
academic.oup.com/jrsssa
The Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A (@jrssa.bsky.social) invites submissions for a special issue exploring historical data practices and their impact on modern data science. @royalstatsoc.bsky.social
🔍 Explore the full call: oxford.ly/4rgfcdl

The Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A (@jrssa.bsky.social) invites submissions for a special issue exploring historical data practices and their impact on modern data science. @royalstatsoc.bsky.social
🔍 Explore the full call: oxford.ly/4rgfcdl
🧪Apsemidis and Demiris adopt the Bayesian paradigm and synthesize publicly available data via a discrete-time stochastic epidemic modelling framework doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

🧪Apsemidis and Demiris adopt the Bayesian paradigm and synthesize publicly available data via a discrete-time stochastic epidemic modelling framework doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
🏈Nguyen and Yurko snap into the passing lanes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

🏈Nguyen and Yurko snap into the passing lanes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
Nason,Salnikov & Cortina-Borja present the following discussion paper (and you can find contributions to the discussion from other authors in the journal!) doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
Nason,Salnikov & Cortina-Borja present the following discussion paper (and you can find contributions to the discussion from other authors in the journal!) doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
Submissions are now welcomed for invited topic sessions and workshops with a deadline of 21 November. Full details: rss.org.uk/training-eve...
Submissions are now welcomed for invited topic sessions and workshops with a deadline of 21 November. Full details: rss.org.uk/training-eve...
rss.org.uk/training-eve...
We are looking for new editors for JRSSA! (details at the link)
We are seeking associate editors for a four-year term starting in January 2026.
We are looking for new editors for JRSSA! (details at the link)
We are seeking associate editors for a four-year term starting in January 2026.
rss.org.uk/training-eve...
rss.org.uk/training-eve...
💡@barross993.bsky.social and
@afarcome.bsky.social
analyze time spent after release with a quantile regression approach
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

💡@barross993.bsky.social and
@afarcome.bsky.social
analyze time spent after release with a quantile regression approach
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
🪶Wang, Chen, et al with a very clear purpose in the title of their paper
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
🪶Wang, Chen, et al with a very clear purpose in the title of their paper
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💱Chen et al delve in Blockchain networks
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
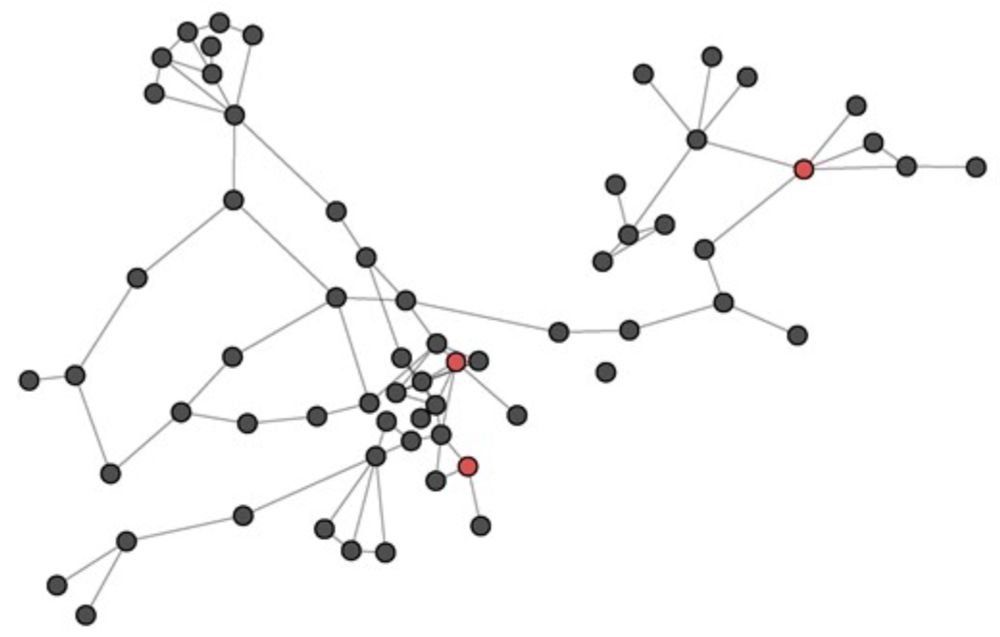
💱Chen et al delve in Blockchain networks
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Um , Sweet and Adhikari show a framework to disentangle homophily from causal peer influence
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Um , Sweet and Adhikari show a framework to disentangle homophily from causal peer influence
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Bouranis et al. develop a flexible Bayesian evidence synthesis approach to model age-specific transmission dynamics of COVID-19 based on daily death counts
💡Bouranis et al. develop a flexible Bayesian evidence synthesis approach to model age-specific transmission dynamics of COVID-19 based on daily death counts
💡Beppu, Choi, Morikawa & Im try to respond what happens when people don't respond to surveys because of their actual (unobserved) answer?
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

