
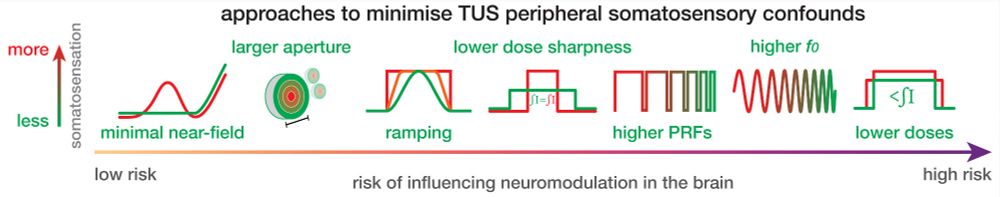
- Eliminate near-field intensity peaks in the scalp
- Use larger aperture areas
- Apply ramping
- Deliver equivalent doses via longer, lower intensity pulses
- Apply higher PRFs (≥200 Hz)
- Apply higher f0 (e.g., 500 vs 250 kHz)
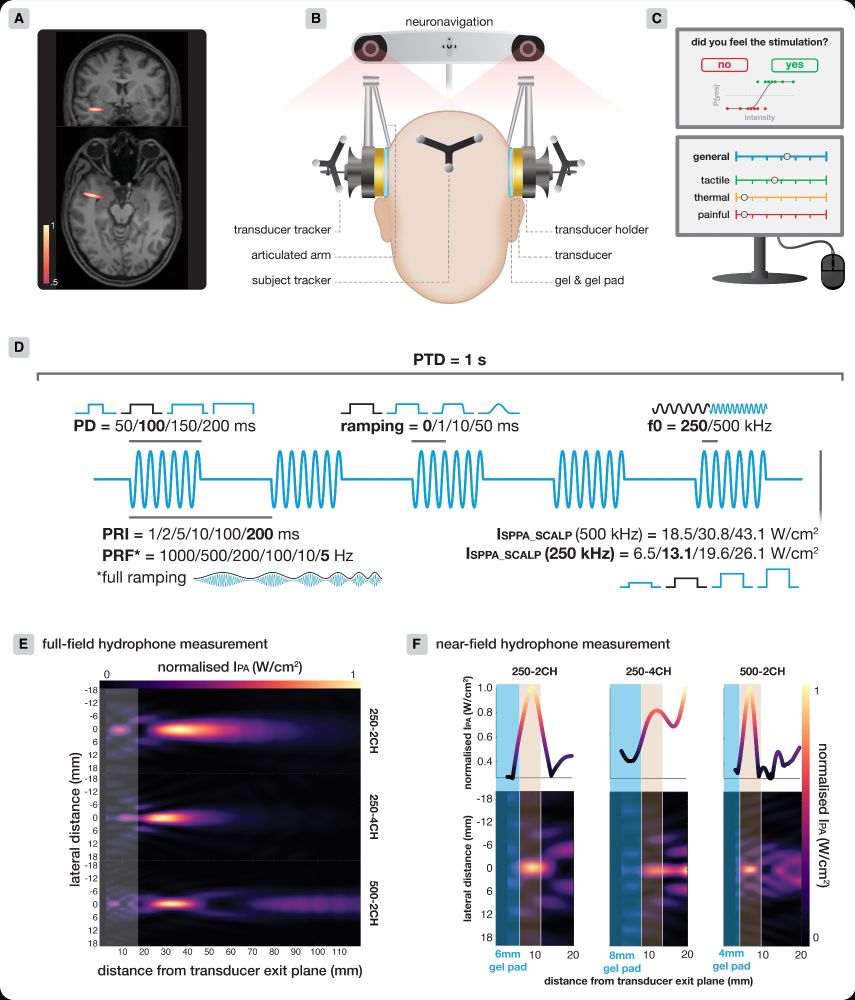
- Eliminate near-field intensity peaks in the scalp
- Use larger aperture areas
- Apply ramping
- Deliver equivalent doses via longer, lower intensity pulses
- Apply higher PRFs (≥200 Hz)
- Apply higher f0 (e.g., 500 vs 250 kHz)
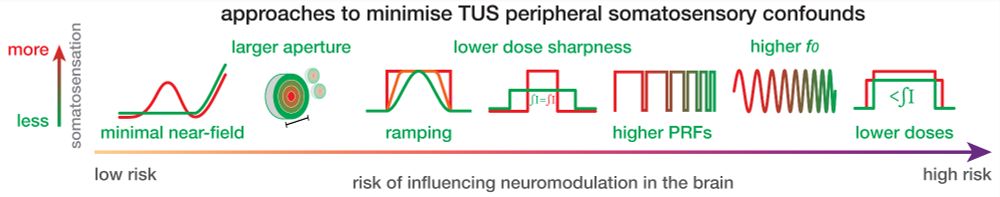
- Eliminate near-field intensity peaks in the scalp
- Use larger aperture areas
