
Implementation Science Journals
@implementsci.bsky.social
BMC's Implementation Science & Implementation Science Communications focus on the implementation of research evidence into healthcare practice and policy. Posts about #impsci & companion journal #ImpSciComms
https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
Pinned
Cassyni | Science starts with a seminar
Seamlessly organise, run and publish academic research seminars. Get started in minutes.
cassyni.com
Join us for an implementation science webinar "SDG 3: Implementation of Evidence-Based Practices for Improving Maternal and Neonatal Health" chaired by Jessica Callghan-Koru, Rebecca Hamm and Michelle Moniz
📅 Wednesday 19th Mar 2025
⏰ 16.00 PM GMT (London)
Attend via cassyni.com/events/PwH8s...
📅 Wednesday 19th Mar 2025
⏰ 16.00 PM GMT (London)
Attend via cassyni.com/events/PwH8s...
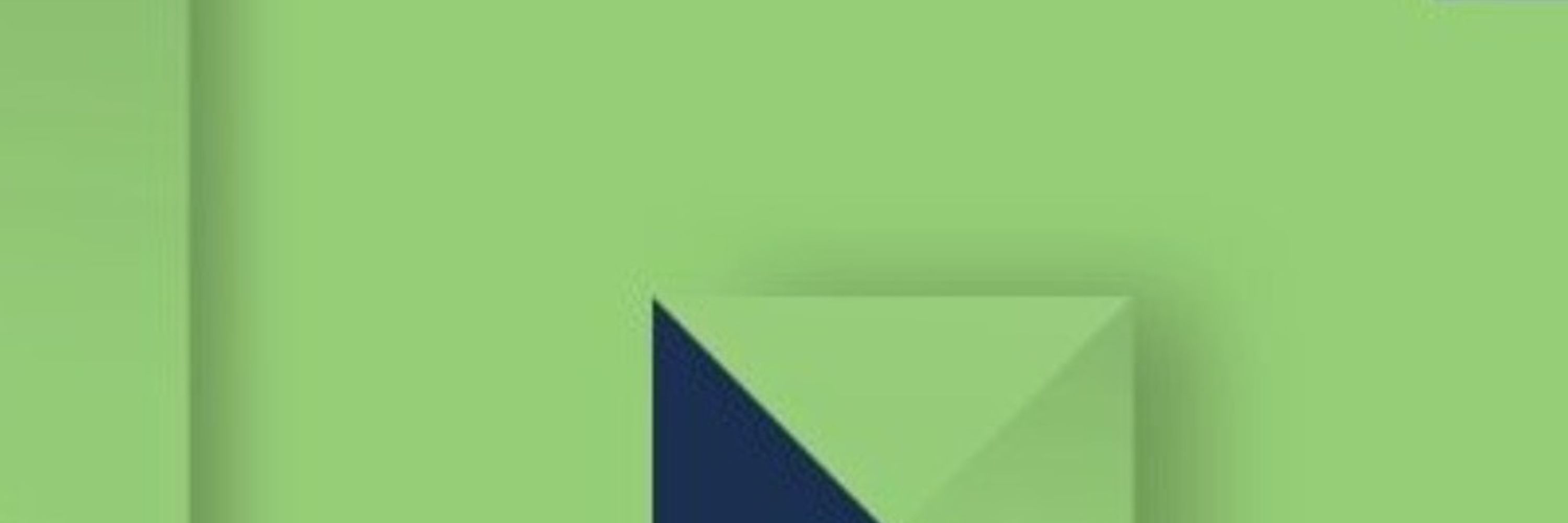
Achieving cardiovascular health equity in community mental health: study protocol for a cluster-randomized hybrid Type 3 effectiveness-implementation trial #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
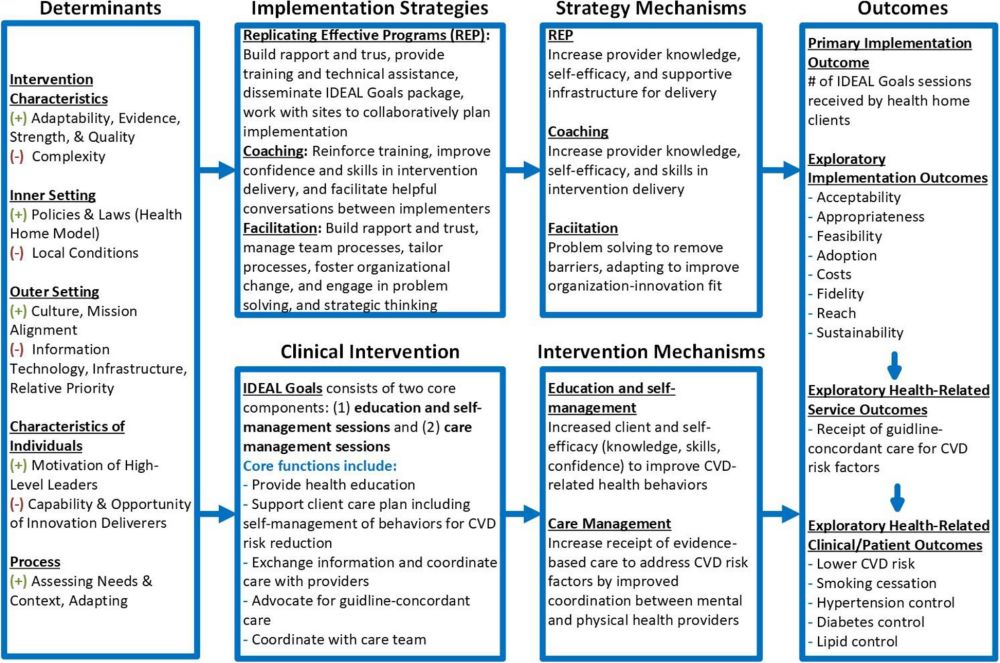
Achieving cardiovascular health equity in community mental health: study protocol for a cluster-randomized hybrid Type 3 effectiveness-implementation trial - Implementation Science
Background People with serious mental illness die 10–20 years earlier than the overall population, mainly from cardiovascular disease. Although effective interventions to manage cardiovascular disease...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
November 6, 2025 at 10:13 AM
Achieving cardiovascular health equity in community mental health: study protocol for a cluster-randomized hybrid Type 3 effectiveness-implementation trial #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Implementation Strategies Applied in Communities Matching Process (ISAC Match): Expanded Guidance and Case Study #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Implementation Strategies Applied in Communities Matching Process (ISAC Match): Expanded Guidance and Case Study - Implementation Science
Background Implementation strategies are methods or techniques to improve the adoption, implementation, sustainment, and scale-up of evidence-based interventions. Limited guidance exists on feasible p...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
October 18, 2025 at 2:22 PM
Implementation Strategies Applied in Communities Matching Process (ISAC Match): Expanded Guidance and Case Study #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
A pragmatic approach to estimating the cost to deliver and participate in implementation strategies #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

A pragmatic approach to estimating the cost to deliver and participate in implementation strategies - Implementation Science
Background Implementation costs—the combined costs of delivering expert support and participating in an implementation endeavor—are often omitted from economic evaluations. When included, delivery and...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