💡Beppu, Choi, Morikawa & Im try to respond what happens when people don't respond to surveys because of their actual (unobserved) answer?
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Kendall et al analyze how smaller, sub-municipal boundaries like police districts, precincts, and service areas also influence police outcomes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

💡Kendall et al analyze how smaller, sub-municipal boundaries like police districts, precincts, and service areas also influence police outcomes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Austin Denteh and Helge Liebert
estimate the heterogeneous impacts of Medicaid on ED use and characterize them
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

💡Austin Denteh and Helge Liebert
estimate the heterogeneous impacts of Medicaid on ED use and characterize them
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
🌬️Lee and Lee develop a long-memory extreme series model using a copula transformation to quantify long-term trends of extreme ozone
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

🌬️Lee and Lee develop a long-memory extreme series model using a copula transformation to quantify long-term trends of extreme ozone
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
🤔Jia Ben-Michael and Imai examine whether a security assessment algorithm deployed during the Vietnam War could have been improved
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
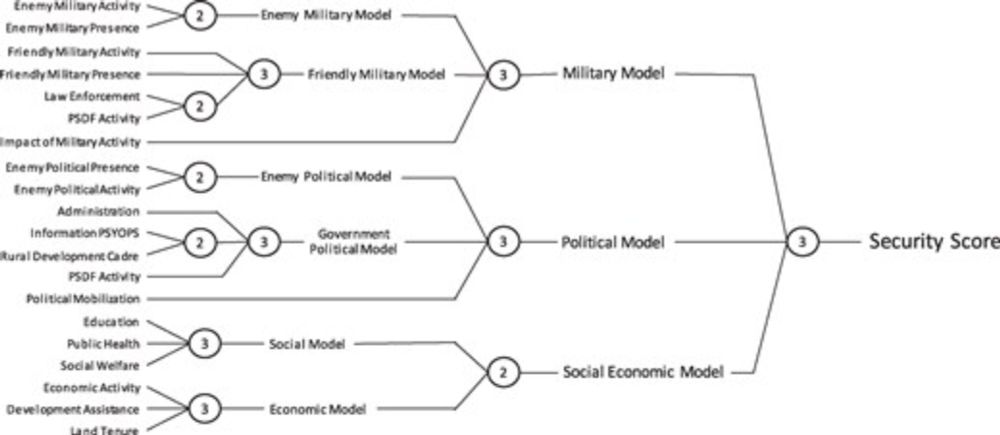
🤔Jia Ben-Michael and Imai examine whether a security assessment algorithm deployed during the Vietnam War could have been improved
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
‼️Lee and Kim introduce the Counterfactual Buckley–James Q-Learning framework, to address challenges arising from longitudinal survival data.
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...

