discord: https://discord.com/invite/2QWN9y3B9M
tech blogs: https://mohitmishra786.github.io/chessman/
twitter: https://x.com/chessMan786

The Pentium III processor is designed with an elegant architecture that separates training and statistics handling into wonderful devices. It consists of a 16 KB instruction cache and a 16 KB statistics cache.
#intel #pentium

The PE format begins with a DOS header, followed by NT headers that include file information and optional directories for data types. Section headers then categorize the file into sections for code, data, and debugging, among others.
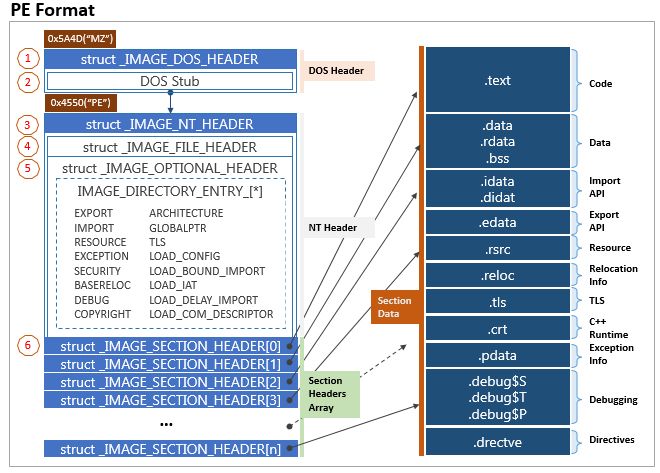
The PE format begins with a DOS header, followed by NT headers that include file information and optional directories for data types. Section headers then categorize the file into sections for code, data, and debugging, among others.
Drop any questions, you have on this architecture or whatever comes to your mind 😉

Drop any questions, you have on this architecture or whatever comes to your mind 😉

Not just each process, each thread has its kernel stack (and, in fact, its user stack as well). Remember the only difference between processes and threads (to Linux) is the fact that multiple threads can share an address space (forming a process).

Not just each process, each thread has its kernel stack (and, in fact, its user stack as well). Remember the only difference between processes and threads (to Linux) is the fact that multiple threads can share an address space (forming a process).
In this article, I explained Banker's Algorithms, Conditions for Deadlock, and prevention strategies.
Do let me know what you think 😉
mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...

In this article, I explained Banker's Algorithms, Conditions for Deadlock, and prevention strategies.
Do let me know what you think 😉
mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...

Today is Day-9 of our 69 Days of Exploring Operating System. In this article, In this I clarify the differences of Threads vs Process and added some good practical code examples.
Article: mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...

Today is Day-9 of our 69 Days of Exploring Operating System. In this article, In this I clarify the differences of Threads vs Process and added some good practical code examples.
Article: mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...
ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) files are a standard format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps in Unix-like systems.
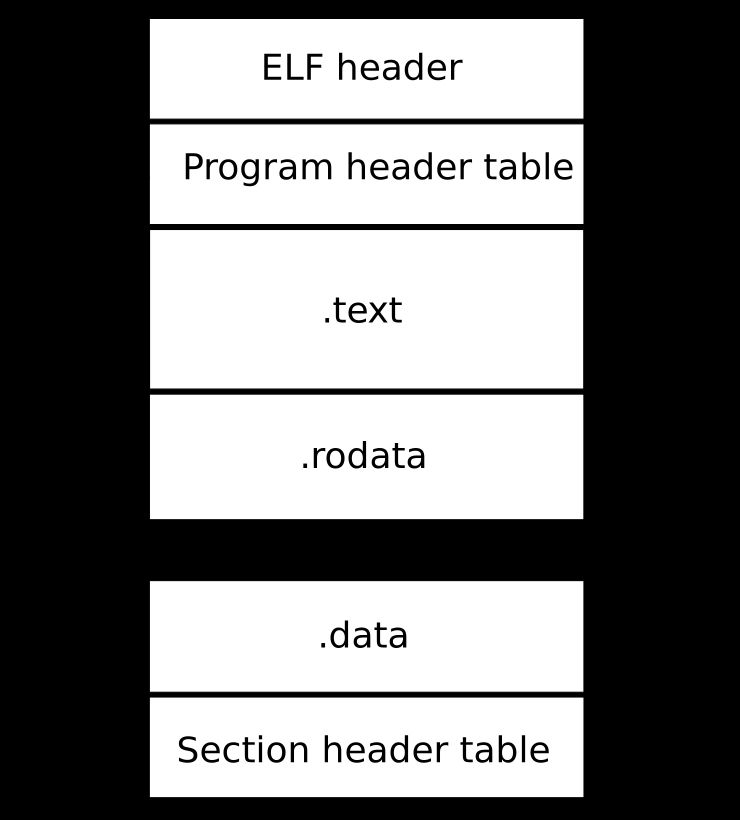
ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) files are a standard format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps in Unix-like systems.