- Apply ramping
- Deliver equivalent doses via longer, lower intensity pulses
- Apply higher PRFs (≥200 Hz)
- Apply higher f0 (e.g., 500 vs 250 kHz)
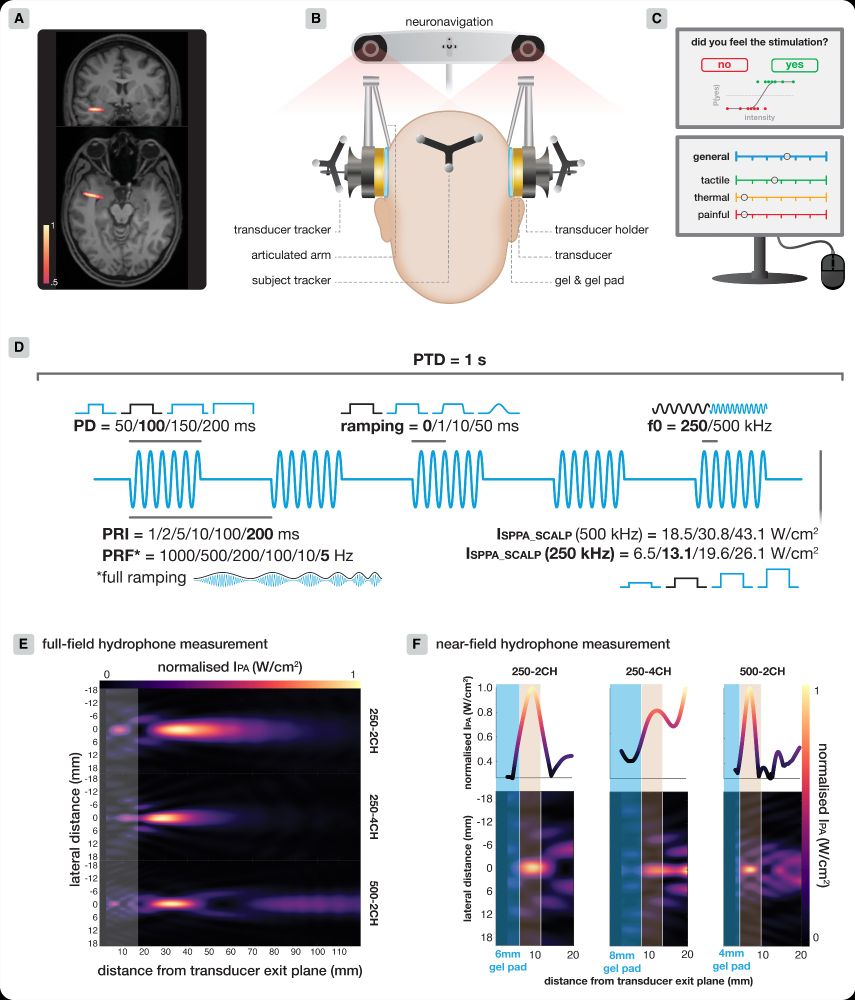
- Eliminate near-field intensity peaks in the scalp
- Use larger aperture areas
- Apply ramping
- Deliver equivalent doses via longer, lower intensity pulses
- Apply higher PRFs (≥200 Hz)
- Apply higher f0 (e.g., 500 vs 250 kHz)
How were such consistent excitatory effects found in prior work with variable hotspot-based targeting? Particularly considering that another independent study using 5Hz-rTUS with confirmed structural targeting reported opposite (inhibitory) effects! 🤔
