIT, LAG3, NKG2A)
☝🏼An immunophenotype of activation-induced exhaustion.
Using CyTOF, when co-cultured with tumor, CREM-high NK cells were enriched in a cluster (red🔴) expressing both:
⬆️Activation markers (CD25, GZMB, NKp30, NKG2D)
⬆️Exhaustion/inhibitory receptors (TIGIT, LAG3, NKG2A)
☝🏼An immunophenotype of activation-induced exhaustion.
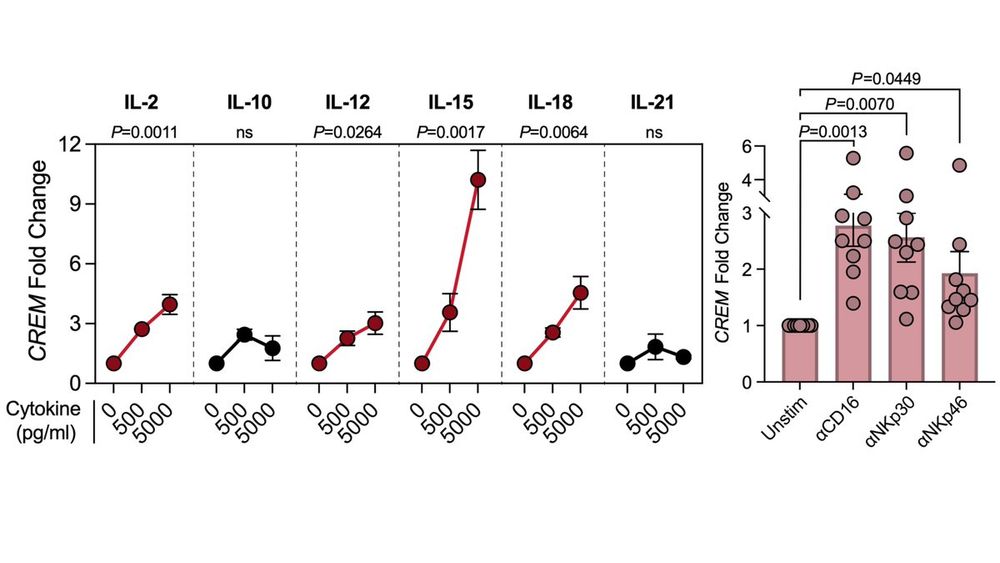
CREM upregulation isn't unique to CARs. We found it’s broadly induced by NK cell activation, including by:
✨Cytokines: IL-2, IL-12, IL-18➡️moderate dose-dependent CREM induction
✨Receptor stimulation: CD16, NKp30, NKp46➡️ ITAM-driven CREM upregulation
CREM upregulation isn't unique to CARs. We found it’s broadly induced by NK cell activation, including by:
✨Cytokines: IL-2, IL-12, IL-18➡️moderate dose-dependent CREM induction
✨Receptor stimulation: CD16, NKp30, NKp46➡️ ITAM-driven CREM upregulation
How is CREM induced?
We demonstrate that both CAR CD3ζ ITAM signaling (lost when⚡️to CD3ζ.Y6F) and IL-15 can independently ⬆️CREM.

How is CREM induced?
We demonstrate that both CAR CD3ζ ITAM signaling (lost when⚡️to CD3ζ.Y6F) and IL-15 can independently ⬆️CREM.
We used scRNA-seq on CD19-targeting, IL-15-secreting CAR-NK cells (CAR19/IL-15) before and after infusion into a Raji lymphoma 🐁 model.
CREM emerged as one of the top⬆️transcription factors after infusion.

We used scRNA-seq on CD19-targeting, IL-15-secreting CAR-NK cells (CAR19/IL-15) before and after infusion into a Raji lymphoma 🐁 model.
CREM emerged as one of the top⬆️transcription factors after infusion.