October 18, 2025 at 2:22 PM
A pragmatic approach to estimating the cost to deliver and participate in implementation strategies #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Considerations for evaluating pragmatic design elements in digital health intervention trials: the case of Keep It Up! 3.0 #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Considerations for evaluating pragmatic design elements in digital health intervention trials: the case of Keep It Up! 3.0 - Implementation Science Communications
Background Digital health interventions are increasingly promoted in healthcare and prevention practices due to their potential for reaching key populations in a cost-efficient manner. Yet there has been limited research on how to effectively implement them with pragmatic approaches that can facilitate scale-up. Keep It Up! (KIU!) 3.0 was a hybrid type 3 implementation–effectiveness trial comparing two delivery strategies (i.e. trial arms) of an HIV prevention intervention for cisgender, young men who have sex with men. We aimed to determine the level of pragmatism of our two-armed trial before and after changes to the county-randomized design. Methods We applied different versions of the PRagmatic Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary (PRECIS) tool to the two trial arms: delivery of KIU! by community-based organizations (CBO) versus centralized, direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery. We scored PRECIS-2 for the original study design and the modified design in which the DTC strategy expanded nationally. We applied PRECIS-2-PS to the modified study design. Nine coders in three groups independently scored the tools. Scores were iteratively discussed to arrive at one consensus score per domain, tool, design stage, and arm. We plotted results using the PRECIS-2 and PRECIS-2-PS wheels and averaged domains scores to describe overall score along the Pragmatic–Explanatory Continuum. Results Using PRECIS-2, the trial was on the pragmatic side of the spectrum for both arms and design stages, with average ratings ranging from 3.89–4.33. Both arms were highly pragmatic in the original and modified design in the Setting and Primary Analysis domains and least pragmatic in the Follow-up domain. In the modified trial design, the CBO and DTC arms again scored rather pragmatic using the PRECIS-2-PS tool, but CBO arm scored higher in the eligibility, recruitment, and organization domains compared to PRECIS-2 (5 vs. 4, respectively). Conclusions Application of both the PRECIS-2 and PRECIS-2-PS tools validated the pragmatic design of KIU! 3.0 as originally designed and after modifications during trial implementation. Our findings highlight instances where one tool may be more suitable than the other to assess the pragmatic–explanatory continuum for emerging digital health interventions delivered in diverse settings and with different implementation strategies.