‼️Lee and Kim introduce the Counterfactual Buckley–James Q-Learning framework, to address challenges arising from longitudinal survival data.
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡@dracek.bsky.social Thurner and Kauermann develop a statistical model to capture the spatio-temporal
diffusion effects of armed conflict (@lmumuenchen.bsky.social)
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
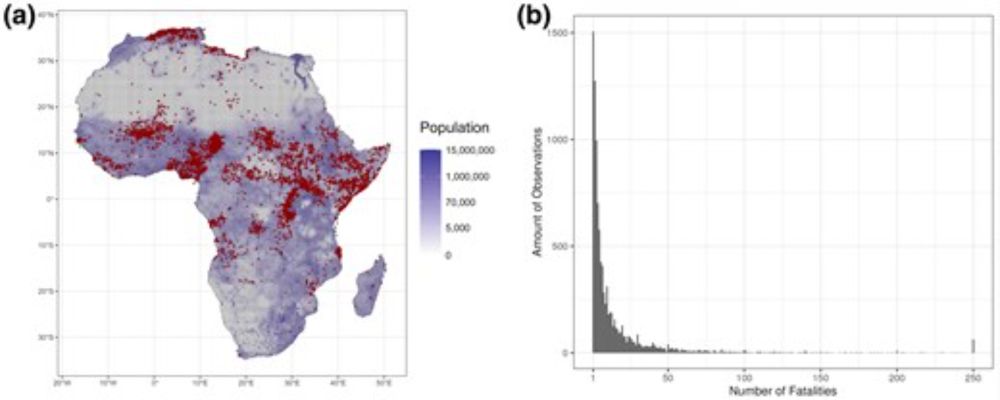
💡@dracek.bsky.social Thurner and Kauermann develop a statistical model to capture the spatio-temporal
diffusion effects of armed conflict (@lmumuenchen.bsky.social)
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
♟️Adriaan Kalwij investigates the momentum effects to assess chess tournament performance
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
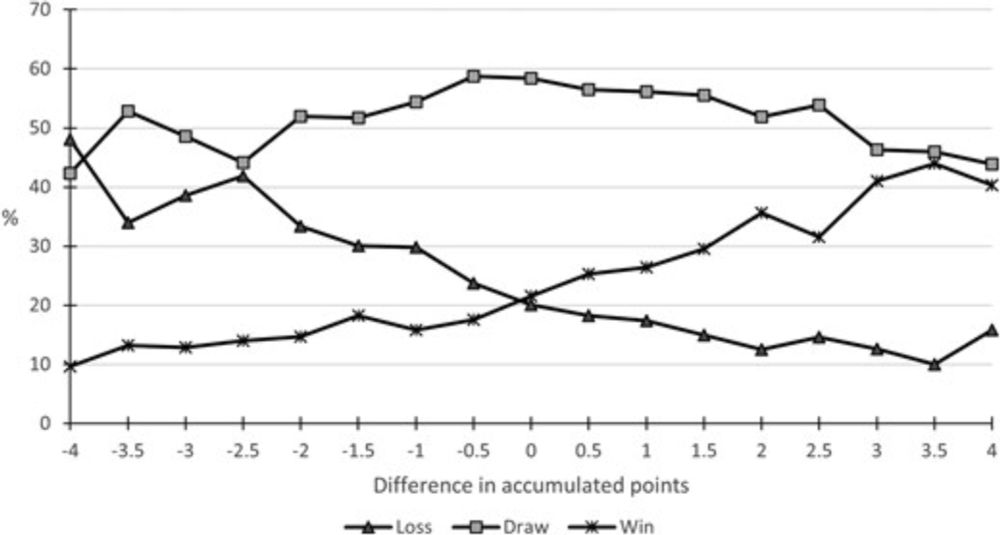
♟️Adriaan Kalwij investigates the momentum effects to assess chess tournament performance
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Damann, Knox & Lucas develop a formal causal framework to overcome limitations of text-only analyses
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
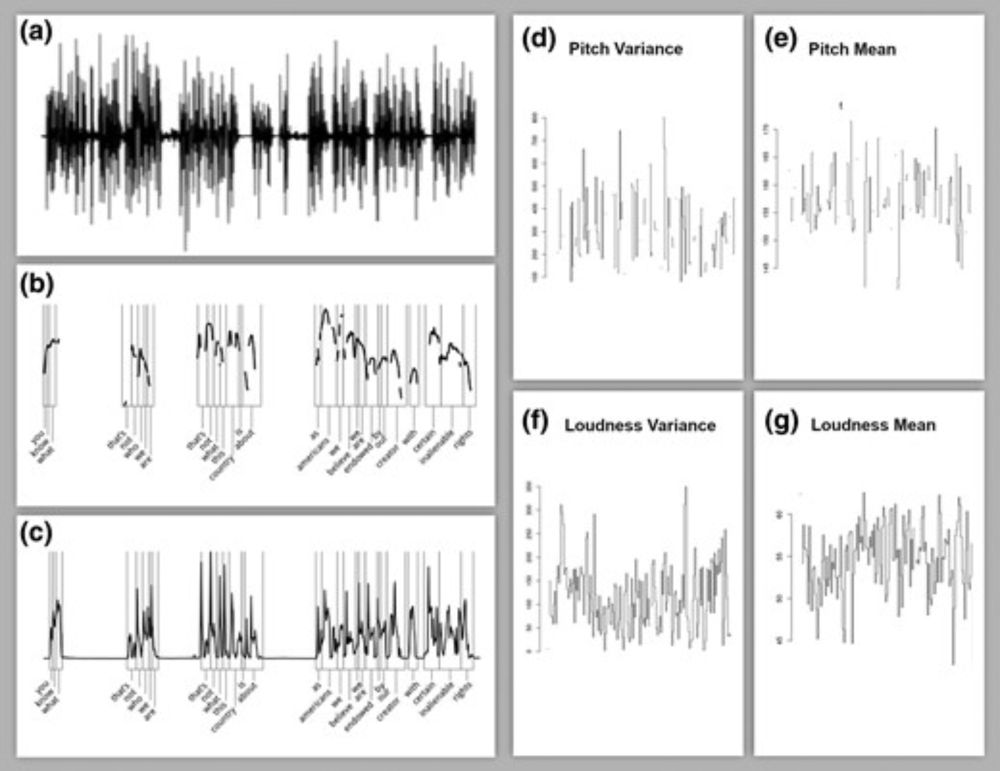
