
#MedSky

#MedSky
#MedSky

#MedSky
#MedSky #OncoSky

#STS
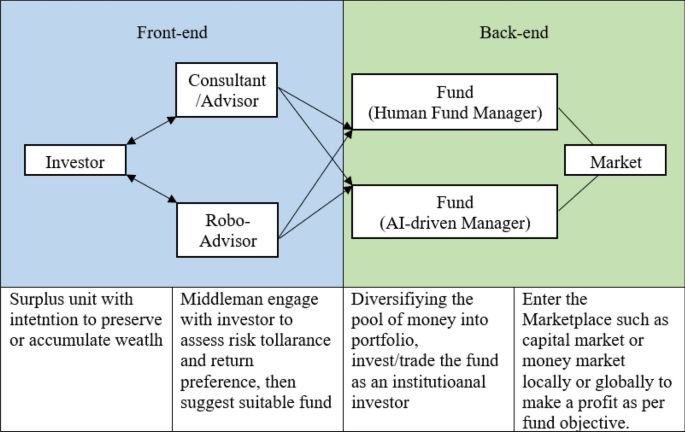
#STS
#Epigenetics

#Epigenetics
Read more here: bit.ly/3X5VCCC
#MedSky #DiscoverJournals #CleanWater #Sanitation
Read more here: bit.ly/3X5VCCC
#MedSky #DiscoverJournals #CleanWater #Sanitation
#STS

#STS
#PsychSciSky

#PsychSciSky

Read more here: bit.ly/3LZW96E




Read more here: bit.ly/3LZW96E
This case study shows how a Springer Nature collection published in a Discover journal led to WHO citations & worldwide recognition: bit.ly/4hZEyYB
#MedSky

This case study shows how a Springer Nature collection published in a Discover journal led to WHO citations & worldwide recognition: bit.ly/4hZEyYB
#MedSky
bit.ly/4jzPUSK
#MedSky

bit.ly/4jzPUSK
#MedSky
This #WorldDiabetesDay, we highlight how pharmacist-led education in Nigeria helps people with diabetes and hypertension take charge of their health. Awareness is the first step.
bit.ly/49RMhWt
#MedSky




This #WorldDiabetesDay, we highlight how pharmacist-led education in Nigeria helps people with diabetes and hypertension take charge of their health. Awareness is the first step.
bit.ly/49RMhWt
#MedSky
#MedSky
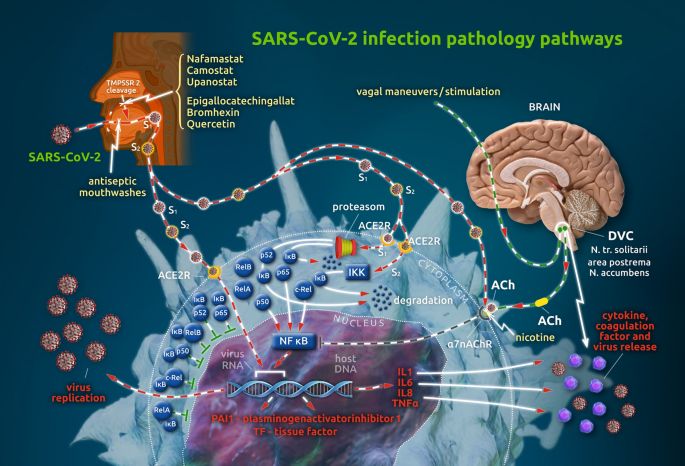
#MedSky
bit.ly/42PM01g
#OncoSky #MedSky

bit.ly/42PM01g
#OncoSky #MedSky
bit.ly/3S28GX8
#PsychSciSky
#STS

bit.ly/3S28GX8
#PsychSciSky
#STS
bit.ly/4jYcHYC
#STS

bit.ly/4jYcHYC
#STS
bit.ly/45d5O18
#MedSky

bit.ly/45d5O18
#MedSky
bit.ly/476oSxs

bit.ly/476oSxs
#STS

#STS
Submission closes: 31 December 2025.
bit.ly/4ocVooI

Submission closes: 31 December 2025.
bit.ly/4ocVooI
This #WorldRadiographyDay, we celebrate researchers taking imaging beyond hospital walls, making it faster, lighter, and more accessible for all.
Read more here: bit.ly/4qUmYJJ
#MedSky
This #WorldRadiographyDay, we celebrate researchers taking imaging beyond hospital walls, making it faster, lighter, and more accessible for all.
Read more here: bit.ly/4qUmYJJ
#MedSky
#STS #AcademicSky
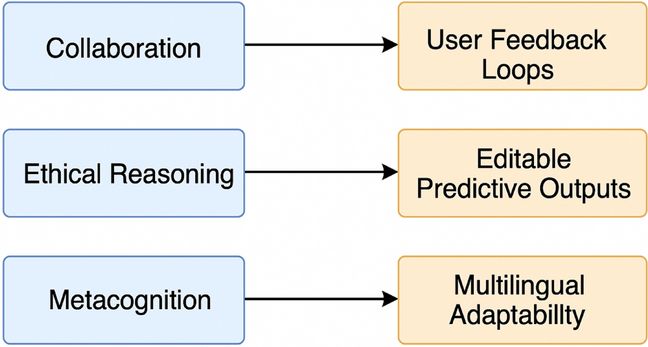
#STS #AcademicSky
#MedSky #PsychSciSky

#MedSky #PsychSciSky
bit.ly/41HwxRH
#PsychSciSky #STS

bit.ly/41HwxRH
#PsychSciSky #STS

