

But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11

But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11

Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11
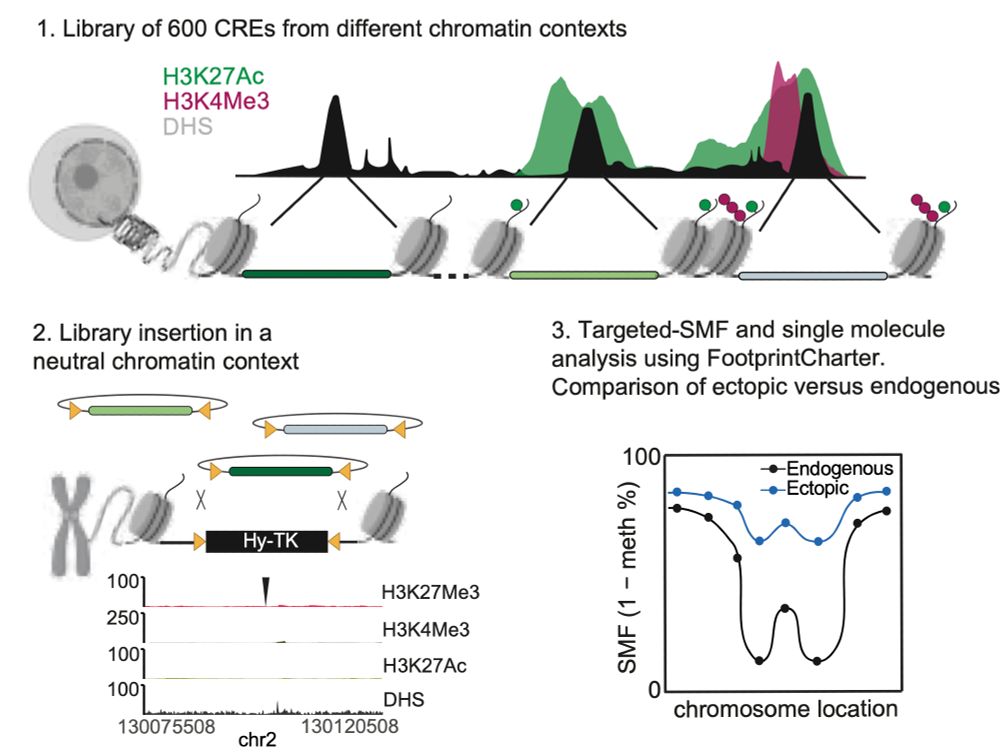







But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11

But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11

Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11






But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11

But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11

Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11