💡Damann, Knox & Lucas develop a formal causal framework to overcome limitations of text-only analyses
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Kawano Parker & Li we introduce a model that accounts for spatial dependence in random effects as well and effect selection latent processes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Kawano Parker & Li we introduce a model that accounts for spatial dependence in random effects as well and effect selection latent processes
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Zens proposes a Bayesian model for the joint analysis of age-specific counts in many, potentially small, demographic subpopulations
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
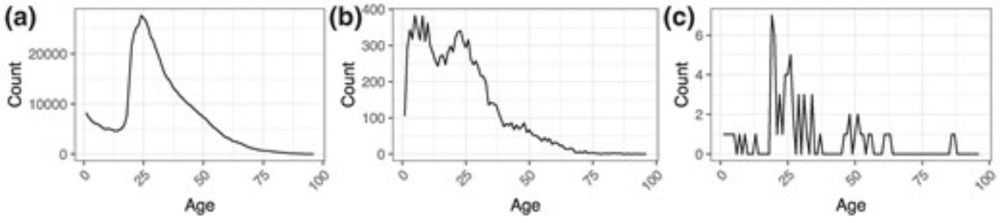
💡Zens proposes a Bayesian model for the joint analysis of age-specific counts in many, potentially small, demographic subpopulations
doi.org/10.1093/jrss...
💡Wigle and Béliveau provide a method for estimating methane inventories that are simple to interpret
t.co/wWXhJhmTGq
💡Wigle and Béliveau provide a method for estimating methane inventories that are simple to interpret
t.co/wWXhJhmTGq