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:43 PM
Considerations for evaluating pragmatic design elements in digital health intervention trials: the case of Keep It Up! 3.0 #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Scaling-up an mHealth system to deliver financial incentives to improve adherence to antiretroviral therapy in Tanzania #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Scaling-up an mHealth system to deliver financial incentives to improve adherence to antiretroviral therapy in Tanzania - Implementation Science Communications
Background Financial incentives are increasingly used to achieve UNAIDS' 95–95-95 goals for ending HIV by 2030. While evidence supports their effectiveness, scaling these interventions remains challenging. This study examines the implementation successes and challenges of a financial incentive intervention in Tanzania, delivered via an mHealth application that provides automated mobile money disbursements, biometric identification, and SMS reminders. Methods Conducted alongside a Hybrid Type 1 Effectiveness-Implementation trial, the study evaluated financial incentives given to adults starting ART at 32 clinics. We used the Structured Assessment of Feasibility, Compatibility Beliefs in Technology (CBIT) scales, and the Program Sustainability Assessment Tool. Perspectives from 657 participants living with HIV and 90 clinic staff were collected using Proctor’s implementation science framework. Results Clinic staff rated the mHealth system highly on CBIT subscales for perceived usefulness, ease of use, and compatibility, each scoring over 6 out of 7. Integration and applicability of the financial incentive within the mHealth system were well received, with 93.0% of staff agreeing it improved job performance. Among participants, 86.4% found SMS reminders helpful for attending appointments, and 76.7% felt the cash delivery met their expectations. Challenges included unreliable fingerprint identification and undelivered SMS reminders. Conclusions Despite issues with fingerprint identification and SMS delivery, the financial incentive intervention via mHealth was found to be acceptable, feasible, and potentially sustainable in resource-limited settings, with support from host governments. Future research should enhance the intervention's effectiveness and optimize biometric identification methods. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04201353. Registered 17 December 2019, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04201353
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:42 PM
Scaling-up an mHealth system to deliver financial incentives to improve adherence to antiretroviral therapy in Tanzania #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Implementation research in forensic mental health: a scoping review #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Implementation research in forensic mental health: a scoping review - Implementation Science Communications
Background Forensic mental health (FMH) serves as a critical juncture between the mental health and criminal justice systems. Factors on multiple levels – including sociopolitical, organizational, and individual— pose challenges to conducting implementation research in these settings. This hinders the uptake of evidence-based interventions and improvements to patient outcomes. This study examined implementation research conducted in FMH settings to understand its current state and inform future implementation research and practice. Methods We conducted a scoping review following the Joanna Briggs Institute methodology. A comprehensive literature search was performed across seven databases from their inception through April 2024, supplemented by searches in Google Scholar and six review studies, to identify relevant research. We analyzed included studies descriptively to explore determinants, strategies, and outcomes associated with the implementation of evidence-, or policy-based interventions in FMH. Results Of the 1327 records retrieved, 41 implementation studies were included. All studies were conducted in high-income countries and focused on interventions such as risk assessment, rehabilitation, patient support, and technology interventions, primarily using qualitative approaches. Key determinants for implementing interventions in FMH included individual characteristics (e.g., motivation, capacity) and inner setting factors (e.g., intervention compatibility with existing practices, access to knowledge and information). Various strategies, such as using evaluative and iterative strategies, training and educating stakeholders, changing infrastructure, and engaging consumers have been used to facilitate intervention uptake in FMH. Implementation outcomes primarily focused on uptake, fidelity, and acceptability. Conclusions There is a clear need for more implementation research using rigorous study designs in FMH. Multilevel implementation strategies should be employed to address barriers from both the inner settings and individual characteristics, thereby promoting the successful implementation of interventions in FMH. Future implementation research should incorporate a health equity lens throughout the research process to enhance inclusivity and improve reporting on implementation strategies to support replications of interventions in FMH.
