Mike Dolan
@dolanmjg.bsky.social
Assistant Professor @ Trinity College Dublin
Neuroimmunology | CNS disease and repair.
🇮🇪🇪🇺🏳️🌈
https://dolanlab-tcd.com/
Neuroimmunology | CNS disease and repair.
🇮🇪🇪🇺🏳️🌈
https://dolanlab-tcd.com/
None of this work would be possible without the mentorship of @bethstevenslab.bsky.social and Evan Macosko. Or the hard work of two phenomenal RAs: @raphaelrakosi.bsky.social and Eric Garcia!
Thank you to all our collaborators and coauthors!
Thank you to all our collaborators and coauthors!
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
None of this work would be possible without the mentorship of @bethstevenslab.bsky.social and Evan Macosko. Or the hard work of two phenomenal RAs: @raphaelrakosi.bsky.social and Eric Garcia!
Thank you to all our collaborators and coauthors!
Thank you to all our collaborators and coauthors!
8/
Summary:
Remyelination depends on a glial-immune axis, initiated by type I interferon signaling that summons lymphocytes. Surprisingly, these cytotoxic CD8 T-cells enhance remyelination.
Full story ➡️ www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Summary:
Remyelination depends on a glial-immune axis, initiated by type I interferon signaling that summons lymphocytes. Surprisingly, these cytotoxic CD8 T-cells enhance remyelination.
Full story ➡️ www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
8/
Summary:
Remyelination depends on a glial-immune axis, initiated by type I interferon signaling that summons lymphocytes. Surprisingly, these cytotoxic CD8 T-cells enhance remyelination.
Full story ➡️ www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Summary:
Remyelination depends on a glial-immune axis, initiated by type I interferon signaling that summons lymphocytes. Surprisingly, these cytotoxic CD8 T-cells enhance remyelination.
Full story ➡️ www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
7/
Critically, depleting the most abundant of these lymphocytes — CD8 T-cells — led to reduced oligodendrocyte maturation, directly linking lymphocyte infiltration to successful remyelination.
This was surprising, we expected CD8 T-cells to exert a negative effect on the brain
Critically, depleting the most abundant of these lymphocytes — CD8 T-cells — led to reduced oligodendrocyte maturation, directly linking lymphocyte infiltration to successful remyelination.
This was surprising, we expected CD8 T-cells to exert a negative effect on the brain
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
7/
Critically, depleting the most abundant of these lymphocytes — CD8 T-cells — led to reduced oligodendrocyte maturation, directly linking lymphocyte infiltration to successful remyelination.
This was surprising, we expected CD8 T-cells to exert a negative effect on the brain
Critically, depleting the most abundant of these lymphocytes — CD8 T-cells — led to reduced oligodendrocyte maturation, directly linking lymphocyte infiltration to successful remyelination.
This was surprising, we expected CD8 T-cells to exert a negative effect on the brain
6/
What’s the function of IRG?
We demonstrate that IRG secrete CXCL10, a chemokine that recruits lymphocytes into the repairing white matter.
Without this glial-driven recruitment, lymphocyte
infiltration was impaired.
What’s the function of IRG?
We demonstrate that IRG secrete CXCL10, a chemokine that recruits lymphocytes into the repairing white matter.
Without this glial-driven recruitment, lymphocyte
infiltration was impaired.
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
6/
What’s the function of IRG?
We demonstrate that IRG secrete CXCL10, a chemokine that recruits lymphocytes into the repairing white matter.
Without this glial-driven recruitment, lymphocyte
infiltration was impaired.
What’s the function of IRG?
We demonstrate that IRG secrete CXCL10, a chemokine that recruits lymphocytes into the repairing white matter.
Without this glial-driven recruitment, lymphocyte
infiltration was impaired.
5/
Third, we discovered a shared interferon-response program across multiple glial types.
These interferon-responsive glia (IRG) clustered around remyelinating white matter — and their formation was dependent on type I interferon signaling.
Third, we discovered a shared interferon-response program across multiple glial types.
These interferon-responsive glia (IRG) clustered around remyelinating white matter — and their formation was dependent on type I interferon signaling.
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
5/
Third, we discovered a shared interferon-response program across multiple glial types.
These interferon-responsive glia (IRG) clustered around remyelinating white matter — and their formation was dependent on type I interferon signaling.
Third, we discovered a shared interferon-response program across multiple glial types.
These interferon-responsive glia (IRG) clustered around remyelinating white matter — and their formation was dependent on type I interferon signaling.