The memory map for a Linux thread on a 32-bit Linux/MIPS system shows that user-accessible memory is in the lower half of the map. The 64-bit version follows similar principles but is more complex.
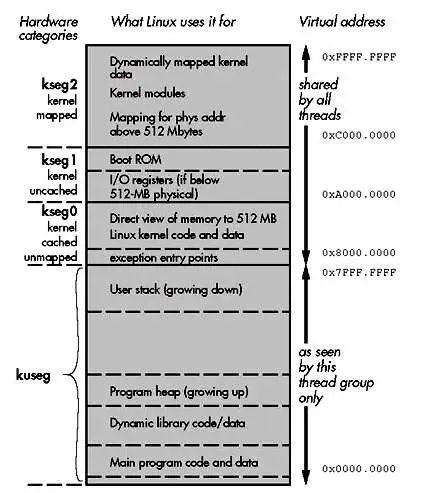
The memory map for a Linux thread on a 32-bit Linux/MIPS system shows that user-accessible memory is in the lower half of the map. The 64-bit version follows similar principles but is more complex.
Article: mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...

Article: mohitmishra786.github.io/exploring-os...
- Very much theoretical videos
- Explanations are well and informative
👇Source link in the below comment

- Very much theoretical videos
- Explanations are well and informative
👇Source link in the below comment
These flags help the CPU make decisions and control program execution, especially during conditional instructions like jumps. Programmers can also access and manipulate these flags with specific instructions for branching in their programs.
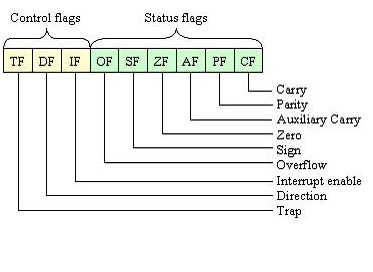
These flags help the CPU make decisions and control program execution, especially during conditional instructions like jumps. Programmers can also access and manipulate these flags with specific instructions for branching in their programs.
We need to know the features of a processor for memory mapping:
1. The ability to walk a page table to find a physical address from a virtual one.
2. The TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) cache.

We need to know the features of a processor for memory mapping:
1. The ability to walk a page table to find a physical address from a virtual one.
2. The TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) cache.
The below image explains the memory mapping schemes for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems in Kernel Mode Address Space

The below image explains the memory mapping schemes for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems in Kernel Mode Address Space
- In a file system, inodes are data structures that store information about files in UNIX-based systems
- Each file has one inode containing metadata like file type, access permissions, owner info, size, links count, and pointers to data blocks

- In a file system, inodes are data structures that store information about files in UNIX-based systems
- Each file has one inode containing metadata like file type, access permissions, owner info, size, links count, and pointers to data blocks

Below image explains the network stack in the Linux kernel, which is divided into different layers: User Space, Kernel Space, Application Layer Kernel, Transport Layer, Network Layer, Host to Host Layer, Hardware Specific, and Physical Transmission

Below image explains the network stack in the Linux kernel, which is divided into different layers: User Space, Kernel Space, Application Layer Kernel, Transport Layer, Network Layer, Host to Host Layer, Hardware Specific, and Physical Transmission