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:41 PM
Implementation research in forensic mental health: a scoping review #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
De-implementation of low-value home-based nursing care: an effect and process evaluation #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

De-implementation of low-value home-based nursing care: an effect and process evaluation - Implementation Science Communications
Background The demand for homecare is increasing, and reducing low-value care is essential for achieving sustainable healthcare. Low-value care refers to practices that are ineffective, inefficient, unwanted, or potentially harmful to the client. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of a tailored, multifaceted deimplementation strategy in reducing low-value home-based nursing care. Methods A prospective, multicenter, convergent parallel mixed method design was employed, including a before-and-after study, using the Reach-Effectiveness-Adoption-Implementation-Maintenance (RE-AIM) framework. The effect of reducing low-value home-based nursing care was assessed from client records, focusing on the number of clients receiving care, minutes of care per week, frequency of visits per week, and clients no longer requiring care. The de-implementation process was evaluated qualitatively through individual interviews with de-implementation ambassadors, registered nurses, and nurse assistants, using Directed Qualitative Content Analysis. This approach served to interpret the effects of the deployment of de-implementation ambassadors and the strategies they implemented. Results We observed a reduction in low-value home-based nursing care, with a decrease of 130 h per week in daily showering, bathing and/or dressing; 54 h per week in the assistance with compression stockings; and 8 h per week in changing bandages enabling clients to regain their independence. Important de-implementation strategies included involving clients and relatives in decision making, organizing informational meetings for homecare professionals, and fostering collaboration with other healthcare professionals. Factors that influenced adoption included providing reassurance and using a stepwise approach with clients and relatives. Homecare professionals noted that the de-implementation ambassadors were highly committed to reducing care. De-implementation ambassadors found their role to be intense, challenging, and exciting. Conclusions This evaluation found that the deployment of de-implementation ambassadors, paired with additional de-implementation strategies, enhanced the reduction of low-value home-based nursing care. Providing reassurance and involving clients and their relatives were identified as beneficial for the de-implementation process.
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:40 PM
De-implementation of low-value home-based nursing care: an effect and process evaluation #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Type 3 hybrid effectiveness-implementation cluster randomized trial to evaluate multi-ethnic, multilevel strategies and community engagement to eliminate hypertension disparities in Los Angeles County #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Protocol for a Type 3 hybrid effectiveness-implementation cluster randomized trial to evaluate multi-ethnic, multilevel strategies and community engagement to eliminate hypertension disparities in Los Angeles County - Implementation Science
Background In the U.S., racial and ethnic disparities in hypertension control contribute to disparities in cardiovascular mortality. Evidence-based practices (EBPs) for improving hypertension control have not been consistently applied across patient subgroups, especially in safety-net settings, contributing to observed disparities. The Los Angeles County Department of Health Services serves racially and ethnically diverse, low-income patients with hypertension and represents a valuable setting for research to reduce disparities. We designed a hybrid Type 3 effectiveness-implementation study using a three-arm, crossover randomized controlled trial to compare the effects of patient- and provider-focused strategies and usual implementation strategy on key implementation and clinical outcomes. Methods We will enroll 27 primary care clinics. Patient-focused implementation strategies aim to increase patient access to culturally and linguistically tailored educational materials on hypertension and improve patient engagement in hypertension care. Provider-focused strategies include training in culturally tailored hypertension care and activities to strengthen clinic workflows for home blood pressure monitoring, medication titration, referral to nurse-directed blood pressure clinics, and social needs screening and referral. Implementation facilitators provide support for these EBPs. The primary implementation outcome is provider EBP adoption clustered at the clinic level, based on a scoring system using medical records, clinic observation, and webinar participation. The primary health-related outcome is the proportion of patients in a clinic with controlled hypertension by race and ethnicity. We will use the constrained generalized Poisson mixed-effects model to compare changes in event rate of provider EBP adoption between usual implementation strategy and either provider- or patient-focused strategies. We will use constrained logistic mixed-effects models to assess the effect on change in blood pressure control. We will record implementation progress using the Stages of Implementation Completion tool and identify costs and resource use using the Cost of Implementing New Strategies tool. Discussion Our study contributes to the implementation science literature on cardiovascular health equity by examining alternative implementation strategies to increase use of culturally and linguistically tailored hypertension EBPs and social needs screening and intervention. Findings from our study will build evidence for implementation of hypertension EBPs in safety-net and other health systems serving racial and ethnic minority patients. Trial registration Clinicaltrials.gov NCT06359691, registered April 10, 2024.