4/
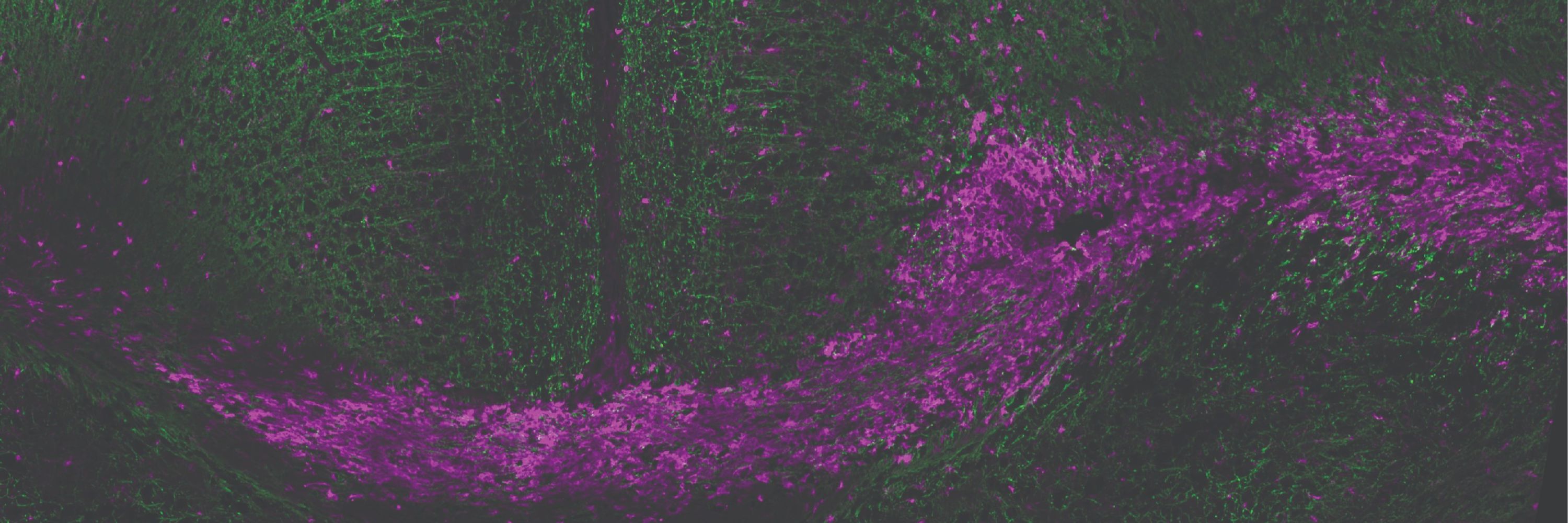
Second, we observed a selective infiltration of immune cells specifically during remyelination:
➡️ CD8 T-cells
➡️ Natural killer (NK) cells
These lymphocytes were specifically enriched during the repair phase, not just during damage.
Second, we observed a selective infiltration of immune cells specifically during remyelination:
➡️ CD8 T-cells
➡️ Natural killer (NK) cells
These lymphocytes were specifically enriched during the repair phase, not just during damage.
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
4/
Second, we observed a selective infiltration of immune cells specifically during remyelination:
➡️ CD8 T-cells
➡️ Natural killer (NK) cells
These lymphocytes were specifically enriched during the repair phase, not just during damage.
Second, we observed a selective infiltration of immune cells specifically during remyelination:
➡️ CD8 T-cells
➡️ Natural killer (NK) cells
These lymphocytes were specifically enriched during the repair phase, not just during damage.
3/
First, glial and monocyte-derived macrophage states are highly dynamic.
We found extensive transcriptional remodeling across microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocyte lineage cells from demyelination through to repair.
First, glial and monocyte-derived macrophage states are highly dynamic.
We found extensive transcriptional remodeling across microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocyte lineage cells from demyelination through to repair.
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
3/
First, glial and monocyte-derived macrophage states are highly dynamic.
We found extensive transcriptional remodeling across microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocyte lineage cells from demyelination through to repair.
First, glial and monocyte-derived macrophage states are highly dynamic.
We found extensive transcriptional remodeling across microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocyte lineage cells from demyelination through to repair.
2/
We used a focal demyelination model to study the entire process of white matter injury and repair at high spatial and molecular resolution.
Our goal: capture the real-time cellular and molecular dynamics driving remyelination.
We used a focal demyelination model to study the entire process of white matter injury and repair at high spatial and molecular resolution.
Our goal: capture the real-time cellular and molecular dynamics driving remyelination.
April 28, 2025 at 9:09 AM
2/
We used a focal demyelination model to study the entire process of white matter injury and repair at high spatial and molecular resolution.
Our goal: capture the real-time cellular and molecular dynamics driving remyelination.
We used a focal demyelination model to study the entire process of white matter injury and repair at high spatial and molecular resolution.
Our goal: capture the real-time cellular and molecular dynamics driving remyelination.

