
In early July, I attended the Animal Advocacy Conference of PHAIR in Edinburgh, Scotland. In celebration of World Animal Day, I want to share some insights from this year’s gathering:
bendegroeve.wordpress.com/sentience-sp...

In early July, I attended the Animal Advocacy Conference of PHAIR in Edinburgh, Scotland. In celebration of World Animal Day, I want to share some insights from this year’s gathering:
bendegroeve.wordpress.com/sentience-sp...
▶️ Use transport as a lever for cooler cities and promote green spaces 🚌🌳
▶️ Promote energy-efficient mobility


▶️ Use transport as a lever for cooler cities and promote green spaces 🚌🌳
▶️ Promote energy-efficient mobility
I just received a fact sheet on traffic-induced urban heat stress by an Austrian organization specialized in mobility (VCÖ): vcoe.at/files/vcoe/u...


I just received a fact sheet on traffic-induced urban heat stress by an Austrian organization specialized in mobility (VCÖ): vcoe.at/files/vcoe/u...
🔗 www.researchgate.net/publication/...
Animal cruelty can “push” people to avoid meat by triggering emotions like empathy and anger, while the “pull” of meat’s taste can spark reactance and counter-justification.

🔗 www.researchgate.net/publication/...
Animal cruelty can “push” people to avoid meat by triggering emotions like empathy and anger, while the “pull” of meat’s taste can spark reactance and counter-justification.
🐷🦝💗 Caring about animals ("animal solidarity") predicts moral emotions and (to a lesser extent) willingness to change.
🥩🥓❤️ Loving meat ("hedonic motivation") negatively predicts willingness to change and (to a lesser extent) moral emotions.

🐷🦝💗 Caring about animals ("animal solidarity") predicts moral emotions and (to a lesser extent) willingness to change.
🥩🥓❤️ Loving meat ("hedonic motivation") negatively predicts willingness to change and (to a lesser extent) moral emotions.
It's as if moral emotions are, to some extent, ignored.

It's as if moral emotions are, to some extent, ignored.
But there’s a twist...


But there’s a twist...

💔 More emotions like empathy and pity for pigs (victim-oriented emotions)
😳 More self-oriented emotions like guilt and shame
👏 Less praising emotions for people involved in making pork chops

💔 More emotions like empathy and pity for pigs (victim-oriented emotions)
😳 More self-oriented emotions like guilt and shame
👏 Less praising emotions for people involved in making pork chops
🥩 A pork chop (control condition)
🥩🐷🥰 A pork chop + someone petting a pig (caring appeal)
🥩🐷🔪 A pork chop + someone stunning a pig before slaughter (cruelty appeal)
What happened? (2/n)

🥩 A pork chop (control condition)
🥩🐷🥰 A pork chop + someone petting a pig (caring appeal)
🥩🐷🔪 A pork chop + someone stunning a pig before slaughter (cruelty appeal)
What happened? (2/n)
So what happens when they do make that connection?
🐖 If you're curious, check out our new study:
"‘Meating’ the animal and moral emotions"
🔎 doi.org/10.1016/j.ap...
🧵👇 (1/10)
#MoralPsychology #MeatParadox #AnimalCruelty

So what happens when they do make that connection?
🐖 If you're curious, check out our new study:
"‘Meating’ the animal and moral emotions"
🔎 doi.org/10.1016/j.ap...
🧵👇 (1/10)
#MoralPsychology #MeatParadox #AnimalCruelty
A healthy plant-based diet:
❤️ Lowers risk of diabetes, heart disease & metabolic issues
🌿 Counters inflammation
💪 Rich in antioxidants, micronutrients & fiber
🦠 Improves gut microbiome diversity
🧠 Supports cognitive function & well-being
🔎
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

A healthy plant-based diet:
❤️ Lowers risk of diabetes, heart disease & metabolic issues
🌿 Counters inflammation
💪 Rich in antioxidants, micronutrients & fiber
🦠 Improves gut microbiome diversity
🧠 Supports cognitive function & well-being
🔎
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
- Thomas Hertog
youtu.be/6akmv1bsz1M?...

- Thomas Hertog
youtu.be/6akmv1bsz1M?...
If you want to know more, there are also several books on the psychology of eating meat that may be more digestible. Even Wikipedia talks about the meat paradox: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychol...
Feel free to share this🧵 if you want. 😉
16/16


If you want to know more, there are also several books on the psychology of eating meat that may be more digestible. Even Wikipedia talks about the meat paradox: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychol...
Feel free to share this🧵 if you want. 😉
16/16
In 2023, a theoretical framework has been proposed to better understand it. 15/16
sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

In 2023, a theoretical framework has been proposed to better understand it. 15/16
sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34509545/

pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34509545/


Rothgerber (extensions shown in bold circles below), showing how various factors affect moral (dis)engagement from animals. 9/16 doi.org/10.32872/spb...

Rothgerber (extensions shown in bold circles below), showing how various factors affect moral (dis)engagement from animals. 9/16 doi.org/10.32872/spb...

csblab.com/wp-content/u...
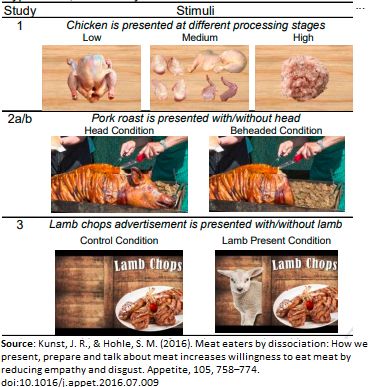
csblab.com/wp-content/u...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
It's a very insightful review on how morally troublesome behaviors in general can become widespread and remain commonplace. 4/16
www.researchgate.net/publication/...

It's a very insightful review on how morally troublesome behaviors in general can become widespread and remain commonplace. 4/16
www.researchgate.net/publication/...