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:36 PM
Type 3 hybrid effectiveness-implementation cluster randomized trial to evaluate multi-ethnic, multilevel strategies and community engagement to eliminate hypertension disparities in Los Angeles County #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
STop UNhealthy substance use now (STUN II) trial: protocol for a 48-site cluster randomized 2 × 2 factorial implementation trial to improve evidence-based screening and interventions for substance use disorder within primary care #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

The STop UNhealthy substance use now (STUN II) trial: protocol for a 48-site cluster randomized 2 × 2 factorial implementation trial to improve evidence-based screening and interventions for substance use disorder within primary care - Implementation Science
Background Despite substance use disorders (SUD) being a leading cause of preventable death in the US, most people who visit primary care in the US are not screened for SUD. There are multiple barriers to screening for, identifying, and managing SUD in primary care. However, there are also promising strategies available to address these barriers, including practice facilitation (PF), learning collaboratives (LC), and performance incentives (PI). Methods This study is a 48-site cluster-randomized 2 × 2 factorial implementation trial that aims to compare the effectiveness of several strategies for implementing evidence-based screening and interventions for SUDs in primary care. Practices will be randomized to one of four implementation strategies: (1) PF only, (2) PF + LC, (3) PF + PI, or (4) all three strategies. An estimated 144 participants from 48 primary care practices will be enrolled. All participants will receive PF to guide them in making changes to implement screening for SUD, focusing on a defined change package and associated tools. PF includes quality improvement (QI) coaching, as well as electronic health record (EHR) support, training, and expert consultation. LC includes monthly virtual education sessions led by content experts to support practice improvement and innovation with didactics on key topics as well as facilitating participant interactions to share experiences. PI includes financial incentives for performance. Primary care practices will be the unit of analysis for both the primary outcome (rate of SUD screening) and secondary outcomes (rates of evidence-based interventions for SUD). Assessments will be conducted during a 12-month implementation phase and 12-month sustainment phase. Discussion This study will produce evidence regarding the comparative effectiveness of several strategies on implementation and sustainment of evidence-based screening and interventions for SUD within primary care. It will also generate knowledge about mechanisms of change in primary care settings. The results are expected to have a positive impact by providing a nuanced understanding of the incremental benefits of LC and/or PI to inform primary care practices, health systems, policymakers, and payers about optimal implementation strategies for SUD screening and evidence-based interventions. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov NCT06524232. July 23, 2024 –registered.