How were such consistent excitatory effects found in prior work with variable hotspot-based targeting? Particularly considering that another independent study using 5Hz-rTUS with confirmed structural targeting reported opposite (inhibitory) effects! 🤔
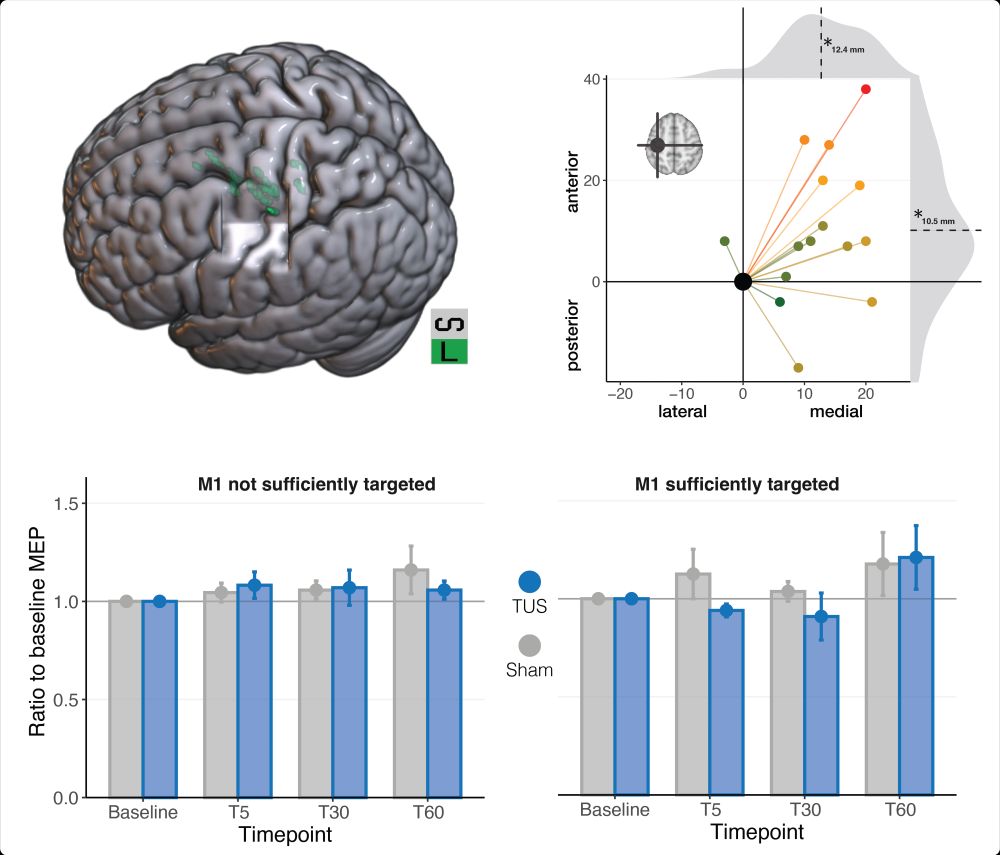
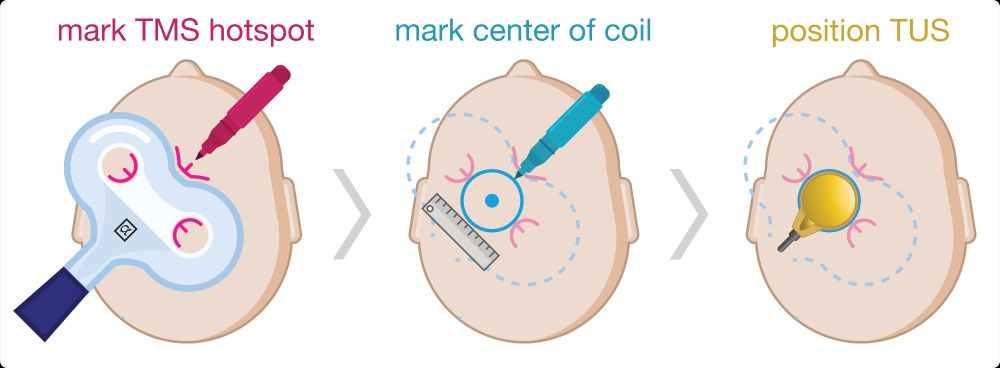
- double-blinding
- TMS neuronavigation
- post-hoc acoustic simulations
TMS and EMG were used to capture intracortical and corticospinal excitability (SICI, ICF, & MEP).
- double-blinding
- TMS neuronavigation
- post-hoc acoustic simulations
TMS and EMG were used to capture intracortical and corticospinal excitability (SICI, ICF, & MEP).