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:35 PM
STop UNhealthy substance use now (STUN II) trial: protocol for a 48-site cluster randomized 2 × 2 factorial implementation trial to improve evidence-based screening and interventions for substance use disorder within primary care #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Integrating implementation science and intervention optimization #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Integrating implementation science and intervention optimization - Implementation Science
Background Implementation scientists increasingly recognize the value of multiple strategies to improve the adoption, fidelity, and scale up of an evidence-based intervention (EBI). However, with this recognition comes the need for alternative and innovative methods to ensure that the package of implementation strategies work well within constraints imposed by the need for affordability, scalability, and/or efficiency. The aim of this article is to illustrate that this can be accomplished by integrating principles of intervention optimization into implementation science. Method We use a hypothetical example to illustrate the application of the multiphase optimization strategy (MOST) to develop and optimize a package of implementation strategies designed to improve clinic-level adoption of an EBI for smoking cessation. Results We describe the steps an investigative team would take using MOST for an implementation science study. For each of the three phases of MOST (preparation, optimization, and evaluation), we describe the selection, optimization, and evaluation of four candidate implementation strategies (e.g., training, treatment guide, workflow redesign, and supervision). We provide practical considerations and discuss key methodological points. Conclusion Our intention in this methodological article is to inspire implementation scientists to integrate principles of intervention optimization in their studies, and to encourage the continued advancement of this integration.
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
October 9, 2025 at 2:32 PM
Integrating implementation science and intervention optimization #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Integrating HIV prevention services into care settings for people with opioid use disorder (OUD): a study protocol for implementation strategy development and modeling #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Integrating HIV prevention services into care settings for people with opioid use disorder (OUD): a study protocol for implementation strategy development and modeling - Implementation Science Communi...
Background The overlapping epidemics of opioid use disorder (OUD) and HIV present a critical public health challenge. Although people with OUD frequently engage with healthcare settings, uptake of HIV...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
September 16, 2025 at 12:38 PM
Integrating HIV prevention services into care settings for people with opioid use disorder (OUD): a study protocol for implementation strategy development and modeling #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Testing a multi-faceted strategy to support the implementation of ACEs screenings in primary care: results of a stepped-wedge pilot trial #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Testing a multi-faceted strategy to support the implementation of ACEs screenings in primary care: results of a stepped-wedge pilot trial - Implementation Science Communications
Background Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) screenings are increasingly being used in primary care clinics to identify toxic stress and potential trauma in children. ACEs are negative life events ...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
September 4, 2025 at 2:10 PM
Testing a multi-faceted strategy to support the implementation of ACEs screenings in primary care: results of a stepped-wedge pilot trial #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Key determinants in implementation processes: a systematic review using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Key determinants in implementation processes: a systematic review using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) - Implementation Science Communications
Background Contextual factors, or determinants, are commonly assessed in implementation studies due to their impact on the implementation process. While a substantial number of determinants have been ...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 26, 2025 at 3:16 PM
Key determinants in implementation processes: a systematic review using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Reposted by Implementation Science Journals
Translational framework for implementation evaluation and research: implementation strategies derived from normalization process theory #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
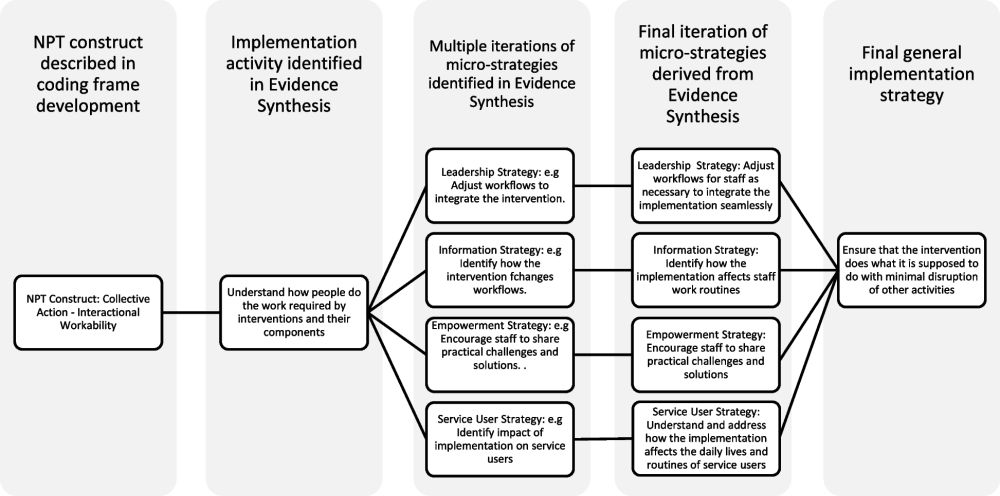
Translational framework for implementation evaluation and research: implementation strategies derived from normalization process theory - Implementation Science
Background Implementation strategies are deliberate systematic actions used to support the uptake of innovations in health and social care. While widely used taxonomies such as ERIC and EPOC have emer...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
August 26, 2025 at 5:32 AM
Beyond the surface of capacity building: a mixed-methods study of the core functions and forms of dissemination and implementation science consultations #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Beyond the surface of capacity building: a mixed-methods study of the core functions and forms of dissemination and implementation science consultations - Implementation Science Communications
Background The number of Dissemination and Implementation Science (DIS) capacity building programs is increasing worldwide. These programs aim to enhance diverse DIS skills through a variety of activi...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 18, 2025 at 11:58 AM
Beyond the surface of capacity building: a mixed-methods study of the core functions and forms of dissemination and implementation science consultations #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Reposted by Implementation Science Journals
New CFIR User Guide out now 👇
It contains:
✅ 5 step guide to using CFIR in implementation research
✅ Essential tools & templates
✅ FAQs from real users
Essential resource for new & experienced CFIR users!
Proud to have contributed to this guide as part of the CFIR Leadership Team. #ImpSci
It contains:
✅ 5 step guide to using CFIR in implementation research
✅ Essential tools & templates
✅ FAQs from real users
Essential resource for new & experienced CFIR users!
Proud to have contributed to this guide as part of the CFIR Leadership Team. #ImpSci
The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research #CFIR User Guide: a five-step guide for conducting implementation research using the framework #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) User Guide: a five-step guide for conducting implementation research using the framework - Implementation Science
Background The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) is a determinant framework that includes constructs from many implementation theories, models, and frameworks; it is used to pr...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
August 18, 2025 at 10:14 AM
New CFIR User Guide out now 👇
It contains:
✅ 5 step guide to using CFIR in implementation research
✅ Essential tools & templates
✅ FAQs from real users
Essential resource for new & experienced CFIR users!
Proud to have contributed to this guide as part of the CFIR Leadership Team. #ImpSci
It contains:
✅ 5 step guide to using CFIR in implementation research
✅ Essential tools & templates
✅ FAQs from real users
Essential resource for new & experienced CFIR users!
Proud to have contributed to this guide as part of the CFIR Leadership Team. #ImpSci
Evidence-informed, community-engaged approach to designing a large-scale, impact-oriented research funding initiative to foster the implementation of transformative integrated care #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

An evidence-informed, community-engaged approach to designing a large-scale, impact-oriented research funding initiative to foster the implementation of transformative integrated care: a multi-methods...
Background Integrated care is a promising strategy to advance system transformation, care coordination, equity, and better health outcomes. Health services and policy research can drive evidence-infor...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 18, 2025 at 11:56 AM
Evidence-informed, community-engaged approach to designing a large-scale, impact-oriented research funding initiative to foster the implementation of transformative integrated care #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research #CFIR User Guide: a five-step guide for conducting implementation research using the framework #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) User Guide: a five-step guide for conducting implementation research using the framework - Implementation Science
Background The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) is a determinant framework that includes constructs from many implementation theories, models, and frameworks; it is used to pr...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
August 18, 2025 at 8:11 AM
The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research #CFIR User Guide: a five-step guide for conducting implementation research using the framework #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Developing implementation strategies for digital ICU diaries targeting ICU professionals: an implementation mapping approach #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Developing implementation strategies for digital ICU diaries targeting ICU professionals: an implementation mapping approach - Implementation Science Communications
Background Digital Intensive Care Unit (ICU) diaries can enhance the mental health of ICU survivors and their relatives by bridging memory gaps, improving understanding of ICU experiences, and providi...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 4:03 PM
Developing implementation strategies for digital ICU diaries targeting ICU professionals: an implementation mapping approach #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Proactive planning for contextual fit: the role of the implementation premortem #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Proactive planning for contextual fit: the role of the implementation premortem - Implementation Science Communications
Background Implementation failure is a major barrier to program success. It is widely acknowledged that context matters—individual, community, and organizational norms, values, environment, and priori...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 4:03 PM
Proactive planning for contextual fit: the role of the implementation premortem #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Longitudinal evaluation examining implementation and sustainment of an opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution among veterans who are unstably housed #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Longitudinal evaluation examining implementation and sustainment of an opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution among veterans who are unstably housed - Implementation Science Communication...
Background Rigorous implementation evaluations are needed to understand factors that influence implementation and sustainability of evidence-based interventions across contexts. In this study, we cond...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 4:02 PM
Longitudinal evaluation examining implementation and sustainment of an opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution among veterans who are unstably housed #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Why engagement matters in policy implementation: an examination of the engagement of policy actors in the implementation of a mental health and addictions strategy #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Why engagement matters in policy implementation: an examination of the engagement of policy actors in the implementation of a mental health and addictions strategy - Implementation Science Communicati...
Background Shifts toward “new public governance” (NPG), where policy decisions and their implementation are “co-produced” by a policy network, have captured the attention of policymakers as an approac...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 4:00 PM
Why engagement matters in policy implementation: an examination of the engagement of policy actors in the implementation of a mental health and addictions strategy #impsci #ImpSciComms
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Comparing the effectiveness of implementation strategies to improve liver and colon cancer screening for Veterans #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

Comparing the effectiveness of implementation strategies to improve liver and colon cancer screening for Veterans: protocol for a large cluster-randomized implementation study - Implementation Science
Background Screening for gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, specifically colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is often inadequately and inequitably implemented, leading to preventab...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 3:55 PM
Comparing the effectiveness of implementation strategies to improve liver and colon cancer screening for Veterans #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability (PRISM)-capabilities model for use of Artificial Intelligence in community-engaged implementation science research #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

The Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability (PRISM)-capabilities model for use of Artificial Intelligence in community-engaged implementation science research - Implementation Science
Background Community-engaged research (CER) leverages knowledge, insights, and expertise of researchers and communities to address complex public health challenges and improve community well-being. CE...
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com
August 12, 2025 at 3:49 PM
Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability (PRISM)-capabilities model for use of Artificial Intelligence in community-engaged implementation science research #impsci
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
Hybrid effectiveness-implementation cluster-RCT evaluating a differentiated point-of-care HIV diagnosis and management model for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV in Malawi #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
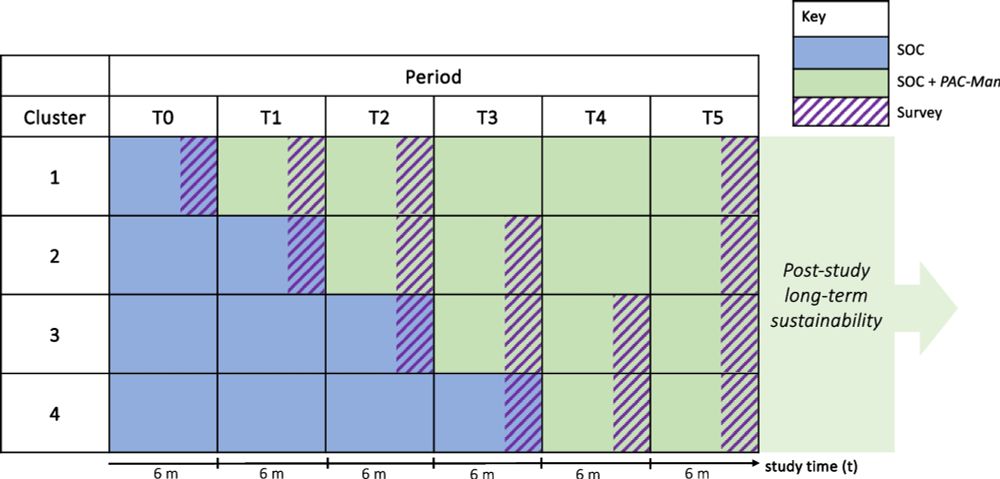
Study design and procedures for a hybrid effectiveness-implementation incomplete stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial to evaluate a differentiated point-of-care HIV diagnosis and management model fo...
Background In Malawi and elsewhere in Africa, many children living with HIV are unaware of their status, often because of missed services for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV (PVTH). Pre...
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com
August 4, 2025 at 2:34 PM
Hybrid effectiveness-implementation cluster-RCT evaluating a differentiated point-of-care HIV diagnosis and management model for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV in Malawi #ImpSciComms #impsci
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
implementationsciencecomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

